Calculating electrons is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry, crucial for understanding the behavior of atoms and molecules. The number of electrons in an atom or molecule determines its chemical properties and reactivity. There are several methods to calculate electrons, each applicable in different contexts. Below, we will explore five ways to calculate electrons, providing a comprehensive overview of the methods and their applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the atomic number and mass number is crucial for calculating electrons in atoms.
- The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory helps in predicting the shape of molecules based on electron distribution.
- Molecular orbital theory is essential for calculating electrons in molecules, especially for understanding bonding and antibonding orbitals.
- The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are fundamental in determining the electron configuration of atoms.
- Calculating electrons in ions involves understanding the gain or loss of electrons to form a stable configuration.
Method 1: Using the Atomic Number for Atoms
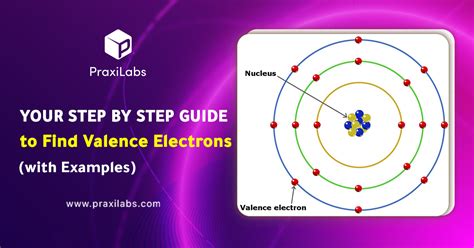
The atomic number of an element, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom. This method is straightforward for calculating the total number of electrons in an atom. For instance, carbon has an atomic number of 6, meaning a neutral carbon atom has 6 electrons. This method is foundational in chemistry and physics, providing a basis for understanding atomic structure.
Application of Atomic Number
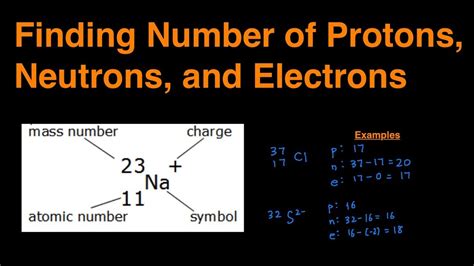
The application of the atomic number in calculating electrons is not only limited to neutral atoms but also extends to ions. When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. The number of electrons in an ion can be calculated by adjusting the atomic number based on the charge of the ion. For example, a sodium ion (Na+) has one less electron than a neutral sodium atom because it loses one electron to achieve a stable configuration.
Method 2: Molecular Orbital Theory for Molecules
Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining the electronic structure of molecules. It combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals, which are a description of the distribution of electrons within a molecule. This theory is crucial for understanding the bonding and antibonding orbitals in molecules, thereby explaining the stability and reactivity of molecules. By applying molecular orbital theory, one can calculate the number of electrons in bonding and antibonding orbitals, providing insights into the molecular structure and properties.
Calculating Electrons with Molecular Orbitals
Calculating electrons in molecules using molecular orbital theory involves several steps, including combining atomic orbitals, determining the energy levels of molecular orbitals, and filling these orbitals with electrons according to the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. For example, in the case of the oxygen molecule (O2), molecular orbital theory helps in understanding the distribution of electrons in the sigma and pi bonds, which is essential for explaining the molecule’s stability and reactivity.
Method 3: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
The VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. While it does not directly calculate the number of electrons, it provides a method to understand the distribution of electron pairs around a central atom, which is crucial for determining the molecular geometry. By understanding the arrangement of electron pairs, one can infer the number of electrons involved in bonding and non-bonding pairs.
Applying VSEPR Theory
Applying the VSEPR theory involves identifying the central atom in a molecule, determining the number of electron pairs around it, and then predicting the molecular shape based on the arrangement of these electron pairs. For instance, in the water molecule (H2O), the VSEPR theory explains the bent shape due to the two bonding pairs and two lone pairs on the oxygen atom, which helps in understanding the distribution of electrons in the molecule.
Method 4: Aufbau Principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle
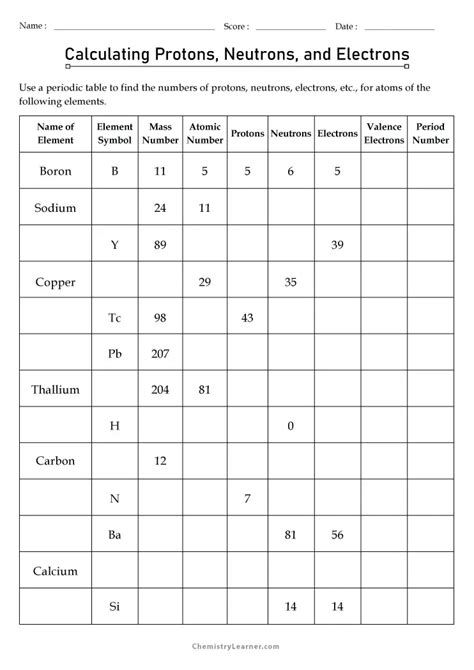
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels, while the Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. These principles are fundamental in determining the electron configuration of atoms. By applying these principles, one can calculate the number of electrons in each energy level and orbital, providing a detailed understanding of the atomic structure.
Calculating Electron Configuration
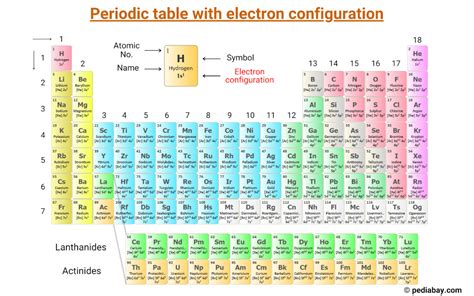
Calculating the electron configuration involves filling the orbitals with electrons according to the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. For example, in the case of the iron atom, which has 26 electrons, the electron configuration can be determined by filling the 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, and 3d orbitals in a specific order, resulting in a configuration that reflects the atom’s chemical properties.
Method 5: Calculating Electrons in Ions
Calculating electrons in ions involves understanding the gain or loss of electrons by an atom to form a stable configuration. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes a cation, and when it gains electrons, it becomes an anion. The number of electrons in an ion can be calculated by adjusting the atomic number based on the charge of the ion. For instance, a chloride ion (Cl-) has one more electron than a neutral chlorine atom, resulting in a stable noble gas configuration.
Understanding Ion Formation
Understanding how ions form and calculating their electrons is crucial for chemistry, as it explains the formation of ionic compounds and their properties. By knowing the number of electrons in an ion, one can predict its chemical behavior and reactivity, which is essential for various chemical reactions and applications.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | Used for calculating electrons in neutral atoms. |
| Molecular Orbital Theory | Applies to molecules for understanding electron distribution and bonding. |
| VSEPR Theory | Helps in predicting molecular shape based on electron pair repulsion. |
| Aufbau Principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle | Fundamental for determining electron configuration in atoms. |
| Calculating Electrons in Ions | Involves understanding the gain or loss of electrons to form a stable ion configuration. |
What is the primary method for calculating electrons in a neutral atom?
+The primary method for calculating electrons in a neutral atom is by using the atomic number, which is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
How does molecular orbital theory help in calculating electrons in molecules?
+Molecular orbital theory helps in calculating electrons in molecules by combining atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals and distributing electrons according to the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle.
What is the role of the VSEPR theory in understanding electron distribution?
+The VSEPR theory helps in predicting the shape of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom, indirectly providing information about electron distribution.
How do the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle aid in calculating electron configuration?
+The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are fundamental in determining the electron configuration of atoms by guiding how electrons fill the available orbitals.
What is the method for calculating electrons in ions?
+Calculating electrons in ions involves understanding the gain or loss of electrons by an atom to form a stable configuration, with the number of electrons adjusted based on the ion's charge.
In conclusion, calculating electrons is a critical aspect of understanding atomic and molecular structures and their properties. By applying the appropriate method—whether using the atomic number, molecular orbital theory, VSEPR theory, the Aufbau principle and Pauli exclusion principle, or calculating electrons in ions—one can gain insights into the distribution of electrons, which is fundamental for predicting chemical behavior and reactivity.



