The money market is a crucial component of the financial system, providing a platform for borrowers and lenders to interact and facilitate the flow of short-term funds. The graph of the money market is a visual representation of the relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded and supplied. Understanding this graph is essential for economists, financial analysts, and policymakers to analyze the dynamics of the money market and make informed decisions.
Key Points
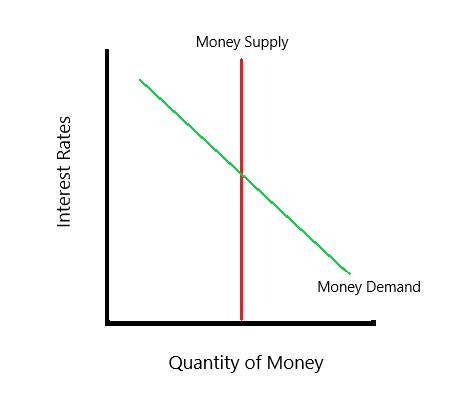
- The money market graph illustrates the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
- The demand for money is influenced by factors such as income, prices, and interest rates.
- The supply of money is determined by the central bank's monetary policy decisions.
- Changes in the demand and supply of money can lead to shifts in the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
- The money market graph is a fundamental tool for analyzing the effects of monetary policy on the economy.
The Demand for Money

The demand for money represents the amount of money that households and businesses are willing to hold at a given interest rate. The demand curve for money is typically downward-sloping, indicating that as the interest rate increases, the quantity of money demanded decreases. This is because higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive and reduce the incentive to hold money. The demand for money is influenced by factors such as income, prices, and interest rates. For example, an increase in income will lead to an increase in the demand for money, as households and businesses have more funds to hold.
Factors Affecting the Demand for Money
Several factors can affect the demand for money, including:
- Income: An increase in income will lead to an increase in the demand for money.
- Prices: An increase in prices will lead to an increase in the demand for money, as households and businesses need to hold more money to purchase goods and services.
- Interest rates: An increase in interest rates will lead to a decrease in the demand for money, as borrowing becomes more expensive.
- Expected inflation: An increase in expected inflation will lead to an increase in the demand for money, as households and businesses may hold more money to protect against inflation.
| Factor | Effect on Demand for Money |
|---|---|
| Income | Increases demand for money |
| Prices | Increases demand for money |
| Interest rates | Decreases demand for money |
| Expected inflation | Increases demand for money |
The Supply of Money

The supply of money represents the amount of money that is available in the economy at a given interest rate. The supply curve for money is typically vertical, indicating that the quantity of money supplied is determined by the central bank’s monetary policy decisions. The central bank can increase or decrease the money supply by buying or selling government securities, which affects the level of reserves in the banking system and the amount of money available for lending.
Monetary Policy and the Supply of Money
Monetary policy plays a crucial role in determining the supply of money. The central bank can use various tools, such as open market operations, reserve requirements, and discount rates, to influence the money supply. For example, an increase in the money supply can lead to a decrease in interest rates, making borrowing cheaper and stimulating economic activity.
Equilibrium in the Money Market
The equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money are determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. At this point, the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied, and the interest rate is at a level that clears the market. Changes in the demand and supply of money can lead to shifts in the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
Changes in the Demand and Supply of Money
Changes in the demand and supply of money can have significant effects on the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money. For example, an increase in the demand for money can lead to an increase in the equilibrium interest rate, making borrowing more expensive. On the other hand, an increase in the supply of money can lead to a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate, making borrowing cheaper.
| Change | Effect on Equilibrium Interest Rate | Effect on Equilibrium Quantity of Money |
|---|---|---|
| Increase in demand for money | Increases equilibrium interest rate | Decreases equilibrium quantity of money |
| Increase in supply of money | Decreases equilibrium interest rate | Increases equilibrium quantity of money |
What is the money market graph, and what does it represent?
+The money market graph is a visual representation of the relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded and supplied. It represents the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money in the economy.
What factors affect the demand for money, and how do they impact the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money?
+Factors such as income, prices, and interest rates affect the demand for money. An increase in income or prices can lead to an increase in the demand for money, while an increase in interest rates can lead to a decrease in the demand for money. These changes can impact the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
How does monetary policy affect the supply of money, and what are the implications for the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money?
+Monetary policy, as implemented by the central bank, can increase or decrease the money supply by buying or selling government securities. An increase in the money supply can lead to a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate, making borrowing cheaper, while a decrease in the money supply can lead to an increase in the equilibrium interest rate, making borrowing more expensive.



