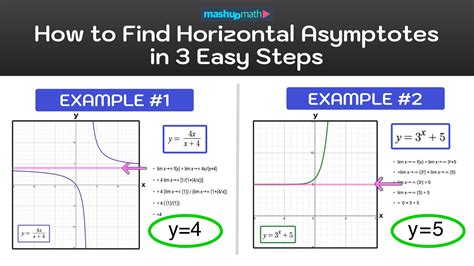
To find horizontal asymptotes, it's essential to understand that these asymptotes represent the behavior of a function as the absolute value of the x-coordinate gets larger and larger. In simpler terms, they are the horizontal lines that a function approaches as x goes towards positive or negative infinity. There are several methods to determine these asymptotes, depending on the type of function you're dealing with. Here, we'll explore five ways to find horizontal asymptotes, which are crucial in understanding the limits and behavior of functions, especially in calculus and algebra.
Understanding Horizontal Asymptotes
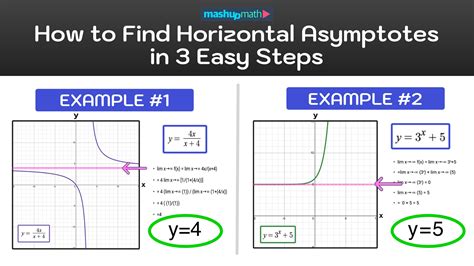
A horizontal asymptote is a horizontal line that the graph of a function approaches as x tends to infinity or negative infinity. Not all functions have horizontal asymptotes, but for those that do, these asymptotes are significant in describing the function’s behavior over large intervals. The equation of a horizontal asymptote is typically of the form y = b, where b is a constant.
Method 1: Comparing Degrees of Polynomials
When dealing with rational functions, which are ratios of polynomials, the degree of the polynomials in the numerator and denominator can help determine if there is a horizontal asymptote and what its equation is. If the degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote is y = 0. If the degrees are equal, the horizontal asymptote is the ratio of the leading coefficients. If the degree of the numerator is greater, there is no horizontal asymptote, but there might be a slant asymptote.
| Comparison of Degrees | Resulting Asymptote |
|---|---|
| Numerator degree < Denominator degree | y = 0 |
| Numerator degree = Denominator degree | y = Leading coefficient of numerator / Leading coefficient of denominator |
| Numerator degree > Denominator degree | No horizontal asymptote |
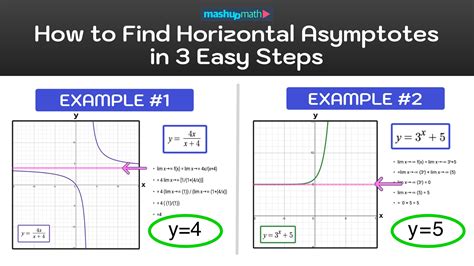
Determining Horizontal Asymptotes for Rational Functions

Rational functions are a common type where horizontal asymptotes are analyzed. The general form of a rational function is f(x) = p(x) / q(x), where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials. By comparing the degrees of p(x) and q(x) and considering their leading coefficients, we can determine the horizontal asymptotes as described in Method 1.
Method 2: Evaluating Limits
Another way to find horizontal asymptotes is by evaluating the limits of the function as x approaches infinity and negative infinity. This method applies to various types of functions, not just rational ones. If the limit as x approaches infinity and the limit as x approaches negative infinity are both finite and equal, then that value is the horizontal asymptote. This method is particularly useful for functions that are not rational or for more complex functions where degree comparison is not applicable.
Practical Application of Horizontal Asymptotes
Horizontal asymptotes have practical applications in modeling real-world phenomena, such as population growth, chemical reactions, and electrical circuits. Understanding the horizontal asymptotes of functions used in these models helps predict long-term behavior and make informed decisions.
Method 3: Analyzing Exponential Functions
Exponential functions, of the form f(x) = a^x, where a is a positive constant not equal to 1, do not have horizontal asymptotes in the traditional sense used for rational functions. However, as x approaches negative infinity, the function approaches 0, which can be considered as a horizontal asymptote at y = 0. For x approaching positive infinity, there is no finite limit, and thus no horizontal asymptote.
Method 4: Considering Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions like sine and cosine are periodic and oscillate between -1 and 1. These functions do not have horizontal asymptotes because they do not approach a constant value as x approaches infinity or negative infinity. Instead, they continue to oscillate within their range.
Method 5: Examining Piecewise Functions
Piecewise functions are defined by different formulas on different intervals. To find the horizontal asymptotes of a piecewise function, analyze each component separately using the methods described above. If different components have different horizontal asymptotes, it may indicate a discontinuity or a change in the function’s behavior at the point where the formula changes.
Key Points
- Horizontal asymptotes are found by comparing the degrees of the numerator and denominator in rational functions or by evaluating limits as x approaches infinity and negative infinity.
- Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote at y = 0 as x approaches negative infinity but no horizontal asymptote as x approaches positive infinity.
- Trigonometric functions do not have horizontal asymptotes due to their periodic nature.
- Piecewise functions require analyzing each component separately to determine horizontal asymptotes.
- Understanding horizontal asymptotes is crucial for predicting the long-term behavior of functions and making informed decisions in real-world applications.
In conclusion, finding horizontal asymptotes involves understanding the behavior of functions as x approaches infinity and negative infinity. By using the methods outlined above, including comparing degrees of polynomials, evaluating limits, analyzing exponential and trigonometric functions, and examining piecewise functions, one can determine the horizontal asymptotes of a wide range of functions. This knowledge is fundamental in calculus and algebra, with applications in various fields where modeling and predicting the behavior of systems are critical.
What is the significance of horizontal asymptotes in real-world applications?
+Horizontal asymptotes are significant in real-world applications as they help in predicting the long-term behavior of systems. For instance, in population growth models, understanding the horizontal asymptote can inform about the carrying capacity of an environment.
Can all functions have horizontal asymptotes?
+No, not all functions have horizontal asymptotes. The presence of a horizontal asymptote depends on the function’s behavior as x approaches infinity or negative infinity. Functions that oscillate or grow without bound do not have horizontal asymptotes.
How do you find the horizontal asymptote of an exponential function?
+For exponential functions of the form f(x) = a^x, where a is a positive constant not equal to 1, there is a horizontal asymptote at y = 0 as x approaches negative infinity. As x approaches positive infinity, there is no horizontal asymptote because the function grows without bound.