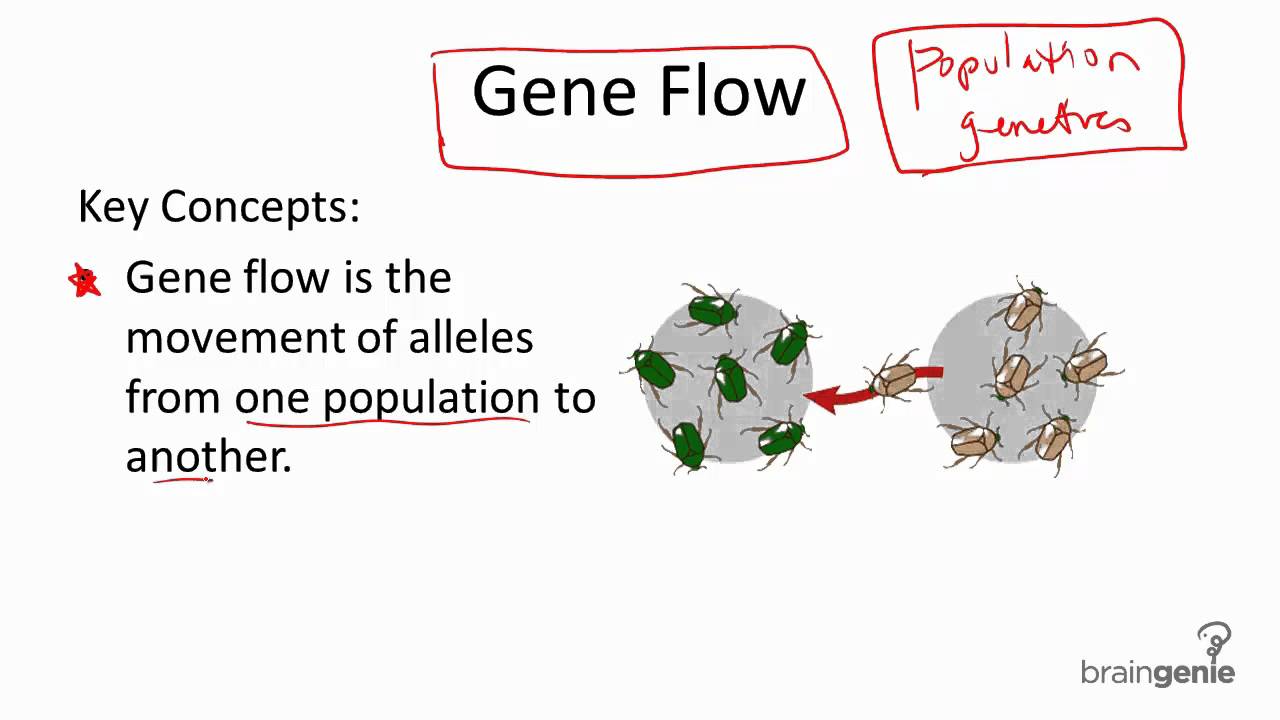
The concept of gene flow is a fundamental aspect of population genetics, describing the transfer of genetic variation from one population to another. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in shaping the genetic structure of populations and can have significant impacts on their evolution. Gene flow can occur through various means, including migration, genetic drift, and hybridization, and its effects can be observed in a wide range of organisms, from bacteria to humans.
A classic example of gene flow can be seen in the movement of humans across the globe. When a group of individuals migrates from one region to another, they bring with them their unique genetic makeup. This influx of new genetic material can lead to the introduction of new alleles, increasing the genetic diversity of the recipient population. For instance, the migration of humans from Africa to Europe and Asia thousands of years ago led to the introduction of new genetic variants, which have since become an integral part of the genetic landscape of these regions.
Key Points
- Gene flow is the transfer of genetic variation from one population to another
- It can occur through migration, genetic drift, and hybridization
- Gene flow increases genetic diversity and can lead to the introduction of new alleles
- It plays a crucial role in shaping the genetic structure of populations
- Gene flow can have significant impacts on the evolution of populations
Types of Gene Flow
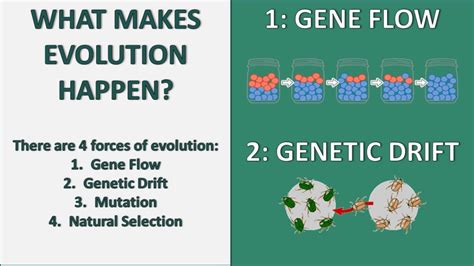
There are several types of gene flow, each with its unique characteristics and effects on population genetics. One of the primary types is migration, where individuals move from one population to another, bringing with them their genetic material. This can occur through various means, such as human migration, animal dispersal, or even the movement of pollen and seeds in plants.
Another type of gene flow is genetic drift, which occurs when a random sample of individuals from one population is transferred to another. This can lead to the loss of genetic variation in the recipient population, as well as the introduction of new alleles. Genetic drift can be particularly significant in small populations, where the random sampling of individuals can have a profound impact on the population's genetic structure.
Hybridization and Gene Flow
Hybridization, the interbreeding of individuals from different populations or species, is another mechanism of gene flow. This can occur when two populations come into contact, either through migration or other means, and exchange genetic material. Hybridization can lead to the creation of new alleles and increased genetic diversity, but it can also result in the loss of genetic variation if the hybrid offspring are less fit than the parental populations.
| Type of Gene Flow | Description | Effects on Population Genetics |
|---|---|---|
| Migration | Individuals move from one population to another | Introduction of new alleles, increased genetic diversity |
| Genetic Drift | Random sampling of individuals from one population to another | Loss of genetic variation, introduction of new alleles |
| Hybridization | Interbreeding of individuals from different populations or species | Creation of new alleles, increased genetic diversity, potential loss of genetic variation |

Case Study: Gene Flow in the Galapagos Finches

A classic example of gene flow in action can be seen in the Galapagos finches. These birds, made famous by Charles Darwin’s observations, have undergone significant changes in their genetic makeup over time. The Galapagos finches are a group of 14 species that are thought to have evolved from a single ancestral species. Gene flow has played a crucial role in shaping the genetic structure of these populations, with different species interbreeding and exchanging genetic material.
Studies have shown that gene flow has occurred between different species of Galapagos finches, leading to the introduction of new alleles and increased genetic diversity. For example, the large ground finch (Geospiza magnirostris) has been found to have exchanged genetic material with the small ground finch (Geospiza fuliginosa). This gene flow has resulted in the creation of new alleles and increased genetic diversity in both species.
Implications of Gene Flow
The implications of gene flow are far-reaching and can have significant effects on population genetics. Gene flow can lead to the introduction of new alleles, increased genetic diversity, and the creation of new species. However, it can also result in the loss of genetic variation, particularly if the hybrid offspring are less fit than the parental populations. Understanding the mechanisms and consequences of gene flow is essential for managing and conserving populations, particularly in the face of climate change, habitat fragmentation, and other environmental pressures.
What is gene flow, and how does it occur?
+Gene flow is the transfer of genetic variation from one population to another. It can occur through migration, genetic drift, and hybridization.
What are the effects of gene flow on population genetics?
+Gene flow can lead to the introduction of new alleles, increased genetic diversity, and the creation of new species. However, it can also result in the loss of genetic variation, particularly if the hybrid offspring are less fit than the parental populations.
Can gene flow occur between different species?
+Yes, gene flow can occur between different species, particularly if they are closely related. This is known as hybridization, and it can result in the creation of new alleles and increased genetic diversity.
In conclusion, gene flow is a fundamental aspect of population genetics, shaping the genetic structure of populations and influencing their evolution. Understanding the mechanisms and consequences of gene flow is essential for managing and conserving populations, particularly in the face of climate change, habitat fragmentation, and other environmental pressures. By recognizing the importance of gene flow, we can work to preserve the genetic diversity of populations and promote their long-term survival.