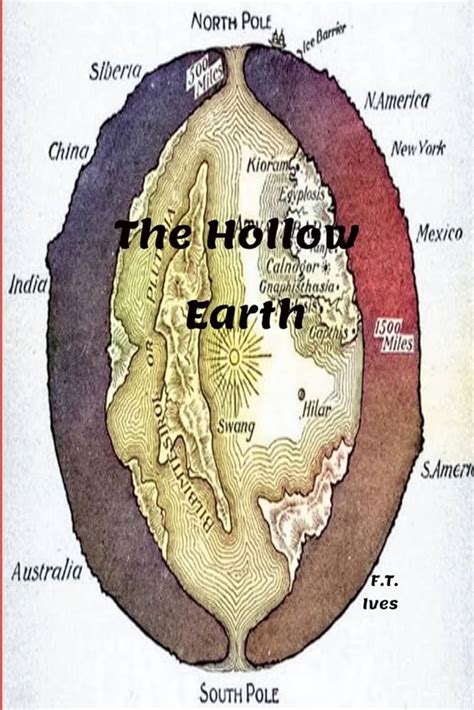
The concept of a hollow Earth has been a topic of fascination and debate for centuries, with various theories and hypotheses emerging over time. The idea that the Earth is completely or partially hollow has been proposed by several individuals, including scientists, philosophers, and conspiracy theorists. In this article, we will delve into the history and development of the hollow Earth theory, exploring its various forms and the evidence presented to support it.
The hollow Earth theory can be traced back to ancient civilizations, with some myths and legends describing the Earth as having a hollow interior. For example, the ancient Greeks believed in the existence of a subterranean world, while the Norse mythology described a hollow Earth with a central sun. However, the modern concept of a hollow Earth as we know it today began to take shape in the 17th and 18th centuries. During this period, several scientists and philosophers proposed theories about the Earth’s internal structure, including the idea that it might be hollow.
One of the earliest and most influential proponents of the hollow Earth theory was Edmund Halley, an English astronomer and mathematician. In 1692, Halley proposed that the Earth was composed of a series of concentric spheres, with a hollow interior. He suggested that the Earth’s magnetic field was caused by the rotation of these spheres, and that the hollow interior was inhabited by a luminous atmosphere. Halley’s theory was widely discussed and debated in scientific circles, and it laid the foundation for later hollow Earth theories.
Primary Theories and Hypotheses
Over time, several primary theories and hypotheses have emerged to explain the hollow Earth concept. These include:
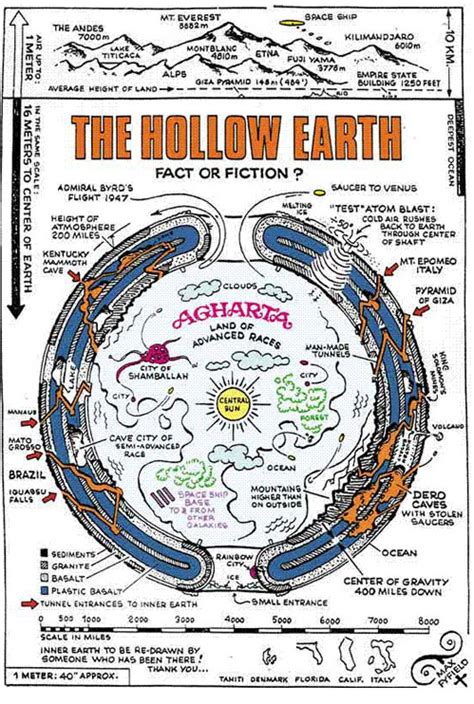
- The Concentric Sphere Theory: This theory proposes that the Earth is composed of multiple concentric spheres, with a hollow interior. Each sphere is thought to be separated by a layer of ice or rock, and the hollow interior is believed to be inhabited by a luminous atmosphere.
- The Hollow Shell Theory: This theory suggests that the Earth is a hollow shell, with a thin crust and a large, empty interior. The hollow interior is thought to be supported by a series of arches or pillars, and the shell is believed to be surrounded by a layer of ice or rock.
- The Inner Earth Theory: This theory proposes that the Earth has a hollow interior, but with a twist. Instead of being completely empty, the interior is thought to be inhabited by a separate ecosystem, complete with its own atmosphere, oceans, and life forms.
Each of these theories has its own strengths and weaknesses, and they have been the subject of much debate and discussion. While some proponents of the hollow Earth theory claim that it can explain various geological and astronomical phenomena, others argue that it is a pseudoscientific concept with no basis in reality.
Evidence and Arguments
Proponents of the hollow Earth theory point to a range of evidence and arguments to support their claims. Some of the most commonly cited evidence includes:
- Gravitational anomalies: Some researchers claim that the Earth’s gravitational field is not consistent with a solid, rocky interior. They argue that the gravitational field is weaker than expected, suggesting that the Earth may be hollow.
- Seismic data: Seismic waves generated by earthquakes can travel through the Earth’s interior, and some researchers claim that the data suggests that the Earth is hollow. They argue that the seismic waves behave differently than expected, indicating that they are passing through a hollow interior.
- Magnetic field: The Earth’s magnetic field is thought to be generated by the movement of molten iron in the Earth’s core. However, some researchers argue that the magnetic field is not consistent with a solid core, and that it may be generated by a hollow interior.
While these arguments and evidence are intriguing, they are not universally accepted by the scientific community. Many experts argue that the evidence can be explained by other factors, such as the Earth’s slightly ellipsoidal shape or the presence of underground caverns and tunnels.
| Theory | Description | Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Concentric Sphere Theory | Earth composed of concentric spheres | Gravitational anomalies, seismic data |
| Hollow Shell Theory | Earth a hollow shell with thin crust | Magnetic field, seismic data |
| Inner Earth Theory | Earth has hollow interior with separate ecosystem | Gravitational anomalies, seismic data, eyewitness accounts |
Key Points
- The hollow Earth theory proposes that the Earth is completely or partially hollow, with various forms and evidence presented to support it.
- The theory has its roots in ancient civilizations and was later developed by scientists and philosophers in the 17th and 18th centuries.
- Primary theories and hypotheses include the Concentric Sphere Theory, the Hollow Shell Theory, and the Inner Earth Theory.
- Evidence and arguments presented to support the hollow Earth theory include gravitational anomalies, seismic data, and magnetic field measurements.
- The scientific community remains skeptical about the hollow Earth theory, and it is not widely accepted as a valid scientific concept.
In conclusion, the hollow Earth theory is a complex and multifaceted concept that has been debated and discussed for centuries. While some proponents of the theory claim that it can explain various geological and astronomical phenomena, others argue that it is a pseudoscientific concept with no basis in reality. As with any scientific theory, it is essential to approach the hollow Earth theory with a critical and nuanced perspective, considering both the evidence and the limitations of our current understanding.
What is the hollow Earth theory?
+The hollow Earth theory proposes that the Earth is completely or partially hollow, with various forms and evidence presented to support it.
What are the primary theories and hypotheses of the hollow Earth theory?
+The primary theories and hypotheses of the hollow Earth theory include the Concentric Sphere Theory, the Hollow Shell Theory, and the Inner Earth Theory.
What evidence and arguments are presented to support the hollow Earth theory?
+Evidence and arguments presented to support the hollow Earth theory include gravitational anomalies, seismic data, and magnetic field measurements.
Is the hollow Earth theory widely accepted by the scientific community?
+No, the hollow Earth theory is not widely accepted by the scientific community, and it remains a speculative idea that requires further research and evidence to be widely accepted.
What are the implications of the hollow Earth theory?
+The implications of the hollow Earth theory are far-reaching and potentially revolutionary, challenging our current understanding of the Earth's internal structure and the nature of our planet.
Meta Description: Explore the hollow Earth theory, a concept that proposes the Earth is completely or partially hollow, and examine the evidence and arguments presented to support it.