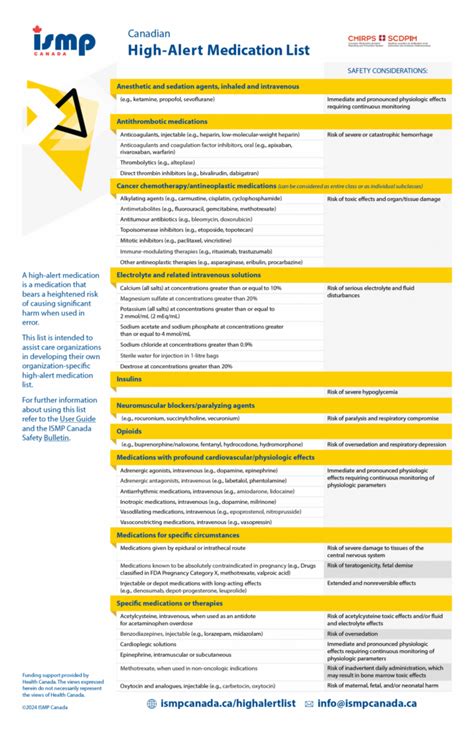
High alert medications are a class of medications that have the potential to cause significant harm to patients if not used correctly. These medications are often referred to as "high-risk" medications because of the potential for adverse events, such as overdose, underdose, or incorrect administration. The use of high alert medications requires careful attention to detail, strict adherence to prescribing guidelines, and ongoing monitoring to minimize the risk of adverse events. According to the Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP), high alert medications account for a significant proportion of medication errors, highlighting the need for vigilant prescribing and administration practices.
The ISMP has identified a list of high alert medications that are commonly associated with adverse events. These medications include, but are not limited to, anticoagulants, such as warfarin and heparin, which can cause bleeding complications if not monitored correctly; opioids, such as morphine and fentanyl, which can cause respiratory depression and overdose; and insulin, which can cause hypoglycemia if not administered correctly. Other high alert medications include chemotherapy agents, such as doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide, which can cause severe side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and bone marrow suppression.
Key Points
- High alert medications have the potential to cause significant harm to patients if not used correctly.
- These medications require careful attention to detail, strict adherence to prescribing guidelines, and ongoing monitoring to minimize the risk of adverse events.
- The ISMP has identified a list of high alert medications that are commonly associated with adverse events, including anticoagulants, opioids, and insulin.
- Chemotherapy agents are also considered high alert medications due to their potential to cause severe side effects.
- Healthcare providers must be vigilant when prescribing and administering high alert medications to minimize the risk of adverse events.
Classification of High Alert Medications
High alert medications can be classified into several categories, including anticoagulants, opioids, and chemotherapy agents. Anticoagulants, such as warfarin and heparin, are used to prevent blood clotting and are commonly used to treat conditions such as atrial fibrillation and deep vein thrombosis. Opioids, such as morphine and fentanyl, are used to treat pain and are commonly used to manage chronic pain and palliative care. Chemotherapy agents, such as doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide, are used to treat cancer and can cause severe side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and bone marrow suppression.
Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants are a class of high alert medications that are used to prevent blood clotting. These medications work by inhibiting the production of clotting factors in the liver or by blocking the action of clotting factors in the blood. Warfarin, for example, is an anticoagulant that works by inhibiting the production of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors in the liver. Heparin, on the other hand, works by blocking the action of thrombin, a key enzyme involved in blood clotting. According to the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), anticoagulants are effective in preventing stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation, but require careful monitoring to minimize the risk of bleeding complications.
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Common Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Warfarin | Inhibits vitamin K-dependent clotting factors | Atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis |
| Heparin | Blocks thrombin | Atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis |
| Aspirin | Inhibits platelet aggregation | Myocardial infarction, stroke |
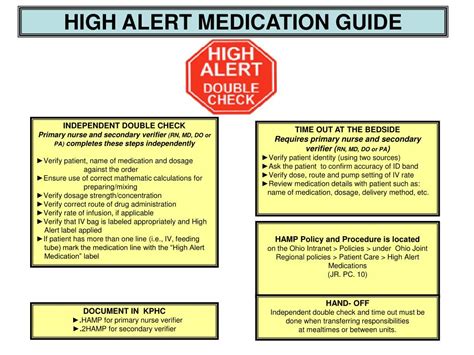
Safe Use of High Alert Medications

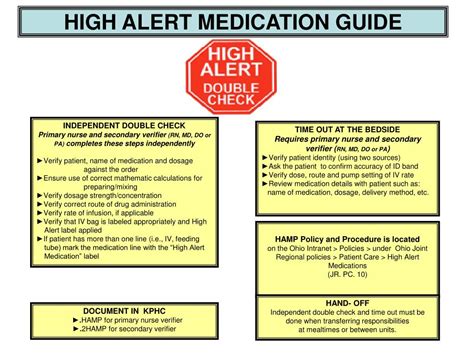
The safe use of high alert medications requires a comprehensive approach that involves healthcare providers, patients, and families. Healthcare providers must be knowledgeable about the medications they prescribe, including their indications, dosages, and potential side effects. Patients and families must also be educated about the medications they are taking, including how to take them correctly and what to expect in terms of side effects. According to the Joint Commission, a comprehensive approach to medication safety includes the use of standardized protocols, ongoing monitoring, and regular feedback to healthcare providers.
Medication Reconciliation
Medication reconciliation is an essential process that involves verifying the accuracy of a patient’s medication list at transitions of care. This process helps to prevent medication errors, such as omissions, duplications, or incorrect dosages. During medication reconciliation, healthcare providers review the patient’s medication list and verify the accuracy of the medications, dosages, and frequencies. Any discrepancies or potential issues are addressed and resolved to ensure that the patient receives the correct medications.
What are high alert medications?
+High alert medications are medications that have the potential to cause significant harm to patients if not used correctly. These medications are often referred to as "high-risk" medications because of the potential for adverse events, such as overdose, underdose, or incorrect administration.
What are some examples of high alert medications?
+Examples of high alert medications include anticoagulants, such as warfarin and heparin, opioids, such as morphine and fentanyl, and chemotherapy agents, such as doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide.
How can healthcare providers ensure the safe use of high alert medications?
+Healthcare providers can ensure the safe use of high alert medications by following a comprehensive approach that involves standardized protocols, ongoing monitoring, and regular feedback. Medication reconciliation is also an essential process that helps to prevent medication errors.
In conclusion, high alert medications are a class of medications that require careful attention to detail and strict adherence to prescribing guidelines to minimize the risk of adverse events. Healthcare providers must be knowledgeable about the medications they prescribe and must educate patients and families about the medications they are taking. A comprehensive approach to medication safety, including medication reconciliation and ongoing monitoring, is essential to ensure the safe use of high alert medications. By following these principles, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of adverse events and ensure that patients receive the best possible care.