The concept of heterogeneity and homogeneity is crucial in various fields, including biology, chemistry, physics, and social sciences. Understanding the differences between these two terms is essential for researchers, scientists, and scholars to accurately describe and analyze complex systems. In this article, we will delve into the hetero vs homogeneous differences, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and implications in different contexts.
Key Points
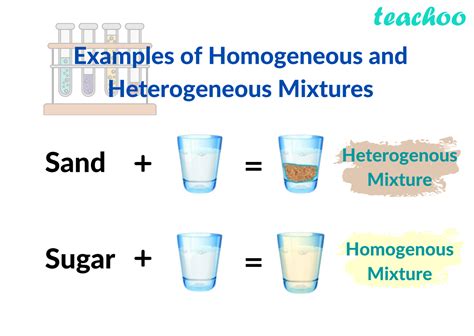
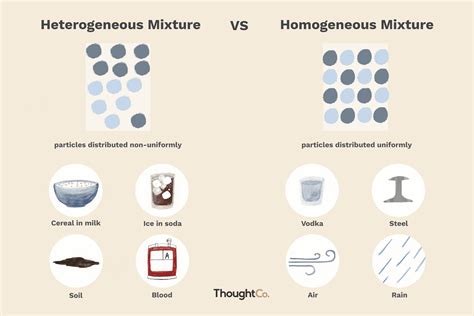
- Heterogeneity refers to the presence of different components or elements within a system, leading to diversity and complexity.
- Homogeneity, on the other hand, describes a system composed of identical or similar components, resulting in uniformity and simplicity.
- The distinction between heterogeneity and homogeneity has significant implications in fields such as biology, chemistry, and social sciences.
- Heterogeneous systems often exhibit emergent properties, which arise from the interactions and organization of individual components.
- Homogeneous systems, by contrast, tend to display more predictable behavior, as the identical components interact in a consistent manner.
Defining Heterogeneity and Homogeneity
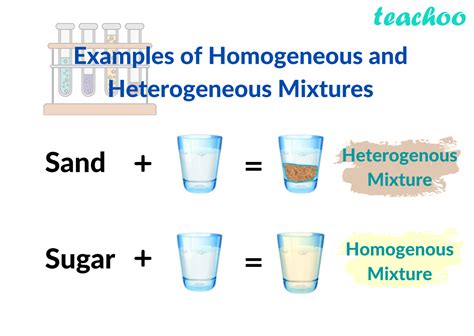
Heterogeneity is a term used to describe a system or population that consists of diverse components, elements, or individuals. This diversity can manifest in various forms, such as differences in size, shape, color, or function. Heterogeneous systems are often characterized by complexity, as the interactions between different components can lead to emergent properties and behaviors. In contrast, homogeneity refers to a system or population composed of identical or similar components, resulting in uniformity and simplicity.
Biological Systems: Heterogeneity and Homogeneity
In biology, heterogeneity is evident in the diversity of species, ecosystems, and populations. For example, a forest ecosystem is heterogeneous, comprising various plant and animal species, each with unique characteristics and functions. This diversity leads to complex interactions and relationships between species, influencing the overall ecosystem dynamics. In contrast, a homogeneous system in biology might be a population of genetically identical organisms, such as a colony of bacteria.
| System Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Heterogeneous | Diverse components, complex interactions, emergent properties |
| Homogeneous | Identical components, uniform behavior, predictable interactions |

Chemical Systems: Heterogeneity and Homogeneity
In chemistry, heterogeneity and homogeneity are essential concepts in understanding the properties and behavior of materials. A heterogeneous material, such as a composite, consists of different components with distinct properties, leading to unique characteristics and behaviors. For example, a composite material composed of carbon fibers and polymer matrix exhibits enhanced strength and stiffness due to the interactions between the different components. In contrast, a homogeneous material, such as a pure metal, consists of identical atoms or molecules, resulting in uniform properties and behavior.
Physical Systems: Heterogeneity and Homogeneity
In physics, heterogeneity and homogeneity are relevant in understanding the behavior of systems at different scales. A heterogeneous system, such as a granular material, consists of particles with different sizes, shapes, and properties, leading to complex behavior and interactions. In contrast, a homogeneous system, such as a crystal, consists of identical atoms or molecules arranged in a regular lattice structure, resulting in predictable behavior and properties.
What are the implications of heterogeneity in social systems?
+Heterogeneity in social systems can lead to increased complexity, diversity, and innovation, as individuals with different backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives interact and collaborate. However, heterogeneity can also lead to conflicts, misunderstandings, and challenges in communication, highlighting the need for effective management and leadership strategies.
How does homogeneity influence the behavior of physical systems?
+Homogeneity in physical systems can lead to predictable behavior, as the identical components interact in a consistent manner. This predictability is essential in designing and optimizing systems, such as electronic devices, mechanical systems, and optical materials.
In conclusion, the distinction between heterogeneity and homogeneity is a fundamental concept in various fields, including biology, chemistry, physics, and social sciences. Understanding the differences between these two terms is essential for researchers, scientists, and scholars to accurately describe and analyze complex systems. By recognizing the implications of heterogeneity and homogeneity, we can develop more effective strategies for managing, conserving, and optimizing complex systems, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a deeper understanding of the world around us.