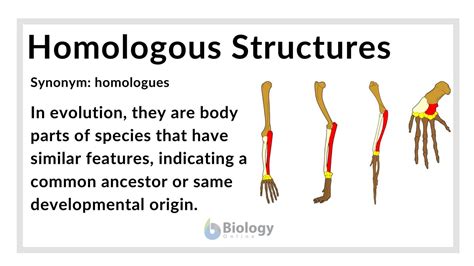
Homologous structures are a fundamental concept in biology, particularly in the fields of anatomy, evolutionary biology, and comparative morphology. These structures refer to body parts or organs that are similar in different species due to a common ancestor, but may have evolved to perform different functions over time. The study of homologous structures provides valuable insights into the evolutionary relationships between organisms and sheds light on the processes that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
The concept of homologous structures was first introduced by Sir Richard Owen in the 19th century, who defined them as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function." Since then, the study of homologous structures has become a crucial tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms and the mechanisms that have driven the evolution of different body plans. In this article, we will explore five examples of homologous structures, their characteristics, and the significance of their study in the context of evolutionary biology.
Key Points
- Homologous structures are similar body parts or organs in different species that have evolved from a common ancestor.
- The study of homologous structures provides insights into evolutionary relationships and the processes that have shaped the diversity of life.
- Examples of homologous structures include the forelimbs of vertebrates, the wings of insects and birds, the eyes of octopuses and humans, the shells of turtles and armadillos, and the skeletons of whales and humans.
- Homologous structures can be used to reconstruct phylogenetic trees and understand the evolutionary history of organisms.
- The study of homologous structures has significant implications for fields such as medicine, conservation, and agriculture.
Forelimbs of Vertebrates

The forelimbs of vertebrates, such as the arms of humans, the wings of birds, and the flippers of whales, are classic examples of homologous structures. Despite their different functions and morphologies, these structures are composed of similar bones, muscles, and nerves, indicating a common ancestry. The forelimbs of vertebrates are thought to have evolved from a common ancestral structure that was present in the early tetrapods (four-legged vertebrates). Over time, this ancestral structure has been modified and adapted to perform different functions in different species, such as flying, swimming, or walking.
Wings of Insects and Birds
The wings of insects and birds are another example of homologous structures. Although they are made of different materials (exoskeleton and feathers, respectively) and have distinct morphologies, they are thought to have evolved from a common ancestral structure. The wings of insects and birds are composed of similar muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, and are controlled by similar genetic pathways. The study of the developmental and genetic mechanisms that control wing formation in insects and birds has provided valuable insights into the evolution of these structures and the mechanisms that have driven their diversification.
| Characteristics | Forelimbs of Vertebrates | Wings of Insects and Birds |
|---|---|---|
| Common Ancestor | Early Tetrapods | Common Ancestor of Insects and Vertebrates |
| Function | Walking, Flying, Swimming | Flying |
| Morphology | Bones, Muscles, Nerves | Exoskeleton, Feathers, Muscles, Nerves |

Eyes of Octopuses and Humans

The eyes of octopuses and humans are a fascinating example of homologous structures. Despite being composed of different materials (tentacles and retina, respectively) and having distinct morphologies, these structures are thought to have evolved from a common ancestral structure. The eyes of octopuses and humans are capable of detecting light and forming images, and are controlled by similar genetic pathways. The study of the developmental and genetic mechanisms that control eye formation in octopuses and humans has provided valuable insights into the evolution of these structures and the mechanisms that have driven their diversification.
Shells of Turtles and Armadillos
The shells of turtles and armadillos are another example of homologous structures. These structures are composed of similar bones, muscles, and nerves, and are thought to have evolved from a common ancestral structure. The shells of turtles and armadillos are used for protection and defense, and are controlled by similar genetic pathways. The study of the developmental and genetic mechanisms that control shell formation in turtles and armadillos has provided valuable insights into the evolution of these structures and the mechanisms that have driven their diversification.
Skeletons of Whales and Humans
The skeletons of whales and humans are a fascinating example of homologous structures. Despite being composed of different materials (bone and cartilage, respectively) and having distinct morphologies, these structures are thought to have evolved from a common ancestral structure. The skeletons of whales and humans are composed of similar bones, muscles, and nerves, and are controlled by similar genetic pathways. The study of the developmental and genetic mechanisms that control skeleton formation in whales and humans has provided valuable insights into the evolution of these structures and the mechanisms that have driven their diversification.
What are homologous structures?
+Homologous structures are body parts or organs that are similar in different species due to a common ancestor, but may have evolved to perform different functions over time.
Why are homologous structures important in evolutionary biology?
+Homologous structures provide valuable insights into the evolutionary relationships between organisms and the mechanisms that have driven the evolution of different body plans.
Can homologous structures be used to reconstruct phylogenetic trees?
+Yes, homologous structures can be used to reconstruct phylogenetic trees and understand the evolutionary history of organisms.
In conclusion, the study of homologous structures provides a fascinating glimpse into the evolutionary history of organisms and the mechanisms that have driven the evolution of different body plans. By comparing the morphology, development, and genetics of homologous structures, we can gain insights into the evolutionary relationships between organisms and reconstruct the evolutionary history of life on Earth. The significance of homologous structures extends beyond the field of evolutionary biology, with implications for fields such as medicine, conservation, and agriculture.