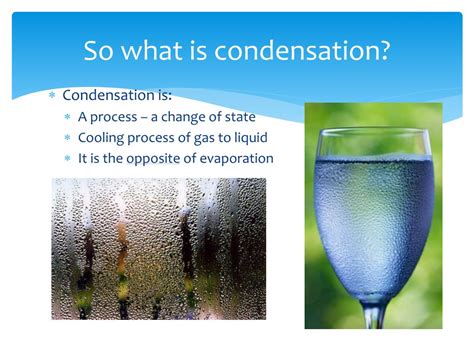
Condensation is a fundamental process that occurs in our daily lives, from the formation of dew on grass to the creation of clouds in the atmosphere. It is an essential aspect of the water cycle, where water vapor in the air is transformed into liquid water. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of condensation, exploring the different ways it works and its significance in various fields. To better understand this complex process, let's first establish a foundational understanding of condensation and its role in the environment.
Key Points
- Condensation occurs when warm air cools down, causing the water vapor to condense into droplets.
- There are several types of condensation, including dew, frost, fog, and cloud formation.
- Condensation plays a crucial role in the water cycle, influencing weather patterns and climate.
- Understanding condensation is essential for various industries, such as agriculture, construction, and refrigeration.
- Condensation can be harnessed and controlled through various techniques, including cooling systems and insulation.
Condensation Processes

Condensation is a multifaceted process that can occur through various mechanisms. One of the primary ways condensation works is through the cooling of warm air. When warm air comes into contact with a cooler surface, it cools down, causing the water vapor to condense into droplets. This process is commonly observed in the formation of dew on grass or the condensation of water vapor on a cold drink. The heat transfer process is crucial in this type of condensation, as it allows the warm air to cool down and the water vapor to condense.
Dew Formation
Dew formation is another significant aspect of condensation. It occurs when the air temperature cools down overnight, causing the water vapor to condense on surfaces. This process is essential for plant growth, as it provides plants with the necessary water for photosynthesis. The dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to dew formation. Understanding dew formation is crucial for agricultural purposes, as it can help farmers optimize crop growth and development.
| Condensation Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Dew | Formation of water droplets on surfaces due to overnight cooling |
| Frost | Formation of ice crystals on surfaces due to freezing temperatures |
| Fog | Cloud formation at ground level due to cooling of air |
| Clouds | Formation of water droplets or ice crystals in the atmosphere |
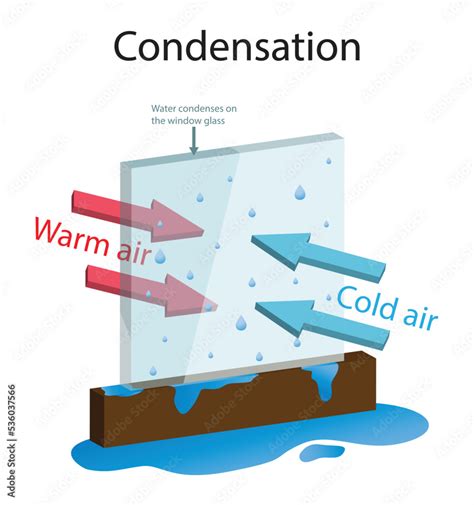
Practical Applications of Condensation
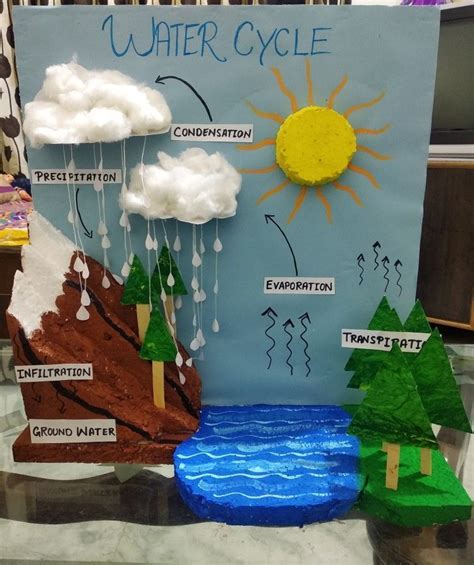

Condensation has numerous practical applications in various industries. In construction, condensation is a critical factor in building design, as it can affect the structural integrity and insulation of buildings. In refrigeration, condensation is used to cool down refrigerants, allowing for the efficient storage of perishable goods. Additionally, condensation is essential for weather forecasting, as it helps predict weather patterns and climate trends.
Condensation Control Techniques
Condensation can be controlled and harnessed through various techniques, including cooling systems and insulation. In cooling systems, condensation is used to cool down fluids, allowing for the efficient transfer of heat. In insulation, condensation is minimized through the use of materials with low thermal conductivity, reducing heat transfer and energy losses. By understanding these techniques, we can optimize condensation control and harness its potential in various applications.
In conclusion, condensation is a complex and multifaceted process that plays a vital role in our environment. By understanding the different types of condensation and their underlying mechanisms, we can better appreciate the significance of condensation in various fields. Whether it's in agriculture, construction, or refrigeration, condensation is an essential aspect of our daily lives, and its control and harnessing can have a significant impact on our environment and industries.
What is the difference between dew and frost?
+Dew and frost are both forms of condensation, but they occur at different temperatures. Dew forms when the air temperature cools down overnight, causing the water vapor to condense on surfaces. Frost, on the other hand, forms when the air temperature drops below freezing, causing the water vapor to freeze into ice crystals.
How does condensation affect weather patterns?
+Condensation plays a significant role in shaping weather patterns. When condensation occurs, it releases heat into the atmosphere, which can influence the formation of clouds and precipitation. Additionally, condensation can affect the amount of moisture in the air, which can impact the development of weather systems.
What are some common applications of condensation control techniques?
+Condensation control techniques are commonly used in various industries, including construction, refrigeration, and air conditioning. These techniques can help minimize condensation, reduce energy losses, and optimize the performance of systems. Additionally, condensation control techniques can be used to prevent mold growth, reduce humidity, and improve indoor air quality.