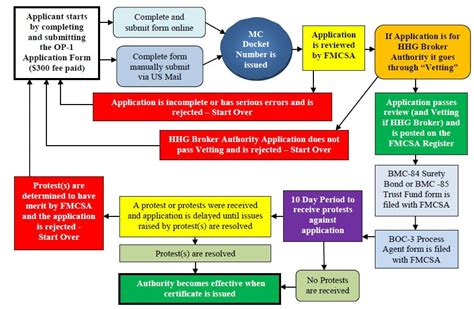
As the logistics and transportation industry continues to grow, the demand for skilled freight brokers is on the rise. Freight brokers play a crucial role in connecting shippers with carriers, ensuring that goods are transported efficiently and safely. If you're interested in pursuing a career in freight brokering, it's essential to undergo comprehensive training to gain the necessary skills and knowledge. In this guide, we'll provide an overview of the freight broker training process, covering key topics, best practices, and expert insights.
Key Points
- Understanding the role and responsibilities of a freight broker
- Knowledge of transportation modes, including truckload, less-than-truckload, and intermodal
- Freight broker software and technology, including transportation management systems (TMS) and load boards
- Building relationships with shippers and carriers, including sales and marketing strategies
- Regulatory compliance, including FMCSA and DOT regulations
- Best practices for freight broker operations, including risk management and customer service
Introduction to Freight Brokering

Freight brokering involves acting as an intermediary between shippers and carriers to arrange the transportation of goods. Freight brokers are responsible for finding available capacity, negotiating rates, and ensuring that shipments are delivered on time and in good condition. To become a successful freight broker, you’ll need to develop a deep understanding of the transportation industry, including the different modes of transportation, regulatory requirements, and best practices for operations.
Transportation Modes and Options
There are several transportation modes and options available, including truckload (TL), less-than-truckload (LTL), intermodal, and air freight. Each mode has its own advantages and disadvantages, and freight brokers need to be able to advise shippers on the best option for their specific needs. For example, TL shipping is often used for large shipments that require a full truckload, while LTL shipping is better suited for smaller shipments that can be combined with other cargo. Intermodal shipping, which involves using multiple modes of transportation, such as truck and rail, can be a cost-effective option for long-haul shipments.
| Transportation Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Truckload (TL) | Full truckload shipping | Fast transit times, high capacity | Higher costs, limited flexibility |
| Less-than-Truckload (LTL) | Shared truckload shipping | Lower costs, flexible scheduling | Slower transit times, limited capacity |
| Intermodal | Multimodal shipping (truck, rail, etc.) | Cost-effective, environmentally friendly | Complex logistics, limited flexibility |

Freight Broker Software and Technology

Freight broker software and technology play a critical role in the success of a freight brokering operation. Transportation management systems (TMS) and load boards are essential tools for freight brokers, enabling them to manage shipments, track capacity, and communicate with shippers and carriers. TMS software can help freight brokers to automate tasks, such as load tendering and carrier selection, while load boards provide a platform for freight brokers to find available capacity and post shipments.
Building Relationships with Shippers and Carriers
Building strong relationships with shippers and carriers is critical to the success of a freight brokering operation. Freight brokers need to be able to communicate effectively with both parties, understand their needs and requirements, and provide excellent customer service. Sales and marketing strategies, such as cold calling, email marketing, and social media marketing, can help freight brokers to build their network and attract new customers.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Freight brokers must comply with a range of regulatory requirements, including those set by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) and the Department of Transportation (DOT). These regulations cover areas such as carrier selection, insurance, and safety standards. Freight brokers must also manage risk effectively, including the risk of cargo loss or damage, carrier insolvency, and regulatory non-compliance.
Best Practices for Freight Broker Operations
To operate a successful freight brokering business, it’s essential to follow best practices, such as maintaining accurate records, providing excellent customer service, and continuously monitoring and improving operations. Freight brokers should also stay up-to-date with industry trends and developments, attend training and networking events, and participate in online forums and discussions.
What is the role of a freight broker in the transportation industry?
+A freight broker acts as an intermediary between shippers and carriers to arrange the transportation of goods. They are responsible for finding available capacity, negotiating rates, and ensuring that shipments are delivered on time and in good condition.
What are the different modes of transportation available to freight brokers?
+There are several modes of transportation available, including truckload (TL), less-than-truckload (LTL), intermodal, and air freight. Each mode has its own advantages and disadvantages, and freight brokers need to be able to advise shippers on the best option for their specific needs.
How do freight brokers manage risk and ensure regulatory compliance?
+Freight brokers must comply with a range of regulatory requirements, including those set by the FMCSA and DOT. They must also manage risk effectively, including the risk of cargo loss or damage, carrier insolvency, and regulatory non-compliance. This can be achieved through careful carrier selection, insurance, and safety standards.
Meta Description: Learn the fundamentals of freight brokering, including transportation modes, freight broker software, and regulatory compliance. Discover how to build a successful freight brokering business with our comprehensive guide.