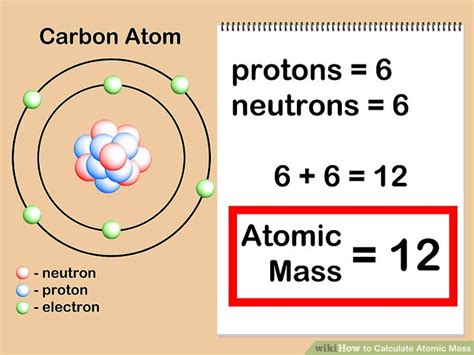
Calculating the atomic mass of an element is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and it can be done with ease if you understand the basic principles. The atomic mass, also known as the atomic weight, is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. To calculate the atomic mass, you need to know the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, which can be found on the periodic table.
Understanding the Periodic Table
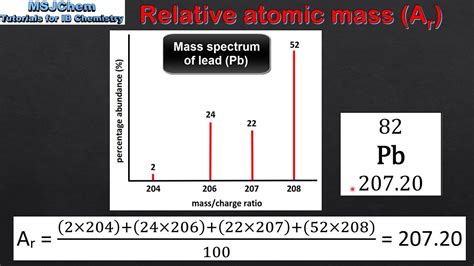
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the elements, where each element is represented by its symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass. The atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus, is usually written as a subscript to the left of the symbol. The atomic mass, on the other hand, is the average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element, and it is usually written as a superscript to the right of the symbol.
Calculating Atomic Mass
To calculate the atomic mass, you need to know the mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The mass of a proton is approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), and the mass of a neutron is also approximately 1 amu. The atomic mass is calculated by summing the masses of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For example, the atomic mass of carbon-12 is calculated as follows:
| Particle | Number | Mass (amu) |
|---|---|---|
| Protons | 6 | 6 x 1 = 6 |
| Neutrons | 6 | 6 x 1 = 6 |
| Total | 6 + 6 = 12 |

As you can see, the atomic mass of carbon-12 is 12 amu, which is the sum of the masses of the 6 protons and 6 neutrons in the nucleus.
Natural Abundance and Atomic Mass
The natural abundance of an isotope is the percentage of that isotope found in nature. To calculate the atomic mass, you need to know the natural abundance of each isotope and its mass. For example, the natural abundance of chlorine-35 is 75.78%, and the natural abundance of chlorine-37 is 24.22%. The atomic mass of chlorine is calculated as follows:
| Isotope | Natural Abundance (%) | Mass (amu) |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorine-35 | 75.78 | 35 |
| Chlorine-37 | 24.22 | 37 |
The atomic mass of chlorine is calculated as the weighted average of the masses of the two isotopes: (0.7578 x 35) + (0.2422 x 37) = 35.45 amu.
Key Points
- The atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom.
- The atomic mass is calculated by summing the masses of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- Natural abundance is the percentage of an isotope found in nature.
- The atomic mass is calculated as the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes.
- Understanding the periodic table is essential for calculating the atomic mass.
Calculating Atomic Mass with Multiple Isotopes
When an element has multiple naturally occurring isotopes, the atomic mass is calculated as the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes. For example, boron has two naturally occurring isotopes, boron-10 and boron-11, with masses of 10 amu and 11 amu, respectively. The natural abundance of boron-10 is 19.9%, and the natural abundance of boron-11 is 80.1%. The atomic mass of boron is calculated as follows:
| Isotope | Natural Abundance (%) | Mass (amu) |
|---|---|---|
| Boron-10 | 19.9 | 10 |
| Boron-11 | 80.1 | 11 |
The atomic mass of boron is calculated as the weighted average of the masses of the two isotopes: (0.199 x 10) + (0.801 x 11) = 10.81 amu.
In conclusion, calculating the atomic mass of an element is a straightforward process that requires understanding the periodic table and the natural abundance of the naturally occurring isotopes. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily calculate the atomic mass of any element.
What is the atomic mass of an element?
+The atomic mass of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom.
How is the atomic mass calculated?
+The atomic mass is calculated by summing the masses of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, taking into account the natural abundance of the naturally occurring isotopes.
What is natural abundance?
+Natural abundance is the percentage of an isotope found in nature.
Meta description: Learn how to calculate the atomic mass of an element with ease, taking into account the natural abundance of isotopes and the periodic table.