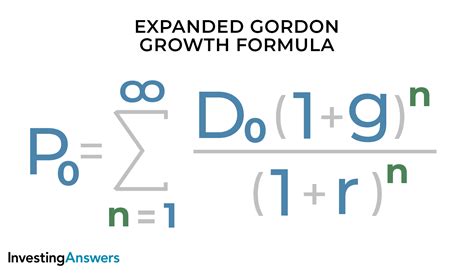The Gordon Growth Formula, also known as the Gordon Growth Model, is a widely used method for valuing stocks and estimating the intrinsic value of a company. This formula is named after Myron J. Gordon, who first introduced it in the 1950s. The model is based on the idea that a company's stock price is determined by its expected future dividend payments and the rate at which those payments are expected to grow. In this article, we will delve into the details of the Gordon Growth Formula, its components, and its applications in finance.
Key Points
- The Gordon Growth Formula is used to estimate the intrinsic value of a company's stock.
- The formula takes into account the company's expected future dividend payments and the rate at which those payments are expected to grow.
- The model assumes that the company's dividend payments will grow at a constant rate forever.
- The formula is sensitive to the input values, particularly the required rate of return and the growth rate of dividends.
- The Gordon Growth Formula is a useful tool for investors and analysts to evaluate the potential return on investment of a stock.
Understanding the Gordon Growth Formula

The Gordon Growth Formula is expressed as follows: Value = D / (r - g), where:
D is the expected dividend per share for the next period, r is the required rate of return, and g is the expected growth rate of dividends. The required rate of return is the minimum rate of return that an investor demands for holding the stock, and it reflects the risk associated with the investment. The growth rate of dividends is the rate at which the company’s dividend payments are expected to increase over time.
Components of the Gordon Growth Formula
The Gordon Growth Formula has three main components: the dividend per share, the required rate of return, and the growth rate of dividends. Each of these components plays a crucial role in determining the value of the stock. The dividend per share is the amount of money that the company distributes to its shareholders for each share they own. The required rate of return is the minimum rate of return that an investor demands for holding the stock, and it reflects the risk associated with the investment. The growth rate of dividends is the rate at which the company’s dividend payments are expected to increase over time.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Dividend per Share (D) | The amount of money distributed to shareholders for each share they own. |
| Required Rate of Return (r) | The minimum rate of return demanded by investors for holding the stock. |
| Growth Rate of Dividends (g) | The rate at which the company's dividend payments are expected to increase over time. |

Applications of the Gordon Growth Formula

The Gordon Growth Formula has several applications in finance, including stock valuation, investment analysis, and portfolio management. The formula can be used to estimate the intrinsic value of a company’s stock, which can help investors determine whether the stock is overvalued or undervalued. The formula can also be used to compare the potential return on investment of different stocks and to evaluate the performance of a portfolio.
Limitations of the Gordon Growth Formula
While the Gordon Growth Formula is a useful tool for valuing stocks, it has several limitations. One of the main limitations is that the formula assumes that the company’s dividend payments will grow at a constant rate forever, which may not be realistic. Additionally, the formula does not take into account other factors that can impact the value of the stock, such as changes in the company’s financial condition or industry trends.
What is the Gordon Growth Formula used for?
+The Gordon Growth Formula is used to estimate the intrinsic value of a company's stock. It takes into account the company's expected future dividend payments and the rate at which those payments are expected to grow.
What are the components of the Gordon Growth Formula?
+The Gordon Growth Formula has three main components: the dividend per share, the required rate of return, and the growth rate of dividends.
What are the limitations of the Gordon Growth Formula?
+The Gordon Growth Formula assumes that the company's dividend payments will grow at a constant rate forever, which may not be realistic. Additionally, the formula does not take into account other factors that can impact the value of the stock, such as changes in the company's financial condition or industry trends.
In conclusion, the Gordon Growth Formula is a widely used method for valuing stocks and estimating the intrinsic value of a company. While the formula has several applications in finance, it is essential to note that it is sensitive to the input values and has several limitations. By understanding the components and limitations of the Gordon Growth Formula, investors and analysts can use it as a tool to evaluate the potential return on investment of a stock and make informed investment decisions.