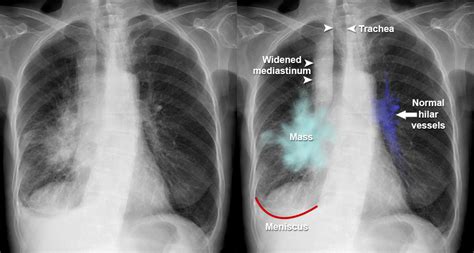
The hilum of the lung is a critical area where various structures such as bronchi, blood vessels, and nerves enter and exit the lung. A hilar lung mass refers to an abnormal growth or lesion located in this region. Such masses can be benign or malignant and may originate from various tissues within the hilum, including lymph nodes, bronchial structures, or vascular tissues. The clinical significance of a hilar lung mass lies in its potential to cause symptoms, compromise lung function, and, in the case of malignancies, spread to other parts of the body.
Diagnosing a hilar lung mass typically involves a combination of imaging studies, such as chest X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and positron emission tomography (PET) scans, along with biopsy and histopathological examination to determine the nature of the mass. Symptoms can vary widely depending on the size, location, and nature of the mass, as well as the patient's overall health. Common symptoms include cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and in some cases, systemic symptoms like weight loss or fever if the mass is malignant or infectious in origin.
Key Points
- Hilar lung masses are abnormal growths in the hilum of the lung and can be benign or malignant.
- Diagnosis involves imaging studies and biopsy, with symptoms varying based on the mass's characteristics and the patient's health.
- Treatment options depend on the nature of the mass, ranging from surveillance for benign masses to surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy for malignant ones.
- Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective management and improving patient outcomes.
- The hilum's complex anatomy and the variety of potential masses make a multidisciplinary approach, including pulmonologists, radiologists, and thoracic surgeons, essential for optimal care.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
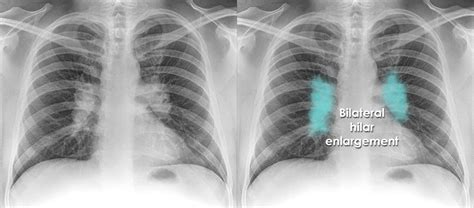
Clinically, patients with a hilar lung mass may present with a range of symptoms, from being asymptomatic to having significant respiratory or systemic complaints. The mass’s impact on surrounding structures, such as airways or major blood vessels, can lead to specific symptoms like coughing, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), or dyspnea (shortness of breath). In cases where the mass is malignant, such as lung cancer, symptoms related to metastasis or paraneoplastic syndromes may also be present.
The diagnostic approach to a hilar lung mass begins with imaging. Chest X-rays can provide an initial indication of a mass, but CT scans offer more detailed information about the mass's size, location, and potential invasion into surrounding structures. PET scans can help assess the mass's metabolic activity, which is useful in distinguishing benign from malignant lesions and identifying potential metastases. Ultimately, a tissue diagnosis through biopsy is necessary to determine the mass's nature and guide treatment.
Benign vs. Malignant Masses
Benign hilar masses, such as hamartomas or bronchogenic cysts, typically have a more favorable prognosis and may not require aggressive treatment. In contrast, malignant masses, including lung carcinomas or lymphomas, necessitate prompt and often multimodal treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy. The distinction between benign and malignant is crucial, as it significantly impacts treatment decisions and patient outcomes.
| Type of Mass | Characteristics | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Benign (e.g., Hamartoma) | Typically slow-growing, well-defined borders | Surveillance or surgical resection |
| Malignant (e.g., Lung Cancer) | Rapid growth, irregular borders, potential for metastasis | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or combination |
Treatment and Prognosis
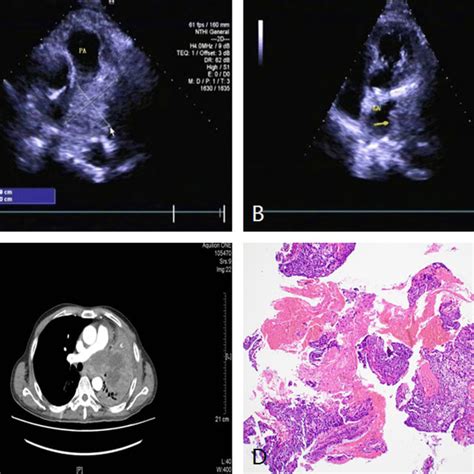
Treatment of a hilar lung mass is highly dependent on its nature, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of any metastases. For benign masses, if symptoms are minimal or absent, a watchful waiting approach with regular imaging may be appropriate. However, if the mass is causing symptoms or there is a risk of complications, surgical resection may be necessary.
Malignant hilar masses require a more aggressive approach. Surgery, when feasible, offers the best chance for a cure, especially in early-stage lung cancers. However, many patients present with advanced disease, necessitating the use of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies. The prognosis varies widely depending on the type of cancer, the stage at diagnosis, and the patient's response to treatment.
Advanced Therapies and Clinical Trials
For patients with malignant hilar lung masses, particularly those with advanced or metastatic disease, participation in clinical trials or the use of advanced therapies such as immunotherapy or targeted therapy may offer additional treatment options. These approaches have shown promise in improving outcomes for certain subsets of patients with lung cancer and continue to be areas of active research.
In conclusion, hilar lung masses present a complex clinical scenario that requires precise diagnosis and tailored treatment. The management of these masses underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration and the need for patients to be evaluated by specialists who can provide the most current and effective therapies.
What is the most common cause of a hilar lung mass?
+The most common causes of hilar lung masses include lung cancer, lymphoma, and benign tumors such as hamartomas. The specific cause can vary based on patient demographics, symptoms, and imaging characteristics.
How are hilar lung masses typically diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging studies (such as CT scans and PET scans) and tissue sampling through biopsy. The choice of diagnostic tests depends on the patient’s symptoms, the mass’s characteristics, and the suspicion of malignancy.
What are the treatment options for a malignant hilar lung mass?
+Treatment options for malignant hilar lung masses include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted or immunotherapies. The choice of treatment depends on the type of cancer, the stage of disease, and the patient’s overall health and preferences.