Head lice, also known as pediculosis capitis, are a common problem affecting millions of people worldwide, particularly children. These tiny, wingless insects feed on human blood and can cause significant discomfort, itching, and embarrassment. Understanding the appearance and behavior of head lice is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. In this article, we will explore the world of head lice images, discussing the different types, stages, and manifestations of these pesky parasites.
What Do Head Lice Look Like?

Head lice are small, flat, and oval-shaped insects that range in color from grayish-white to dark brown. They have six legs and are approximately 2-3 millimeters long, making them barely visible to the naked eye. Adult head lice have a distinctive appearance, with a transparent exoskeleton and a pair of antennae on their heads. The female louse is slightly larger than the male and has a more rounded abdomen.
Stages of Head Lice Development
Head lice undergo three stages of development: egg, nymph, and adult. The eggs, also known as nits, are tiny, yellowish-white capsules that are attached to the hair shaft, usually within 1⁄4 inch of the scalp. Nits are incredibly resilient and can survive for up to 14 days without a host. The nymph stage lasts around 7-10 days, during which the louse molts three times, eventually reaching adulthood.
| Stage | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Egg (Nit) | Tiny, yellowish-white capsule attached to hair shaft | Up to 14 days |
| Nymph | Immature louse that molts three times | 7-10 days |
| Adult | Mature louse that feeds on human blood | Up to 30 days |
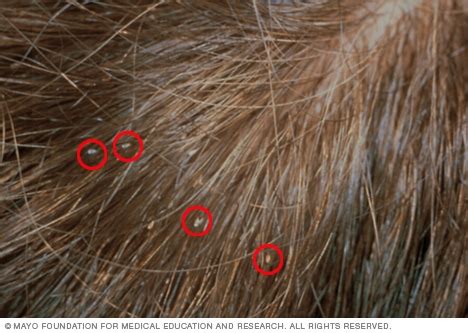
Types of Head Lice Images
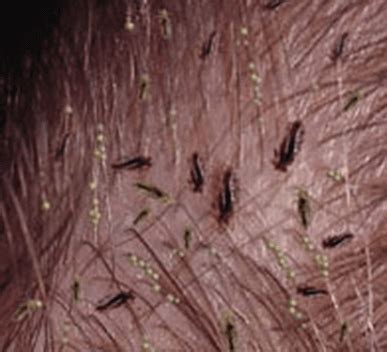
There are several types of head lice images that can be used for diagnostic and educational purposes. These include:
- Macroscopic images: Close-up photographs of head lice, nits, and eggs, which can help identify the parasite's morphology and behavior.
- Microscopic images: High-magnification images of head lice and nits, which can reveal detailed structures and features not visible to the naked eye.
- Infestation images: Photographs of scalp infestations, which can illustrate the severity of the infestation and the presence of secondary symptoms such as redness and scratching.
Diagnosing Head Lice
Diagnosing head lice typically involves a combination of visual examination, medical history, and laboratory testing. A healthcare professional may use a specialized comb or microscope to detect lice or nits in the hair. In some cases, a scalp scraping or biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Key Points
- Head lice are small, flat, and oval-shaped insects that feed on human blood.
- The eggs, or nits, are tiny, yellowish-white capsules attached to the hair shaft.
- Head lice undergo three stages of development: egg, nymph, and adult.
- Diagnosing head lice typically involves visual examination, medical history, and laboratory testing.
- Treatment options include over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, and home remedies such as combing and washing.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment for head lice usually involves a combination of medication and non-medication approaches. Over-the-counter medications such as permethrin and pyrethrin are commonly used to kill lice and nits. Prescription medications such as ivermectin and spinosad may be prescribed for more severe infestations. In addition to medication, combing and washing the hair with a fine-toothed comb and shampoo can help remove lice and nits.
Preventing head lice infestations requires a combination of good hygiene practices, regular scalp checks, and avoidance of head-to-head contact with infected individuals. Parents and caregivers can play a crucial role in preventing the spread of head lice by educating children about the importance of not sharing personal items such as combs, brushes, and hats.
How do I know if I have head lice?
+Common symptoms of head lice include itching, scratching, and the presence of tiny, moving specks on the scalp. If you suspect you have head lice, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Can head lice be prevented?
+Yes, head lice can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding head-to-head contact with infected individuals, and regularly checking the scalp for signs of infestation.
What is the most effective treatment for head lice?
+The most effective treatment for head lice usually involves a combination of medication and non-medication approaches, such as combing and washing the hair with a fine-toothed comb and shampoo.
Meta Description: Learn about head lice images, including the different types, stages, and manifestations of these pesky parasites. Understand the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of head lice infestations.