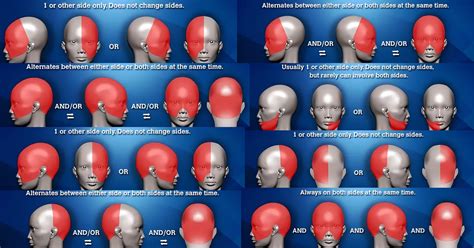
Headaches can be a debilitating and frustrating experience, affecting millions of people worldwide. While the causes of headaches can be diverse, ranging from tension and migraines to cluster headaches, the location of the headache can often provide valuable insights into its underlying cause. Understanding the meaning behind headache locations can help individuals better navigate their symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention when necessary. In this article, we will delve into the different locations where headaches can occur and what these locations might indicate about the headache's cause.
Types of Headaches and Their Locations

Headaches can be broadly categorized into several types, each with distinct characteristics and locations. The primary headache types include tension headaches, migraines, cluster headaches, and sinus headaches, among others. Tension headaches, for instance, are often described as a band or a squeezing sensation around the forehead, usually affecting both sides of the head. Migraines, on the other hand, can cause severe, throbbing pain, typically on one side of the head, though the location can shift during the headache episode. Cluster headaches are known for their excruciating, piercing pain, usually centered around one eye. Understanding these locations and their associated headache types is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Tension Headaches: Forehead and Back of the Neck
Tension headaches are the most common type of headache and are often associated with stress, muscle tension, and poor posture. The pain from tension headaches is usually mild to moderate and is described as a tight band or a squeezing sensation around the forehead or the back of the neck. This type of headache can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, stress management techniques, and improving posture. For example, a study found that 71.8% of participants with tension headaches reported significant improvement in symptoms after engaging in regular exercise and stress management activities.
| Headache Type | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tension Headache | Forehead, Back of the Neck | Mild to moderate, band-like or squeezing sensation |
| Migraine | One side of the head, can shift | Severe, throbbing, can be accompanied by aura, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound |
| Cluster Headache | Around one eye | Excruciating, piercing, usually occurs in cycles or clusters |
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
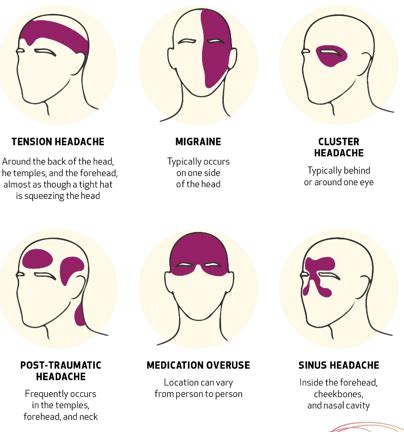
The diagnosis of headaches involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and sometimes, diagnostic tests such as imaging studies. The treatment approach varies depending on the headache type and underlying cause. For tension headaches, lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter medications are often sufficient. Migraines may require prescription medications, including those for acute treatment and prevention. Cluster headaches, due to their severity, may necessitate more aggressive treatment strategies, including injectable medications and oxygen therapy. A balanced approach that considers the patient’s overall health, lifestyle, and preferences is crucial for effective management.
Migraines: One-Sided Pain with Additional Symptoms
Migraines are complex and can involve not only headache pain but also a range of other symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and in some cases, neurological symptoms known as aura. The pain of a migraine is typically one-sided, though it can shift locations during the headache, and is often described as throbbing or pulsating. Managing migraines requires a multifaceted approach, including preventive medications, lifestyle changes, and strategies for managing triggers and symptoms during an episode. For instance, maintaining a headache diary can help identify specific triggers, allowing for more targeted prevention strategies.
Key Points
- Understanding the location of a headache can provide insights into its underlying cause, such as tension, migraine, or cluster headache.
- Tension headaches are characterized by a band-like sensation around the forehead or back of the neck, often associated with stress and muscle tension.
- Migraines involve severe, one-sided pain that can be accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and aura, requiring a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Cluster headaches are known for their severe, piercing pain centered around one eye, occurring in cycles, and may require aggressive treatment strategies.
- A thorough medical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan, considering the patient's overall health and preferences.
In conclusion, the location of a headache can serve as a critical clue in understanding its cause and guiding its treatment. Whether it's the band-like sensation of a tension headache, the severe, one-sided pain of a migraine, or the excruciating, piercing pain of a cluster headache, each type of headache presents unique challenges and opportunities for management. By combining a deep understanding of headache types with a patient-centered approach to care, individuals can better navigate their symptoms and work towards finding relief and improving their quality of life.
What are the primary types of headaches and their characteristic locations?
+The primary types of headaches include tension headaches, which are typically characterized by a band-like sensation around the forehead or the back of the neck; migraines, which cause severe, one-sided pain that can shift locations; and cluster headaches, known for their severe, piercing pain centered around one eye.
How is the diagnosis of headaches approached, and what role does the location of the headache play in this process?
+The diagnosis of headaches involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and sometimes, diagnostic tests. The location of the headache, along with its characteristics and accompanying symptoms, plays a significant role in guiding the diagnosis and subsequent treatment plan.
What are some common triggers for migraines, and how can they be managed?
+