Determining velocity, a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, can be a complex task, especially when dealing with objects in motion. However, understanding velocity is crucial in various fields, including mechanics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics. In this article, we will delve into the world of velocity, exploring its definition, types, and calculation methods, making it easier to comprehend and apply in real-world scenarios.
Key Points
- Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate of change of an object's position with respect to time.
- There are two primary types of velocity: instantaneous velocity and average velocity.
- The calculation of velocity involves the use of kinematic equations, which relate displacement, time, and acceleration.
- Velocity is essential in understanding various physical phenomena, including motion, forces, and energy transfer.
- Real-world applications of velocity include projectile motion, circular motion, and relativity.
Understanding Velocity

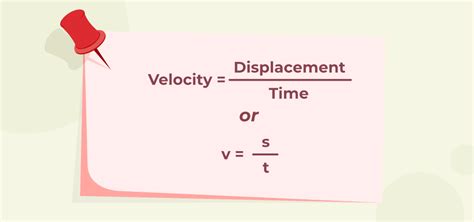
Velocity is defined as the rate of change of an object’s position with respect to time. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude (amount of movement) and direction. The unit of velocity is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h). To calculate velocity, we use the formula: velocity = displacement / time. This formula is the foundation of kinematics, the study of motion.
Types of Velocity
There are two primary types of velocity: instantaneous velocity and average velocity. Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific point in time, whereas average velocity is the velocity of an object over a given time interval. The distinction between these two types of velocity is crucial, as it affects the calculation and interpretation of motion.
| Velocity Type | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Instantaneous Velocity | v = Δx / Δt | Velocity at a specific point in time |
| Average Velocity | v_avg = Δx / Δt | Velocity over a given time interval |
Calculating Velocity
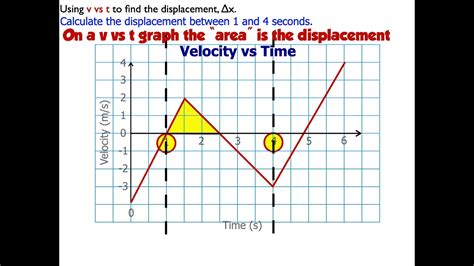
The calculation of velocity involves the use of kinematic equations, which relate displacement, time, and acceleration. The most common kinematic equations are:
- v = v0 + at (equation of motion)
- v^2 = v0^2 + 2as (equation of motion with acceleration)
- s = s0 + v0t + (1⁄2)at^2 (equation of motion with displacement)
These equations can be used to calculate velocity, given the initial velocity, acceleration, and time. The choice of equation depends on the specific problem and the given information.
Real-World Applications of Velocity
Velocity has numerous real-world applications, including:
- Projectile motion: The calculation of velocity is crucial in understanding the trajectory of projectiles, such as balls, arrows, and rockets.
- Circular motion: Velocity is essential in understanding circular motion, including the calculation of centripetal acceleration and centripetal force.
- Relativity: Velocity plays a critical role in special relativity, where it is used to describe the relationship between space and time.
These applications demonstrate the significance of velocity in understanding various physical phenomena and its relevance to real-world problems.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, determining velocity is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering. By understanding the definition, types, and calculation methods of velocity, we can better comprehend and apply it in real-world scenarios. As we continue to explore and understand the complexities of motion, the importance of velocity will only continue to grow. Future research directions include the application of velocity in emerging fields, such as quantum mechanics and materials science, and the development of new technologies that rely on precise velocity calculations.
What is the difference between velocity and speed?
+Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction, whereas speed is a scalar quantity that only refers to the magnitude of velocity.
How do you calculate instantaneous velocity?
+Instantaneous velocity can be calculated using the formula: v = Δx / Δt, where Δx is the displacement and Δt is the time interval.
What are some real-world applications of velocity?
+Velocity has numerous real-world applications, including projectile motion, circular motion, and relativity. It is also essential in understanding various physical phenomena, such as motion, forces, and energy transfer.