A graduated cylinder is a fundamental piece of laboratory equipment used to accurately measure the volume of liquids. Its function is based on the principle of precise calibration, allowing users to determine the volume of a liquid with a high degree of accuracy. The graduated cylinder is an essential tool in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and physics, where the measurement of liquids is a crucial aspect of experiments and research. The graduated cylinder's design features a tall, narrow cylindrical body with graduated markings on the side, indicating different volume levels. This simple yet effective design enables users to easily read the volume of a liquid contained within the cylinder.
The operation of a graduated cylinder involves filling the cylinder with a liquid to a certain level, and then reading the volume from the graduated markings. The cylinder is typically made of glass or plastic and has a pouring spout to facilitate the transfer of liquids. The graduated markings on the side of the cylinder are usually in units of milliliters (mL) or liters (L), and the cylinder is designed to be read from the bottom of the meniscus, which is the curved surface of the liquid. This ensures that the volume reading is accurate and consistent. The graduated cylinder's function is not limited to measuring the volume of liquids; it can also be used to mix and stir substances, making it a versatile tool in laboratory settings.
Key Points
- The graduated cylinder is a laboratory equipment used to measure the volume of liquids accurately.
- Its design features a tall, narrow cylindrical body with graduated markings on the side, indicating different volume levels.
- The operation of a graduated cylinder involves filling the cylinder with a liquid to a certain level and reading the volume from the graduated markings.
- The cylinder is typically made of glass or plastic and has a pouring spout to facilitate the transfer of liquids.
- The graduated cylinder's function is not limited to measuring the volume of liquids; it can also be used to mix and stir substances.
Calibration and Accuracy of Graduated Cylinders
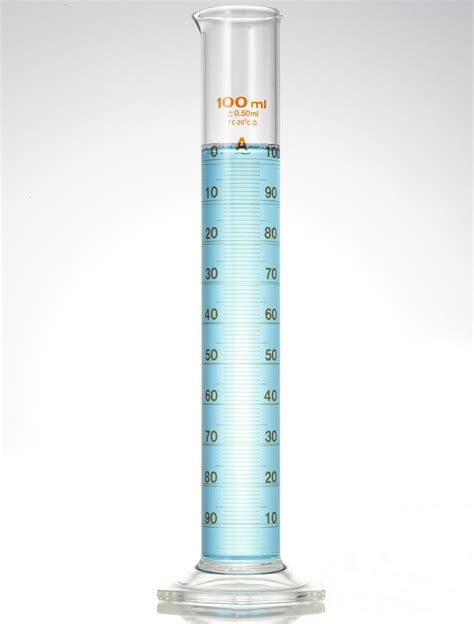

Graduated cylinders are calibrated to ensure accuracy in measurements. The calibration process involves verifying that the graduated markings on the cylinder correspond to the actual volumes of liquid contained within. This is typically done by comparing the cylinder’s measurements to those of a more precise instrument, such as a pipette or a volumetric flask. The accuracy of a graduated cylinder is critical in laboratory settings, where small errors in measurement can have significant consequences. To maintain accuracy, graduated cylinders should be handled with care, and users should follow proper techniques when reading the volume of a liquid.
The accuracy of a graduated cylinder can be affected by several factors, including the material of construction, the design of the cylinder, and the technique used to read the volume. For example, glass graduated cylinders are generally more accurate than plastic ones, as they are less prone to scratches and other forms of damage that can affect the accuracy of the measurements. Additionally, the technique used to read the volume of a liquid can also impact the accuracy of the measurement. It is essential to read the volume from the bottom of the meniscus, as this ensures that the measurement is consistent and accurate.
Types of Graduated Cylinders
There are several types of graduated cylinders available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of graduated cylinders include glass graduated cylinders, plastic graduated cylinders, and borosilicate glass graduated cylinders. Glass graduated cylinders are the most common type and are known for their accuracy and durability. Plastic graduated cylinders are less expensive than glass ones but may be less accurate and more prone to scratches. Borosilicate glass graduated cylinders are made from a type of glass that is resistant to thermal shock and are often used in applications where the cylinder will be exposed to extreme temperatures.
| Type of Graduated Cylinder | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Graduated Cylinder | Accurate, durable, and resistant to scratches | General laboratory use, measuring the volume of liquids |
| Plastic Graduated Cylinder | Less demanding laboratory applications, measuring the volume of non-corrosive liquids | |
| Borosilicate Glass Graduated Cylinder | Resistant to thermal shock, accurate, and durable | Applications where the cylinder will be exposed to extreme temperatures, measuring the volume of liquids in high-temperature environments |
Best Practices for Using Graduated Cylinders
To ensure accurate measurements and prolong the life of a graduated cylinder, it is essential to follow best practices when using the equipment. This includes handling the cylinder with care, avoiding scratches and other forms of damage, and cleaning the cylinder regularly. Additionally, users should always read the volume of a liquid from the bottom of the meniscus, as this ensures that the measurement is consistent and accurate. It is also essential to use the correct technique when filling the cylinder, as this can affect the accuracy of the measurement.
When filling a graduated cylinder, it is essential to pour the liquid slowly and carefully, avoiding spills and splashes. The cylinder should be placed on a flat surface, and the liquid should be poured down the side of the cylinder, rather than directly into the center. This helps to prevent the formation of air bubbles, which can affect the accuracy of the measurement. Once the cylinder is filled to the desired level, the user should read the volume from the graduated markings, taking care to read from the bottom of the meniscus.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Graduated Cylinders
Despite their durability, graduated cylinders can be prone to certain issues, including scratches, cracks, and contamination. Scratches can affect the accuracy of the measurements, while cracks can render the cylinder unusable. Contamination can also affect the accuracy of the measurements, as well as the safety of the user. To troubleshoot these issues, users should first inspect the cylinder for any visible damage or contamination. If the cylinder is damaged, it should be replaced immediately. If the cylinder is contaminated, it should be cleaned and dried before use.
In addition to these issues, graduated cylinders can also be prone to errors in measurement, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including the technique used to read the volume, the accuracy of the graduated markings, and the material of construction. To minimize the risk of errors, users should always follow best practices when using the equipment, including handling the cylinder with care, avoiding scratches and other forms of damage, and cleaning the cylinder regularly.
What is the purpose of a graduated cylinder?
+The purpose of a graduated cylinder is to accurately measure the volume of liquids in a laboratory setting.
How do I calibrate a graduated cylinder?
+To calibrate a graduated cylinder, compare its measurements to those of a more precise instrument, such as a pipette or a volumetric flask.
What are the different types of graduated cylinders?
+The most common types of graduated cylinders include glass graduated cylinders, plastic graduated cylinders, and borosilicate glass graduated cylinders.
How do I troubleshoot common issues with graduated cylinders?
+To troubleshoot common issues with graduated cylinders, inspect the cylinder for any visible damage or contamination, and replace or clean the cylinder as needed.
What are the best practices for using graduated cylinders?
+The best practices for using graduated cylinders include handling the cylinder with care, avoiding scratches and other forms of damage, and cleaning the cylinder regularly.
In conclusion, graduated cylinders are a fundamental piece of laboratory equipment used to accurately measure the volume of liquids. Their function is based on the principle of precise calibration, and they are available in various types, including glass, plastic, and borosilicate glass. To ensure accurate measurements and prolong the life of a graduated cylinder, it is essential to follow best practices when using the equipment, including handling the cylinder with care, avoiding scratches and other forms of damage, and cleaning the cylinder regularly. By understanding the function, calibration, and best practices for using graduated cylinders, laboratory professionals can ensure accurate and reliable measurements in a variety of applications.