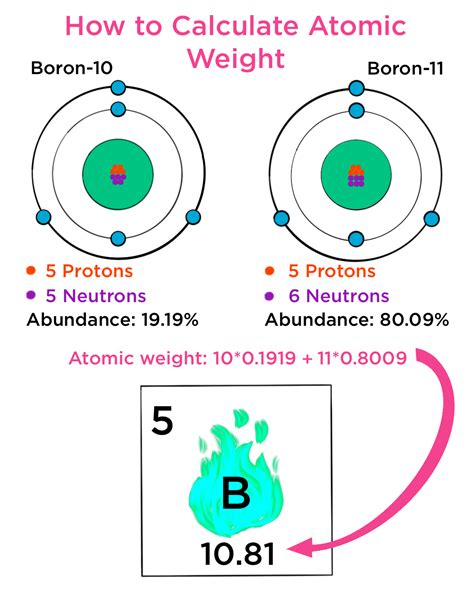
Calculating atomic weight is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for understanding the properties and behavior of elements. The atomic weight of an element is the average mass of its naturally occurring isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. To calculate atomic weight easily, it's essential to understand the basics of isotopes and their relative abundance.
The process begins with identifying the isotopes of an element and their respective masses. Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element that differ in neutron number, and consequently in nucleon number, in each atom. The mass of an isotope is typically expressed in units of atomic mass units (amu), where one amu is equal to one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Knowing the masses of the isotopes and their relative abundance (the percentage of each isotope found in nature) allows for the calculation of the atomic weight.
Key Points
- The atomic weight of an element is the average mass of its naturally occurring isotopes.
- Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons.
- Relative abundance of isotopes is crucial for calculating atomic weight.
- Atomic mass units (amu) are used to express the mass of isotopes and elements.
- Calculating atomic weight involves summing the products of the mass of each isotope and its relative abundance.
Understanding Isotopes and Their Masses
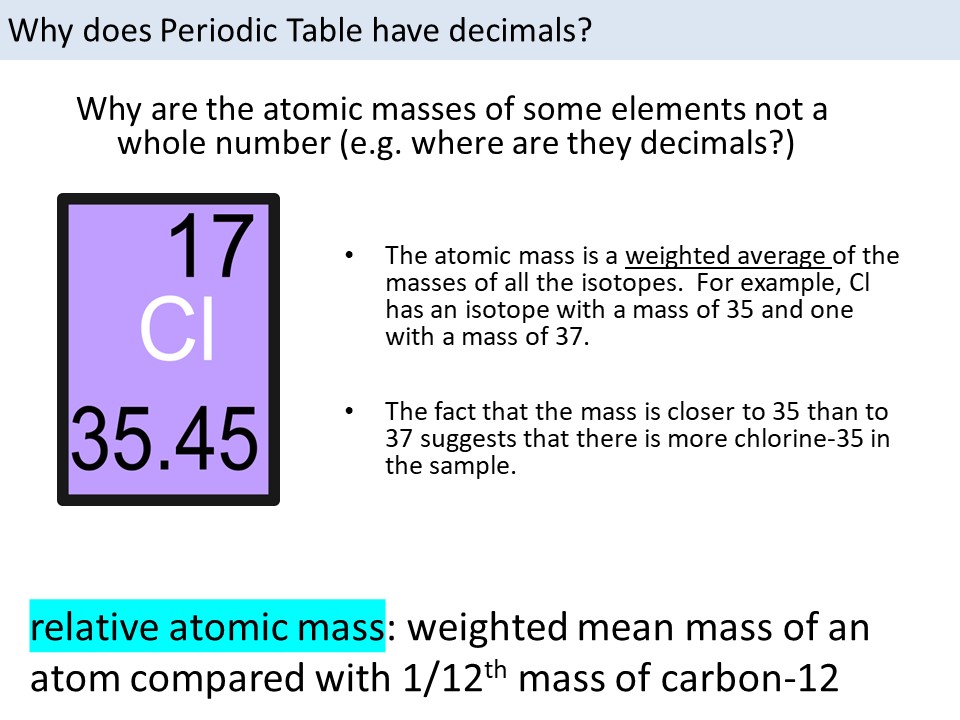
Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons (which defines the element) but vary in the number of neutrons, leading to different masses. For example, carbon has two main isotopes: carbon-12 (6 protons and 6 neutrons) and carbon-13 (6 protons and 7 neutrons), with carbon-12 being more abundant. The masses of these isotopes are used in calculating the atomic weight of carbon.
Calculating Atomic Weight
The formula to calculate atomic weight is the sum of the products of the mass of each isotope and its fractional abundance. Mathematically, this can be represented as: Atomic Weight = (Mass of Isotope 1 * Fractional Abundance of Isotope 1) + (Mass of Isotope 2 * Fractional Abundance of Isotope 2) +… for all isotopes of the element. The fractional abundance is the relative abundance of each isotope divided by 100 to convert it into a fraction.
| Isotope | Mass (amu) | Relative Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon-12 | 12.000000 | 98.93 |
| Carbon-13 | 13.003354 | 1.07 |
Practical Application and Examples
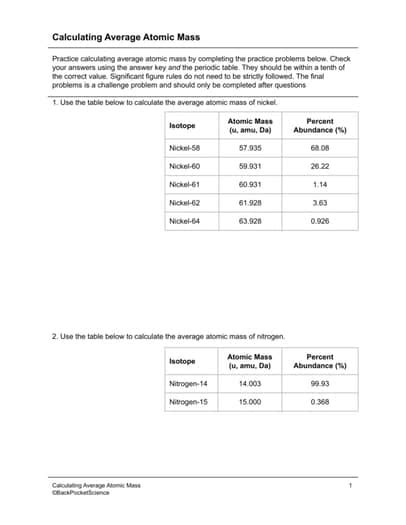
Understanding how to calculate atomic weight is not only essential for theoretical knowledge but also has practical applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering. For instance, in nuclear reactions, knowing the exact masses of isotopes involved is critical for calculating energy changes. Similarly, in materials science, the properties of materials can depend on the isotopic composition of their constituent elements.
A common example is the calculation of the atomic weight of chlorine. Chlorine has two main isotopes: chlorine-35 (17 protons and 18 neutrons) and chlorine-37 (17 protons and 20 neutrons), with masses of approximately 34.9689 amu and 36.9659 amu, respectively, and relative abundances of about 75.78% and 24.22%, respectively. Using the formula, the atomic weight of chlorine can be calculated as: (34.9689 * 0.7578) + (36.9659 * 0.2422), resulting in an atomic weight of approximately 35.453 amu.
Implications and Future Directions
The calculation of atomic weight has implications beyond basic chemistry. It influences fields such as geology, where isotopic analysis can be used to date rocks and understand Earth’s history, and medicine, where isotopes are used in diagnostic imaging and treatment. As research continues to refine our understanding of isotopic abundances and masses, the accuracy of atomic weight calculations will improve, further expanding our ability to apply this knowledge in diverse scientific and technological contexts.
What is the significance of calculating atomic weight?
+Calculating atomic weight is significant because it allows us to understand the average mass of an element's naturally occurring isotopes, which is crucial for various chemical, physical, and engineering applications.
How do variations in isotopic abundance affect atomic weight calculations?
+Variations in isotopic abundance directly affect atomic weight calculations because the atomic weight is the average mass of the isotopes. Changes in abundance alter this average, leading to differences in the calculated atomic weight.
What are some practical applications of atomic weight calculations?
+Practical applications include nuclear reactions, materials science, geology for dating rocks, and medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Accurate atomic weights are essential for these applications.
In conclusion, calculating atomic weight is a fundamental skill in chemistry that involves understanding isotopes, their masses, and relative abundances. With practical applications across various scientific disciplines, mastering this skill is essential for advancing our knowledge and capabilities in these fields. By following the steps outlined and understanding the principles behind atomic weight calculation, individuals can easily and accurately determine the atomic weights of elements, contributing to a deeper understanding of the chemical and physical world.