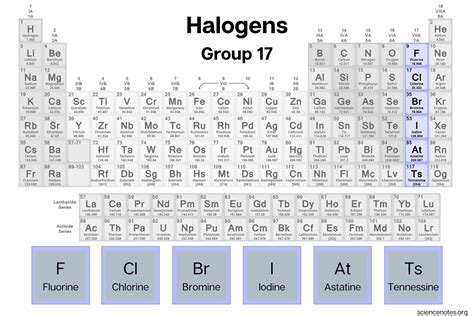
The halogens are a group of nonmetal elements in the periodic table, consisting of fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). These elements are known for their highly reactive nature, which makes them essential in various chemical reactions and applications. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of halogens, exploring their properties, uses, and interesting facts.
Key Points
- The halogens are a group of highly reactive nonmetal elements in the periodic table.
- Fluorine is the most reactive halogen, while astatine is the least reactive due to its radioactive nature.
- Halogens are essential in various applications, including water purification, pharmaceuticals, and lighting.
- The reactivity of halogens decreases as you move down the group in the periodic table.
- Halogens can form a wide range of compounds, including acids, bases, and salts.
- The name "halogen" comes from the Greek words "halos" meaning salt and "genes" meaning producer.
Introduction to Halogens
The term “halogen” is derived from the Greek words “halos,” meaning salt, and “genes,” meaning producer. This refers to the fact that halogens were first discovered as compounds in salt deposits. The halogens are located in group 17 of the periodic table and are characterized by their seven valence electrons, which makes them highly reactive. They readily form ions with a -1 charge, known as halide ions, by gaining one electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
Physical Properties of Halogens
The physical properties of halogens vary significantly, ranging from fluorine, which is a pale yellow gas, to iodine, which is a violet-black solid. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas, while bromine is a reddish-brown liquid. Astatine, being highly radioactive, is not commonly encountered in its elemental form. The melting and boiling points of halogens also increase as you move down the group, due to the increasing strength of the intermolecular forces between the molecules.
| Halogens | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass | Physical State at Room Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorine (F) | 9 | 18.998403163 | Gas |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 17 | 35.453 | Gas |
| Bromine (Br) | 35 | 79.904 | Liquid |
| Iodine (I) | 53 | 126.90447 | Solid |
| Astatine (At) | 85 | 209.9871 | Solid ( radioactive ) |
Chemical Properties of Halogens

Halogens are highly reactive due to their strong tendency to gain electrons and form ions with a -1 charge. They react with metals to form salts, and with nonmetals, they form covalent compounds. The reactivity of halogens towards metals increases as you move up the group, with fluorine being the most reactive. Halogens also react with water to form acids and with other compounds to form a wide range of products.
Uses of Halogens
Halogens have numerous applications in various industries. Fluorine is used in the production of fluoridated water, toothpaste, and other dental products to prevent tooth decay. Chlorine is used as a disinfectant in swimming pools and water treatment plants. Bromine is used in the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and photographic films. Iodine is used as a disinfectant and in the production of thyroid hormones. Astatine, due to its highly radioactive nature, has limited applications but is used in some medical research.
What are the most common uses of halogens?
+The most common uses of halogens include water purification, pharmaceuticals, and lighting. They are also used in the manufacture of dyes, photographic films, and as disinfectants.
Why are halogens highly reactive?
+Halogens are highly reactive due to their strong tendency to gain electrons and form ions with a -1 charge. This is because they have seven valence electrons, which makes it easy for them to gain one electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
What is the difference between halogens and halides?
+Halogens refer to the elements in group 17 of the periodic table, such as fluorine, chlorine, and iodine. Halides, on the other hand, refer to the ions formed when halogens gain an electron, such as fluoride (F-) or chloride (Cl-).
Meta Description: Discover the fascinating world of halogens, including their properties, uses, and interesting facts. Learn about the reactivity of halogens, their applications in various industries, and their importance in our daily lives.