The HBR Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps predict the shape and reactivity of molecules. Developed by Gilbert N. Lewis, this structure represents the arrangement of electrons in a molecule, providing valuable insights into its chemical properties. In this article, we will delve into the world of HBR Lewis structures, exploring their significance, applications, and the step-by-step process of drawing them.
Introduction to HBR Lewis Structures
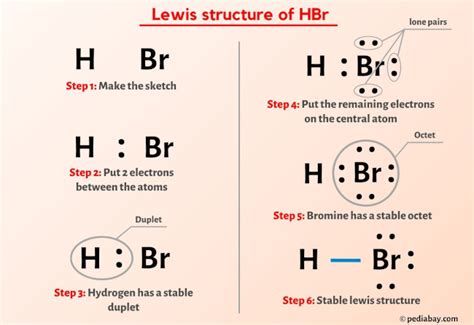
To understand the HBR Lewis structure, it is essential to first grasp the basics of molecular bonding. The HBR molecule, composed of hydrogen (H), boron (B), and bromine (Br), is a simple yet intriguing compound. The Lewis structure of HBR is crucial in determining its molecular geometry, polarity, and reactivity. By mastering the art of drawing HBR Lewis structures, chemists can better comprehend the underlying principles of molecular interactions.
Understanding the Octet Rule
The octet rule is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level, typically eight electrons. This rule is crucial in drawing Lewis structures, as it helps determine the arrangement of electrons around each atom. In the case of HBR, the octet rule guides the placement of electrons around the hydrogen, boron, and bromine atoms, ultimately influencing the molecule’s shape and properties.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Octet Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | Forms a single bond to achieve a full outer energy level |
| Boron (B) | 3 | Forms three bonds to achieve a full outer energy level |
| Bromine (Br) | 7 | Forms a single bond to achieve a full outer energy level |

Drawing HBR Lewis Structures
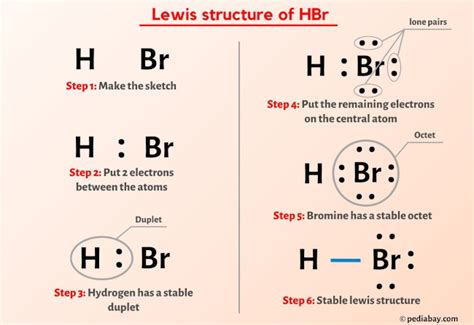
Now that we have a solid understanding of the octet rule, let’s dive into the step-by-step process of drawing HBR Lewis structures. This process involves several key steps:
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
The first step in drawing an HBR Lewis structure is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. This is done by summing the valence electrons of each atom: 1 (H) + 3 (B) + 7 (Br) = 11 valence electrons.
Step 2: Draw the Skeleton Structure
Next, we draw the skeleton structure of the molecule, connecting the atoms with single bonds. In the case of HBR, the skeleton structure consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to a boron atom, which is in turn bonded to a bromine atom.
Step 3: Distribute the Remaining Valence Electrons
With the skeleton structure in place, we distribute the remaining valence electrons around the atoms, ensuring that each atom has a full outer energy level. In HBR, the remaining electrons are distributed as lone pairs around the boron and bromine atoms.
Step 4: Verify the Octet Rule
Finally, we verify that each atom in the HBR molecule has a full outer energy level, satisfying the octet rule. The resulting Lewis structure provides a clear representation of the molecule’s electronic configuration and predicts its chemical properties.
Key Points
- The HBR Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that predicts the shape and reactivity of molecules.
- The octet rule guides the placement of electrons around each atom, influencing the molecule's shape and properties.
- The step-by-step process of drawing HBR Lewis structures involves determining the total number of valence electrons, drawing the skeleton structure, distributing the remaining valence electrons, and verifying the octet rule.
- The resulting Lewis structure provides a clear representation of the molecule's electronic configuration and predicts its chemical properties.
- Understanding HBR Lewis structures is essential for predicting the chemical behavior of molecules and anticipating the formation of bonds, the shape of molecules, and the reactivity of atoms.
Applications of HBR Lewis Structures
The HBR Lewis structure has numerous applications in chemistry, ranging from predicting molecular geometry and polarity to understanding chemical reactivity and reaction mechanisms. By mastering the art of drawing HBR Lewis structures, chemists can better comprehend the underlying principles of molecular interactions and develop a deeper understanding of chemical reactions.
Predicting Molecular Geometry
The HBR Lewis structure provides valuable insights into the molecular geometry of the HBR molecule. By analyzing the arrangement of electrons around each atom, chemists can predict the shape of the molecule and its overall polarity.
Understanding Chemical Reactivity
The HBR Lewis structure also helps predict the chemical reactivity of the molecule. By identifying the electron-rich and electron-poor regions of the molecule, chemists can anticipate the formation of bonds and the reactivity of atoms.
What is the significance of the HBR Lewis structure in chemistry?
+The HBR Lewis structure is significant in chemistry because it provides a clear representation of the molecule's electronic configuration and predicts its chemical properties, such as molecular geometry and polarity.
How does the octet rule influence the HBR Lewis structure?
+The octet rule guides the placement of electrons around each atom in the HBR molecule, ensuring that each atom has a full outer energy level and influencing the molecule's shape and properties.
What are the applications of HBR Lewis structures in chemistry?
+The HBR Lewis structure has numerous applications in chemistry, including predicting molecular geometry and polarity, understanding chemical reactivity, and anticipating the formation of bonds and the reactivity of atoms.
In conclusion, the HBR Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides valuable insights into the electronic configuration and chemical properties of molecules. By mastering the art of drawing HBR Lewis structures, chemists can better comprehend the underlying principles of molecular interactions and develop a deeper understanding of chemical reactions. As we continue to explore the world of chemistry, the significance of HBR Lewis structures will only continue to grow, offering a powerful tool for predicting the chemical behavior of molecules and anticipating the formation of bonds, the shape of molecules, and the reactivity of atoms.