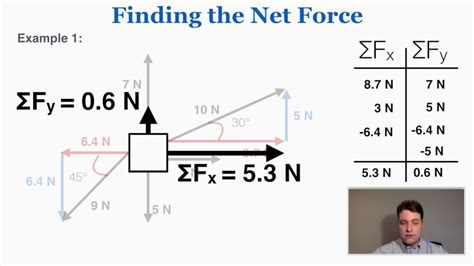
Calculating the net force acting on an object is a fundamental concept in physics, crucial for understanding the motion of objects in various environments. The net force, also known as the resultant force, is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object. It determines the acceleration of the object, according to Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to its mass. In this article, we will explore how to find the net force easily, including the primary, secondary, and tertiary steps involved in the calculation process.
Understanding Forces and Vectors
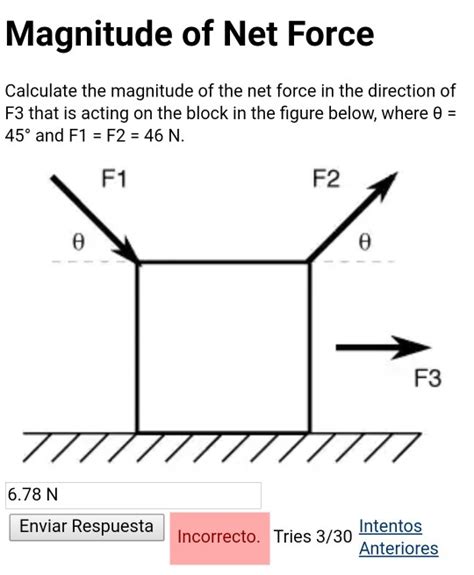
To calculate the net force, it’s essential to understand the basics of forces and vectors. Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause an object to change its state of motion. They are vector quantities, characterized by both magnitude (amount of force) and direction. When multiple forces act on an object, they can be added vectorially to find the net force. This involves considering the magnitude and direction of each force. For instance, forces acting in the same direction can be added directly, while forces acting in opposite directions are subtracted.
Breaking Down Forces into Components
Often, forces are not aligned with the coordinate axes (x, y, z), making it necessary to break them down into their vector components. This is achieved by using trigonometry, specifically sine and cosine functions, to resolve the force into its components along each axis. For example, a force acting at an angle θ to the x-axis can be resolved into its x and y components using Fx = F*cos(θ) and Fy = F*sin(θ), where F is the magnitude of the force and θ is the angle with the x-axis.
| Force Type | Magnitude | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Gravity | 9.81 m/s^2 (on Earth's surface) | Downwards |
| Normal Force | Varies | Perpendicular to the surface |
| Friction | Varies | Opposite to the direction of motion |
Calculating Net Force

The net force (F_net) is calculated by summing all the forces acting on an object. This can be done graphically using force diagrams or mathematically by adding the vector components of the forces. For forces acting in one dimension, the net force is simply the algebraic sum of the forces. For forces acting in two or three dimensions, the net force is found by adding the components of the forces along each axis and then using the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the net force.
Example Calculation
Consider an object on a horizontal surface with two forces acting on it: a 10 N force to the east and a 5 N force to the west. The net force acting on the object can be calculated as F_net = 10 N (east) - 5 N (west) = 5 N (east). This means the object will accelerate to the east due to the net force of 5 N acting upon it.
Key Points
- The net force acting on an object determines its acceleration.
- Forces are vector quantities that must be considered in terms of both magnitude and direction.
- Breaking down forces into their components along the coordinate axes can simplify calculations.
- The net force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
- Calculating the net force involves considering the magnitude and direction of each force.
Real-World Applications
Understanding how to find the net force has numerous real-world applications, from designing safer vehicles and buildings to predicting the motion of projectiles and the stability of structures. It’s also crucial in biomechanics, where the forces acting on the human body during movement or impact need to be understood to prevent injuries and improve performance.
Biomechanical Example
In sports, understanding the net force acting on an athlete can help in optimizing performance and preventing injuries. For instance, the forces acting on a runner’s joints during sprinting can be analyzed to develop training programs that reduce the risk of injury and enhance speed.
What is the importance of calculating the net force in physics?
+Calculating the net force is crucial because it determines the acceleration of an object, according to Newton's second law of motion. This understanding is foundational in predicting the motion of objects, designing mechanical systems, and analyzing the stability of structures.
How do you calculate the net force acting on an object when multiple forces are involved?
+The net force is calculated by summing all the forces acting on an object. For forces acting in one dimension, this is a straightforward algebraic sum. For forces in two or three dimensions, the forces are broken down into their vector components along each axis, summed, and then the magnitude of the net force is found using the Pythagorean theorem.
What role does the mass of an object play in determining its acceleration due to a net force?
+According to Newton's second law of motion (F = ma), the acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to its mass. This means that for a given net force, a smaller mass will result in a greater acceleration, and a larger mass will result in a smaller acceleration.
In conclusion, finding the net force acting on an object is a critical skill in physics and engineering, allowing for the prediction of motion, design of systems, and analysis of complex phenomena. By understanding the principles of force and vector addition, and applying them to real-world scenarios, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation for the underlying mechanics that govern our universe.