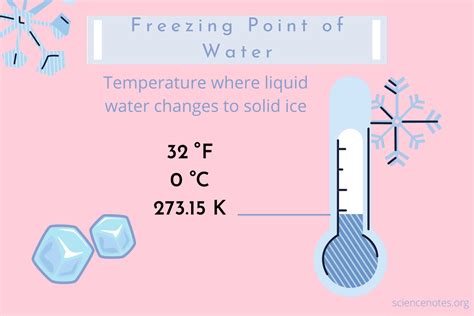
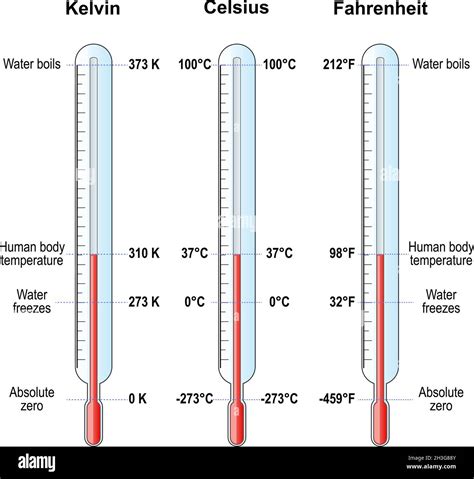
The freezing point is a fundamental physical constant that defines the temperature at which a liquid transforms into a solid. In the context of water, the freezing point is a crucial parameter that has numerous implications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering. The freezing point of water in Celsius is a widely recognized and utilized reference point. The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. In this scale, the freezing point of water is defined as 0 degrees Celsius (°C), while the boiling point is defined as 100 °C.
The precise value of the freezing point of water in Celsius is 0.00 °C, which is equivalent to 32.00 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or 273.15 kelvins (K). This value is a fundamental constant that is used as a reference point in various scientific and engineering applications. The freezing point of water is an essential parameter in understanding the behavior of water and its interactions with other substances. It is also a critical factor in determining the physical properties of water, such as its density, viscosity, and surface tension.
Key Points
- The freezing point of water in Celsius is 0.00 °C.
- The freezing point of water is a fundamental physical constant that defines the temperature at which a liquid transforms into a solid.
- The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with the freezing point defined as 0 °C and the boiling point defined as 100 °C.
- The precise value of the freezing point of water in Celsius is equivalent to 32.00 °F or 273.15 K.
- The freezing point of water is an essential parameter in understanding the behavior of water and its interactions with other substances.
Factors Affecting the Freezing Point
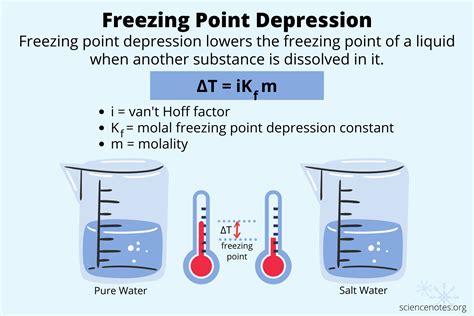
The freezing point of water can be affected by various factors, including pressure, purity, and the presence of dissolved substances. For example, the freezing point of water can be lowered by the addition of solutes, such as salt or sugar, a phenomenon known as freezing-point depression. This effect is widely utilized in various applications, including the production of ice cream and the preservation of food. On the other hand, the freezing point of water can be raised by increasing the pressure, a phenomenon known as freezing-point elevation. This effect is significant in high-pressure applications, such as in the production of ice in high-pressure ice makers.
Freezing-Point Depression
Freezing-point depression is a colligative property of solutions that occurs when a solute is added to a solvent, resulting in a lowering of the freezing point of the solution. This effect is proportional to the molality of the solute and is widely utilized in various applications, including the production of ice cream and the preservation of food. The freezing-point depression of a solution can be calculated using the following equation: ΔT = Kf * m, where ΔT is the change in freezing point, Kf is the freezing-point depression constant, and m is the molality of the solute.
| Substance | Freezing-Point Depression Constant (Kf) |
|---|---|
| Water | 1.86 K kg/mol |
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | 1.86 K kg/mol |
| Sucrose (C12H22O11) | 1.86 K kg/mol |

Applications of the Freezing Point
The freezing point of water has numerous applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering. Some of the significant applications of the freezing point include the production of ice cream, the preservation of food, and the determination of the purity of substances. The freezing point of water is also used as a reference point in various scientific and engineering applications, including the calibration of thermometers and the determination of the physical properties of substances.
Production of Ice Cream
The production of ice cream involves the freezing of a mixture of cream, sugar, and flavorings. The freezing point of the mixture is lowered by the addition of sugar and other solutes, resulting in a smooth and creamy texture. The freezing point of the mixture is also affected by the presence of air bubbles, which can affect the texture and consistency of the ice cream.
In conclusion, the freezing point of water in Celsius is a fundamental physical constant that has numerous implications in various fields. The freezing point of water is affected by various factors, including pressure, purity, and the presence of dissolved substances. The freezing-point depression of a solution is a colligative property that occurs when a solute is added to a solvent, resulting in a lowering of the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point of water has numerous applications in various fields, including the production of ice cream, the preservation of food, and the determination of the purity of substances.
What is the freezing point of water in Celsius?
+The freezing point of water in Celsius is 0.00 °C.
What is the freezing-point depression constant (Kf) for water?
+The freezing-point depression constant (Kf) for water is 1.86 K kg/mol.
What are the applications of the freezing point of water?
+The freezing point of water has numerous applications in various fields, including the production of ice cream, the preservation of food, and the determination of the purity of substances.