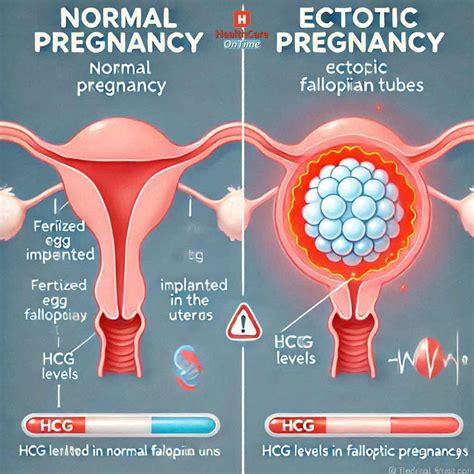
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) levels play a crucial role in monitoring early pregnancy, including ectopic pregnancies. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, commonly in the fallopian tube. This condition can lead to severe complications, including rupture of the fallopian tube, which is a medical emergency. Understanding HCG levels in ectopic pregnancies is essential for early detection and management.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance

In a normal pregnancy, HCG levels typically double every 48 hours during the first trimester. However, in ectopic pregnancies, HCG levels often rise at a slower rate. A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that HCG levels in ectopic pregnancies were significantly lower than those in normal pregnancies at 4-5 weeks of gestation. This discrepancy can be used as an indicator of potential ectopic pregnancy, but it is not definitive.
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
The diagnostic criteria for ectopic pregnancy involve a combination of clinical presentation, ultrasound imaging, and laboratory tests, including HCG levels. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that women with suspected ectopic pregnancy undergo transvaginal ultrasound to visualize the gestational sac. If the HCG level is above the discriminatory zone (typically around 1,500-3,000 mIU/mL), and no intrauterine pregnancy is seen on ultrasound, ectopic pregnancy should be suspected.
| HCG Level | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Below 1,500 mIU/mL | Pregnancy may be too early to detect, or it could be an ectopic pregnancy |
| 1,500-3,000 mIU/mL | Potential ectopic pregnancy if no intrauterine pregnancy is seen on ultrasound |
| Above 3,000 mIU/mL | High suspicion for ectopic pregnancy if no intrauterine pregnancy is visualized |
Key Points
- HCG levels in ectopic pregnancies often rise at a slower rate than in normal pregnancies.
- A combination of clinical presentation, ultrasound imaging, and HCG levels is used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy.
- The discriminatory zone for HCG levels is typically between 1,500-3,000 mIU/mL, above which an intrauterine pregnancy should be visible on ultrasound.
- Early detection of ectopic pregnancy is critical to prevent severe complications and improve outcomes.
- HCG levels should be interpreted in the context of the patient's clinical picture and the trend of levels over time.
Management and Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy

The management of ectopic pregnancy depends on the patient’s condition, the size and location of the ectopic pregnancy, and the HCG levels. Treatment options include expectant management for patients who are asymptomatic and have low, declining HCG levels, medical management with methotrexate for patients who meet specific criteria, and surgical intervention for patients with rupture or significant symptoms.
Medical Management
Methotrexate is a chemotherapeutic agent used to treat ectopic pregnancies by stopping cell growth and promoting absorption of the pregnancy tissue. The effectiveness of methotrexate depends on the HCG level at the time of treatment, with success rates higher when HCG levels are below 5,000 mIU/mL. It’s crucial for patients undergoing medical management to be closely monitored with serial HCG levels and ultrasound to ensure the resolution of the ectopic pregnancy.
In conclusion, understanding HCG levels in the context of ectopic pregnancy is vital for early detection and appropriate management. While HCG levels alone are not diagnostic, their interpretation in conjunction with clinical presentation and ultrasound findings is crucial for identifying ectopic pregnancies and preventing severe complications.
What is the role of HCG levels in diagnosing ectopic pregnancy?
+HCG levels play a significant role in diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. Abnormally slow-rising HCG levels, especially when combined with clinical symptoms and ultrasound findings, can indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
How are HCG levels used in the management of ectopic pregnancy?
+HCG levels are used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, whether it be expectant management, medical management with methotrexate, or surgical intervention. Declining HCG levels indicate resolution of the ectopic pregnancy, while persistently high or rising levels may suggest treatment failure or persistence of the ectopic tissue.
What are the implications of delayed diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy?
+Delayed diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy can lead to severe complications, including rupture of the fallopian tube, which is a life-threatening emergency. Early detection through a combination of clinical evaluation, ultrasound, and HCG level monitoring is critical to prevent such outcomes and improve patient survival and fertility preservation.
Meta Description: Understand the role of HCG levels in diagnosing and managing ectopic pregnancy, and learn about the importance of early detection and appropriate treatment to prevent severe complications.