The Hebrew alphabet, also known as the Aleph-Bet, is a fundamental component of the Hebrew language, with a rich history and cultural significance. The alphabet consists of 22 letters, all of which are consonants, and is written from right to left. Understanding the Hebrew alphabet is essential for reading and writing in Hebrew, as well as for appreciating the language's unique characteristics and nuances.
Key Points
- The Hebrew alphabet has 22 letters, all of which are consonants.
- The alphabet is written from right to left.
- Understanding the Hebrew alphabet is essential for reading and writing in Hebrew.
- The Hebrew alphabet has a rich history and cultural significance.
- Mastering the Hebrew alphabet is crucial for language learners and scholars alike.
Introduction to the Hebrew Alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet has been in use for over 3,000 years, with its earliest known inscriptions dating back to the 10th century BCE. The alphabet has undergone several changes and developments throughout its history, including the introduction of vowel points and other diacritical marks. Today, the Hebrew alphabet is used by millions of people around the world, including native Hebrew speakers, language learners, and scholars.
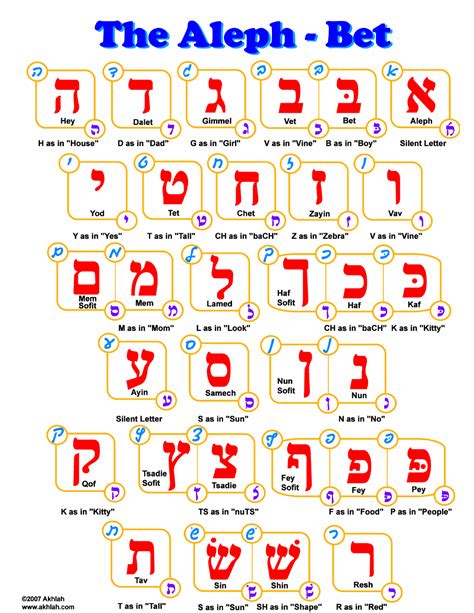
Hebrew Alphabet Chart
A Hebrew alphabet chart is a useful tool for learning and referencing the Hebrew alphabet. The chart typically includes the 22 letters of the alphabet, along with their names, pronunciation, and numerical values. The chart may also include additional information, such as the letters’ shapes and forms, as well as their uses in different contexts.
| Letter | Name | Pronunciation | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| א | Aleph | /ʔ/ or silent | 1 |
| ב | Bet | /b/ or /v/ | 2 |
| ג | Gimel | /ɡ/ | 3 |
| ד | Dalet | /d/ | 4 |
| ה | He | /h/ | 5 |
| ו | Vav | /v/ or /u/ | 6 |
| ז | Zayin | /z/ | 7 |
| ח | Chet | /χ/ | 8 |
| ט | Tet | /tˤ/ | 9 |
| י | Yud | /j/ | 10 |
| כ | Kaf | /k/ or /χ/ | 20 |
| ל | Lamed | /l/ | 30 |
| מ | Mem | /m/ | 40 |
| נ | Nun | /n/ | 50 |
| ס | Samech | /s/ | 60 |
| ע | Ayin | /ʔ/ or silent | 70 |
| פ | Pe | /p/ or /f/ | 80 |
| צ | Tzadi | /ts/ | 90 |
| ק | Kof | /k/ | 100 |
| ר | Resh | /r/ | 200 |
| ש | Shin | /ʃ/ or /s/ | 300 |
| ת | Tav | /t/ or /θ/ | 400 |
Learning the Hebrew Alphabet
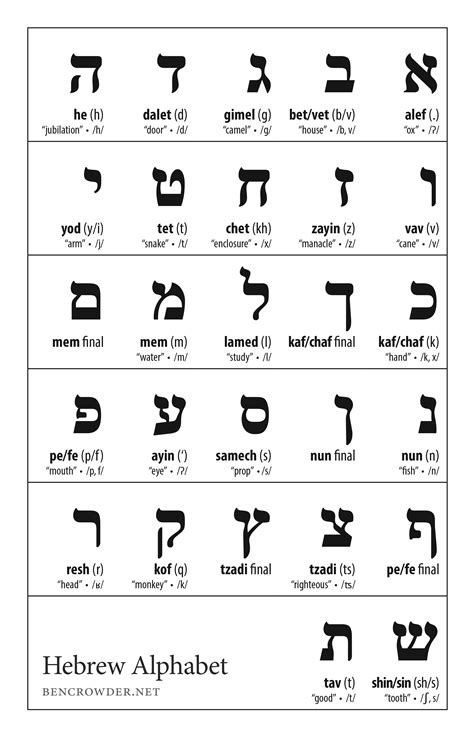
Learning the Hebrew alphabet can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a rewarding and enriching experience. Here are some tips for learning the Hebrew alphabet:
- Start with the basics: Begin by learning the names and pronunciation of the letters.
- Practice regularly: Practice writing and reading the letters regularly to reinforce your learning.
- Use a Hebrew alphabet chart: A Hebrew alphabet chart can be a useful tool for referencing the letters and their pronunciation.
- Immerse yourself in the language: Listen to Hebrew music, watch Hebrew videos, and try to speak with native speakers to immerse yourself in the language.
Advanced Topics in Hebrew Alphabet
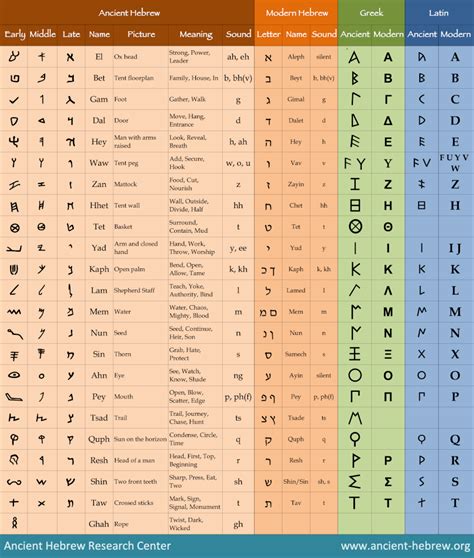
Once you have a solid understanding of the Hebrew alphabet, you can move on to more advanced topics, such as learning the different forms of the letters, understanding the nuances of Hebrew pronunciation, and exploring the cultural and historical significance of the alphabet.
Hebrew Alphabet in Different Contexts
The Hebrew alphabet is used in a variety of contexts, including religious texts, literature, and everyday communication. Understanding the different forms and uses of the alphabet can help you appreciate the richness and diversity of the Hebrew language.
In religious texts, the Hebrew alphabet is used to write sacred texts, such as the Torah and the Talmud. The alphabet is also used in liturgical contexts, such as in prayer books and synagogue services.
In literature, the Hebrew alphabet is used to write novels, poetry, and other forms of creative writing. Hebrew literature is known for its rich imagery and nuanced language, and the alphabet plays a significant role in conveying the author's intended meaning.
In everyday communication, the Hebrew alphabet is used in a variety of contexts, including signage, advertising, and personal correspondence. Understanding the alphabet is essential for communicating effectively in Hebrew.
What is the significance of the Hebrew alphabet in Jewish culture?
+The Hebrew alphabet is a fundamental component of Jewish culture and is used in a variety of contexts, including religious texts, literature, and everyday communication. The alphabet is also a symbol of Jewish identity and is often used in Jewish art and symbolism.
How do I learn the Hebrew alphabet?
+Learning the Hebrew alphabet can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a rewarding and enriching experience. Start by learning the names and pronunciation of the letters, and practice regularly to reinforce your learning. Use a Hebrew alphabet chart to reference the letters and their pronunciation, and immerse yourself in the language by listening to Hebrew music, watching Hebrew videos, and trying to speak with native speakers.
What are some common challenges when learning the Hebrew alphabet?
+Some common challenges when learning the Hebrew alphabet include mastering the correct pronunciation of the letters, understanding the different forms and uses of the alphabet, and developing the necessary skills to read and write in Hebrew. Additionally, learners may struggle with the fact that Hebrew is written from right to left, which can be unfamiliar to those who are used to writing from left to right.



