The terms "homicide" and "murder" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of criminal law. Understanding the differences between these two terms is crucial for professionals in the field, including law enforcement, lawyers, and criminologists. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, nuances, and implications of homicide and murder, exploring the complexities of these concepts and their applications in real-world scenarios.
Defining Homicide and Murder
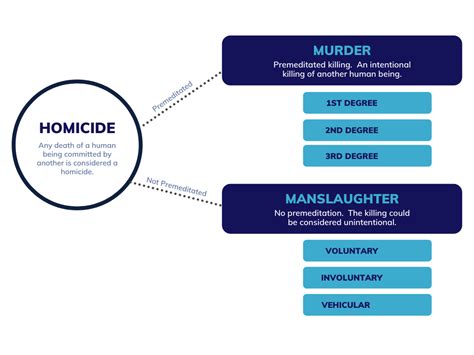
Homicide refers to the act of killing another human being, regardless of the circumstances or intentions behind the act. It is a broad term that encompasses various types of killings, including murder, manslaughter, and justifiable homicide. Homicide can be further categorized into different types, such as voluntary or involuntary, based on the presence or absence of intent. On the other hand, murder is a specific type of homicide that involves the intentional and premeditated killing of another person. Murder is typically considered a more serious crime than other forms of homicide, as it involves a deliberate and calculated act of violence.
Key Distinctions Between Homicide and Murder
The primary distinction between homicide and murder lies in the presence or absence of intent. Homicide can be committed with or without intent, whereas murder requires a deliberate and premeditated intent to kill. Additionally, the level of planning and preparation involved in the crime can also differentiate between homicide and murder. For instance, a killing that occurs in the heat of the moment, without prior planning or deliberation, may be considered manslaughter or voluntary homicide, whereas a killing that involves careful planning and execution may be classified as murder.
| Type of Homicide | Description |
|---|---|
| Murder | Intentional and premeditated killing of another person |
| Manslaughter | Unintentional or reckless killing of another person |
| Justifiable Homicide | Killing in self-defense or to prevent a crime |
| Voluntary Homicide | Intentional killing without premeditation |
| Involuntary Homicide | Unintentional killing due to negligence or recklessness |

Investigating and Prosecuting Homicide and Murder

The investigation and prosecution of homicide and murder cases involve a complex array of procedures and protocols. Law enforcement agencies must carefully collect and analyze evidence, including forensic data, witness statements, and suspect interviews, to determine the circumstances surrounding the crime. Prosecutors must then evaluate the evidence and apply relevant laws and statutes to determine the appropriate charges and penalties. In cases of murder, prosecutors may seek to establish the presence of intent, premeditation, and deliberation, which can impact the severity of the sentence.
Challenges in Prosecuting Homicide and Murder Cases
Prosecuting homicide and murder cases can be challenging due to the complexity of the evidence, the presence of conflicting witness statements, and the need to establish intent and premeditation. Additionally, the emotional toll of these cases on victims’ families, witnesses, and investigators can also impact the investigation and prosecution process. To overcome these challenges, prosecutors must carefully evaluate the evidence, work closely with investigators and experts, and develop effective strategies for presenting the case in court.
Key Points
- Homicide refers to the act of killing another human being, regardless of the circumstances or intentions behind the act
- Murder is a specific type of homicide that involves the intentional and premeditated killing of another person
- The primary distinction between homicide and murder lies in the presence or absence of intent
- The investigation and prosecution of homicide and murder cases involve a complex array of procedures and protocols
- Prosecutors must carefully evaluate the evidence and apply relevant laws and statutes to determine the appropriate charges and penalties
In conclusion, the terms "homicide" and "murder" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of criminal law. Understanding the differences between these two terms is crucial for professionals in the field, including law enforcement, lawyers, and criminologists. By recognizing the nuances of each case and applying relevant laws and statutes, investigators and prosecutors can work to ensure that justice is served and that those responsible for these crimes are held accountable.
What is the main difference between homicide and murder?
+The main difference between homicide and murder lies in the presence or absence of intent. Homicide can be committed with or without intent, whereas murder requires a deliberate and premeditated intent to kill.
What are the different types of homicide?
+The different types of homicide include murder, manslaughter, justifiable homicide, voluntary homicide, and involuntary homicide. Each type of homicide has distinct characteristics and implications for investigation and prosecution.
How do investigators and prosecutors determine the appropriate charges and penalties for homicide and murder cases?
+Investigators and prosecutors determine the appropriate charges and penalties for homicide and murder cases by carefully evaluating the evidence, applying relevant laws and statutes, and considering the circumstances and motivations surrounding the crime.