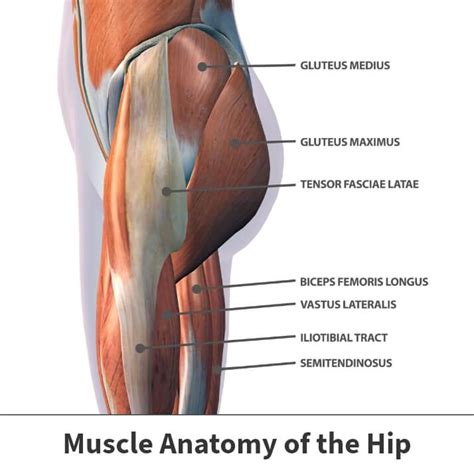
The hip muscles are a complex group of muscles that play a crucial role in our daily movements, from walking and running to climbing stairs and maintaining balance. There are several muscles that make up the hip muscles, but in this article, we will focus on five key muscles that are essential for hip function and mobility. These muscles are the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae, and piriformis.
Understanding the anatomy and function of these muscles is essential for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals who want to improve their hip mobility and reduce their risk of injury. In this article, we will delve into the details of each muscle, their functions, and how they work together to enable us to move and perform various activities. We will also discuss the importance of strengthening and stretching these muscles to maintain optimal hip health and function.
Key Points
- The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the hip and plays a key role in hip extension and external rotation.
- The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscles work together to abduct the hip and stabilize the pelvis.
- The tensor fasciae latae muscle helps to tense the fascia lata and assist in hip abduction and internal rotation.
- The piriformis muscle is a deep muscle that helps to rotate the hip outward and stabilize the hip joint.
- Strengthening and stretching the hip muscles is essential for maintaining optimal hip health and function, and reducing the risk of injury.
The Gluteus Maximus Muscle
The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the hip and plays a key role in hip extension and external rotation. It is a powerful muscle that originates from the ilium and sacrum and inserts into the gluteal tuberosity on the femur. The gluteus maximus is responsible for extending the hip joint, which means it helps to straighten the hip and move the leg backward. It also helps to rotate the hip outward, which is essential for activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Functions of the Gluteus Maximus
The gluteus maximus has several functions, including:
- Hip extension: The gluteus maximus helps to extend the hip joint, which means it helps to straighten the hip and move the leg backward.
- External rotation: The gluteus maximus helps to rotate the hip outward, which is essential for activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
- Hip stabilization: The gluteus maximus helps to stabilize the hip joint and maintain balance during movements such as walking and running.
The Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Minimus Muscles

The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscles are two smaller muscles that work together to abduct the hip and stabilize the pelvis. They originate from the ilium and insert into the greater trochanter on the femur. The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscles are responsible for abducting the hip, which means they help to move the leg away from the midline of the body. They also help to stabilize the pelvis and maintain balance during movements such as walking and running.
Functions of the Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Minimus
The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus have several functions, including:
- Hip abduction: The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus help to abduct the hip, which means they help to move the leg away from the midline of the body.
- Pelvic stabilization: The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus help to stabilize the pelvis and maintain balance during movements such as walking and running.
- Hip rotation: The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus also help to rotate the hip inward, which is essential for activities such as walking and running.
The Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscle
The tensor fasciae latae muscle is a long, thin muscle that originates from the ilium and inserts into the iliotibial tract on the femur. It helps to tense the fascia lata, which is a thick band of connective tissue that runs down the outside of the thigh. The tensor fasciae latae muscle also helps to abduct the hip and assist in hip internal rotation.
Functions of the Tensor Fasciae Latae
The tensor fasciae latae has several functions, including:
- Fascia lata tension: The tensor fasciae latae helps to tense the fascia lata, which helps to stabilize the hip and maintain balance during movements.
- Hip abduction: The tensor fasciae latae helps to abduct the hip, which means it helps to move the leg away from the midline of the body.
- Hip internal rotation: The tensor fasciae latae also helps to rotate the hip inward, which is essential for activities such as walking and running.
The Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle is a deep muscle that originates from the sacrum and inserts into the greater trochanter on the femur. It helps to rotate the hip outward and stabilize the hip joint. The piriformis muscle is also responsible for compressing the sciatic nerve, which can cause pain and numbness in the leg if it becomes irritated.
Functions of the Piriformis
The piriformis has several functions, including:
- Hip external rotation: The piriformis helps to rotate the hip outward, which is essential for activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
- Hip stabilization: The piriformis helps to stabilize the hip joint and maintain balance during movements such as walking and running.
- Sciatic nerve compression: The piriformis is also responsible for compressing the sciatic nerve, which can cause pain and numbness in the leg if it becomes irritated.
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gluteus Maximus | Ilum and Sacrum | Gluteal Tuberosity | Hip Extension and External Rotation |
| Gluteus Medius | Ilum | Greater Trochanter | Hip Abduction and Pelvic Stabilization |
| Gluteus Minimus | Ilum | Greater Trochanter | Hip Abduction and Pelvic Stabilization |
| Tensor Fasciae Latae | Ilum | Iliotibial Tract | Fascia Lata Tension and Hip Abduction |
| Piriformis | Sacrum | Greater Trochanter | Hip External Rotation and Stabilization |
What are the five hip muscles and their functions?
+The five hip muscles are the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae, and piriformis. Each muscle has a unique function, including hip extension, abduction, external rotation, and stabilization.
Why is it essential to strengthen and stretch the hip muscles?
+Strengthening and stretching the hip muscles is essential for maintaining optimal hip health and function, and reducing the risk of injury. Weak or tight hip muscles can lead to poor posture, decreased mobility, and increased risk of injury.
What exercises can help to strengthen the hip muscles?
+Exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg press can help to strengthen the hip muscles. It’s essential to include a variety of exercises in your workout routine to target all the hip muscles and maintain optimal hip health and function.