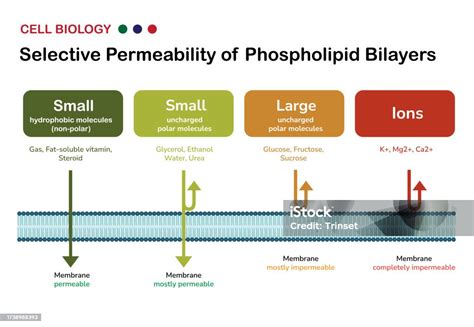
The phospholipid bilayer, a fundamental component of cell membranes, plays a critical role in regulating various cellular processes. Its unique structure, composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules with their hydrophilic heads facing outwards and hydrophobic tails facing inwards, allows it to facilitate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell while maintaining cellular homeostasis. In this article, we will explore five ways the phospholipid bilayer regulates cellular functions, highlighting its importance in maintaining cellular integrity and function.
Key Points
- The phospholipid bilayer regulates the movement of molecules across the cell membrane through selective permeability.
- It maintains cellular homeostasis by controlling the balance of ions and molecules within the cell.
- The bilayer plays a crucial role in cell signaling, allowing for the transmission of signals between cells.
- It regulates the activity of membrane-bound proteins, which are essential for various cellular processes.
- The phospholipid bilayer is involved in the regulation of cellular transport, including endocytosis and exocytosis.
Regulation of Molecular Movement
The phospholipid bilayer regulates the movement of molecules across the cell membrane through a process known as selective permeability. This means that the bilayer allows certain molecules to pass through while restricting others, based on their size, charge, and polarity. For example, water and oxygen molecules can diffuse through the bilayer, while larger molecules such as proteins and carbohydrates require specialized transport mechanisms to cross the membrane. This selective permeability is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the balance of ions and molecules within the cell.
Role in Cell Signaling
The phospholipid bilayer plays a critical role in cell signaling, allowing for the transmission of signals between cells. This is achieved through the movement of signaling molecules, such as hormones and neurotransmitters, across the cell membrane. The bilayer can also interact with signaling proteins, such as receptors and enzymes, to facilitate the transmission of signals. For example, the binding of a hormone to its receptor on the cell surface can trigger a signaling cascade that regulates various cellular processes, including gene expression and metabolism.
| Cell Signaling Mechanism | Role of Phospholipid Bilayer |
|---|---|
| Receptor binding | Facilitates the binding of signaling molecules to their receptors |
| Signal transduction | Allows for the transmission of signals across the cell membrane |
| Enzyme activation | Regulates the activity of enzymes involved in signaling pathways |
Regulation of Membrane-Bound Proteins
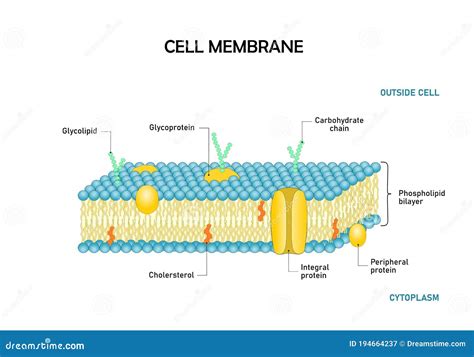
The phospholipid bilayer regulates the activity of membrane-bound proteins, which are essential for various cellular processes, including transport, signaling, and cell adhesion. The bilayer can interact with these proteins, influencing their conformation, activity, and interactions with other molecules. For example, the bilayer can regulate the activity of transport proteins, such as channels and pumps, which are responsible for moving molecules across the cell membrane. Additionally, the bilayer can influence the activity of signaling proteins, such as receptors and enzymes, which are involved in cell signaling pathways.
Regulation of Cellular Transport
The phospholipid bilayer is involved in the regulation of cellular transport, including endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in molecules and particles from outside the cell, while exocytosis is the process by which cells release molecules and particles to the outside environment. The bilayer plays a critical role in these processes, regulating the formation and fusion of vesicles, as well as the movement of molecules across the cell membrane.
In conclusion, the phospholipid bilayer plays a critical role in regulating various cellular processes, including the movement of molecules, cell signaling, and the activity of membrane-bound proteins. Its unique structure and properties allow it to facilitate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, while maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the balance of ions and molecules within the cell. Understanding the regulatory functions of the phospholipid bilayer is essential for understanding cellular biology and developing new treatments for diseases.
What is the main function of the phospholipid bilayer in cell membranes?
+The main function of the phospholipid bilayer is to regulate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, while maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the balance of ions and molecules within the cell.
How does the phospholipid bilayer regulate cell signaling?
+The phospholipid bilayer regulates cell signaling by facilitating the movement of signaling molecules across the cell membrane and interacting with signaling proteins, such as receptors and enzymes.
What is the role of the phospholipid bilayer in regulating membrane-bound proteins?
+The phospholipid bilayer regulates the activity of membrane-bound proteins by interacting with them and influencing their conformation, activity, and interactions with other molecules.