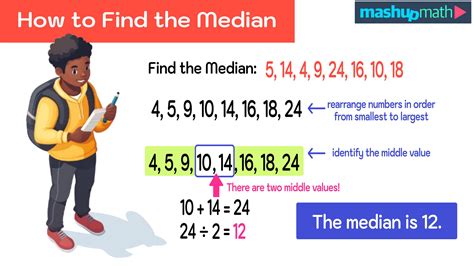
The concept of finding the median in mathematics is a fundamental statistical technique used to determine the middle value of a dataset when it is ordered from the smallest to the largest. The median is a measure of central tendency, offering a snapshot of the data's distribution. Unlike the mean, which can be skewed by outliers, the median provides a better representation of the data's central tendency when the dataset contains extreme values.
Understanding the Concept of Median
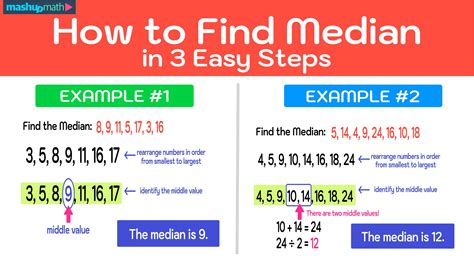
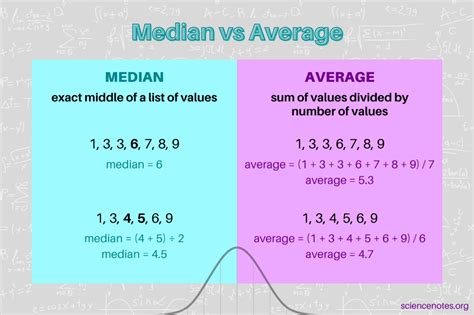
To find the median, one must first arrange the data in ascending or descending order. If the dataset has an odd number of values, the median is the middle number. For example, in a dataset of 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, the median would be 5, as it is the middle value. However, if the dataset has an even number of values, the median is calculated by taking the average of the two middle numbers. For instance, in a dataset of 1, 3, 5, 7, the median would be the average of 3 and 5, which is (3 + 5) / 2 = 4.
Calculating the Median: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the median involves a straightforward process:
- Step 1: Order the Data - Arrange the dataset in ascending order from the smallest to the largest value.
- Step 2: Determine the Middle Position - If the dataset has an odd number of entries, the median is the value at the position given by (n + 1) / 2, where n is the number of entries. If the dataset has an even number of entries, the median is the average of the two middle values at positions n / 2 and (n / 2) + 1.
- Step 3: Calculate the Median - For an odd number of entries, simply find the value at the calculated position. For an even number of entries, calculate the average of the two values at the positions determined in step 2.
| Dataset Example | Ordered Dataset | Median Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 | 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 | Median = 5 (since 5 is the middle value in an odd-numbered dataset) |
| 1, 3, 5, 7 | 1, 3, 5, 7 | Median = (3 + 5) / 2 = 4 (since the dataset has an even number of entries, the median is the average of the two middle values) |
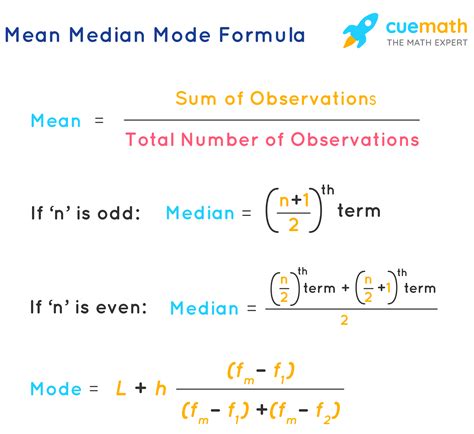
Key Points
- The median is a statistical measure that indicates the middle value in a dataset when it is ordered.
- For datasets with an odd number of entries, the median is the middle value.
- For datasets with an even number of entries, the median is the average of the two middle values.
- The median is less affected by outliers compared to the mean, making it a useful measure for skewed distributions.
- Calculating the median involves ordering the data and then determining the middle position(s) based on whether the dataset has an odd or even number of entries.
Applications and Interpretations of the Median
The median has various applications across different fields, including economics, social sciences, and medical research. It is particularly useful when analyzing income distributions, where the median income can provide a more accurate representation of the average person’s income compared to the mean, which can be skewed by very high incomes. In medical research, the median survival time is often used to describe the length of time from either diagnosis or treatment that patients are still alive. Understanding and calculating the median effectively can thus offer valuable insights into the nature and distribution of data in these and other contexts.
Median in Real-World Scenarios
In real-world scenarios, the median can be more representative of typical values than the mean. For instance, in a neighborhood where there are many modest homes but also a few very expensive mansions, the median house price would give a better idea of what a typical house in the neighborhood costs than the mean, which would be pulled upwards by the expensive mansions.
What is the primary difference between the mean and the median?
+The primary difference between the mean and the median is how they are affected by outliers. The mean is the average of all numbers and can be significantly skewed by extreme values (outliers), whereas the median is the middle value in an ordered list of numbers and is less affected by outliers, making it a better representation of the central tendency in datasets with extreme values.
How do you calculate the median of a dataset with an even number of entries?
+To calculate the median of a dataset with an even number of entries, first, arrange the data in ascending order. Then, find the two middle values. The median is the average of these two middle values, calculated by adding them together and dividing by 2.
What are some common applications of the median in real-world scenarios?
+The median has several common applications in real-world scenarios, including analyzing income distributions, describing house prices in a neighborhood, and determining median survival times in medical research. These applications benefit from the median’s ability to provide a central tendency that is less affected by extreme values compared to the mean.