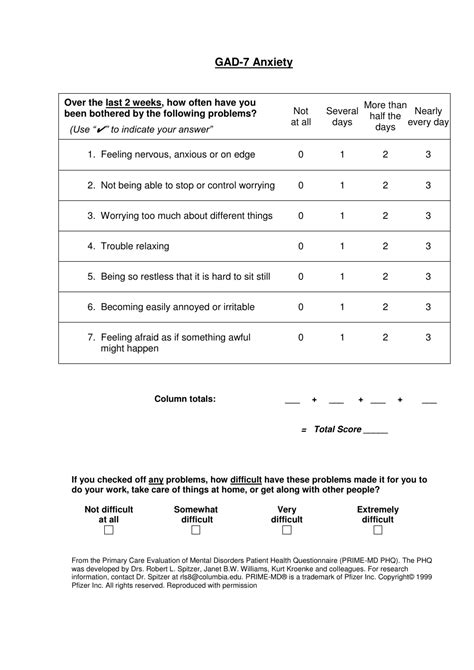
The GAD7 and PHQ9 are two widely used screening tools in the field of mental health, specifically designed to assess the severity of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and major depressive disorder (MDD), respectively. These tools have become essential components of primary care and mental health settings, enabling healthcare providers to quickly identify patients who may require further evaluation or treatment. In this article, we will delve into the details of the GAD7 and PHQ9 screening tools, exploring their development, structure, scoring, and clinical applications.
Key Points
- The GAD7 is a 7-item questionnaire used to assess the severity of generalized anxiety disorder.
- The PHQ9 is a 9-item questionnaire used to assess the severity of major depressive disorder.
- Both tools have been validated for use in primary care and mental health settings.
- The GAD7 and PHQ9 can be used to monitor treatment response and track changes in symptom severity over time.
- These tools should be used in conjunction with a comprehensive clinical evaluation to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Introduction to GAD7 and PHQ9
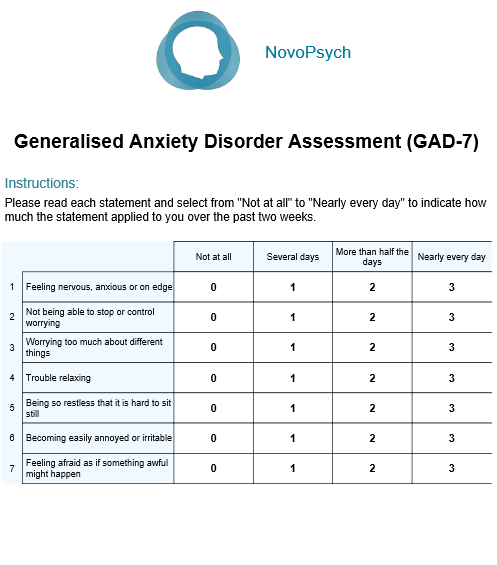
The GAD7 and PHQ9 were developed by Dr. Robert L. Spitzer and his colleagues at Columbia University, with the aim of creating brief, easy-to-use screening tools for common mental health conditions. The GAD7, published in 2006, is a 7-item questionnaire that assesses the severity of generalized anxiety disorder, while the PHQ9, published in 2001, is a 9-item questionnaire that assesses the severity of major depressive disorder. Both tools have undergone extensive validation and have been widely adopted in clinical practice.
GAD7 Structure and Scoring
The GAD7 consists of 7 items, each assessing a different aspect of anxiety, such as feeling nervous, anxious, or on edge, and difficulty controlling worry. Patients rate their symptoms over the past 2 weeks on a 4-point scale, ranging from 0 (not at all) to 3 (nearly every day). The total score ranges from 0 to 21, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity. A score of 5-9 indicates mild anxiety, 10-14 indicates moderate anxiety, and 15 or higher indicates severe anxiety.
| GAD7 Score | Anxiety Severity |
|---|---|
| 0-4 | Minimal anxiety |
| 5-9 | Mild anxiety |
| 10-14 | Moderate anxiety |
| 15-21 | Severe anxiety |
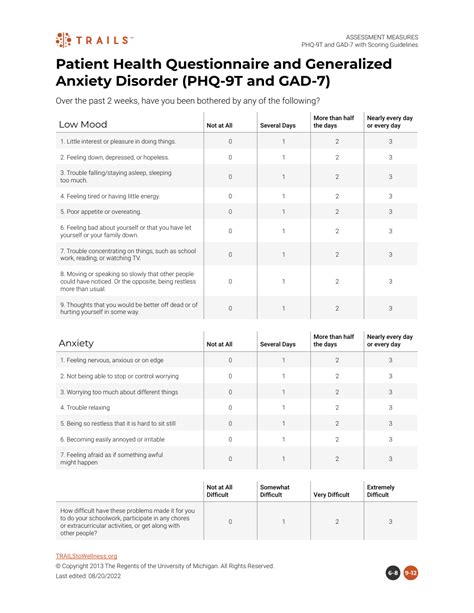
PHQ9 Structure and Scoring
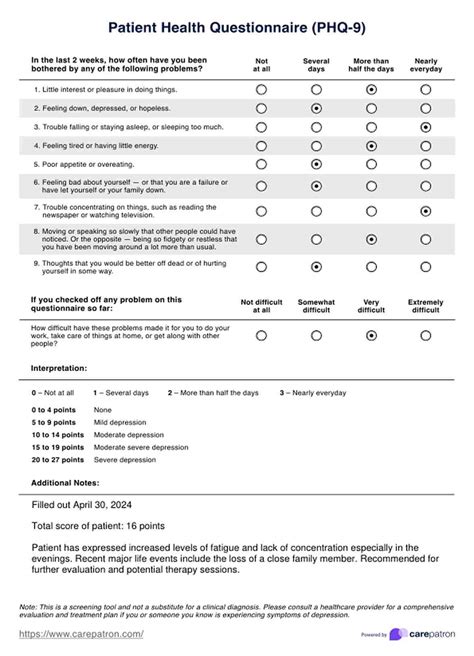
The PHQ9 consists of 9 items, each assessing a different aspect of depression, such as feeling down, depressed, or hopeless, and difficulty concentrating. Patients rate their symptoms over the past 2 weeks on a 4-point scale, ranging from 0 (not at all) to 3 (nearly every day). The total score ranges from 0 to 27, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity. A score of 5-9 indicates mild depression, 10-14 indicates moderate depression, 15-19 indicates moderately severe depression, and 20 or higher indicates severe depression.
| PHQ9 Score | Depression Severity |
|---|---|
| 0-4 | Minimal depression |
| 5-9 | Mild depression |
| 10-14 | Moderate depression |
| 15-19 | Moderately severe depression |
| 20-27 | Severe depression |
Clinical Applications of GAD7 and PHQ9
The GAD7 and PHQ9 have numerous clinical applications, including screening for anxiety and depression in primary care settings, monitoring treatment response, and tracking changes in symptom severity over time. These tools can also be used to assess the severity of anxiety and depression in patients with comorbid medical conditions, such as chronic pain or cancer. By using the GAD7 and PHQ9 in conjunction with other diagnostic tools and clinical evaluations, healthcare providers can develop targeted treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient.
Limitations and Potential Biases
While the GAD7 and PHQ9 are widely used and validated screening tools, they are not without limitations. Both tools rely on patient self-report, which can be subject to biases and inaccuracies. Additionally, the GAD7 and PHQ9 may not capture the full range of symptoms or experiences associated with anxiety and depression, particularly in patients with complex or comorbid conditions. Healthcare providers should be aware of these limitations and use the GAD7 and PHQ9 in conjunction with other diagnostic tools and clinical evaluations to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
What is the primary purpose of the GAD7 and PHQ9 screening tools?
+The primary purpose of the GAD7 and PHQ9 is to assess the severity of generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder, respectively, in primary care and mental health settings.
How are the GAD7 and PHQ9 scored, and what do the scores indicate?
+The GAD7 and PHQ9 are scored based on patient responses to a series of questions, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity. The scores can be used to monitor treatment response and track changes in symptom severity over time.
What are some limitations and potential biases of the GAD7 and PHQ9 screening tools?
+The GAD7 and PHQ9 rely on patient self-report, which can be subject to biases and inaccuracies. Additionally, these tools may not capture the full range of symptoms or experiences associated with anxiety and depression, particularly in patients with complex or comorbid conditions.
In conclusion, the GAD7 and PHQ9 are valuable screening tools for assessing the severity of generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder, respectively. By using these tools in conjunction with comprehensive clinical evaluations and other diagnostic instruments, healthcare providers can develop targeted treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient. As with any screening tool, it’s essential to be aware of the limitations and potential biases of the GAD7 and PHQ9, and to use them in a way that prioritizes patient-centered care and accurate diagnosis.