The hedgehog, a small, spiny mammal, has long fascinated humans with its unique appearance and intriguing behaviors. Belonging to the family Erinaceidae, hedgehogs are found in various parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and New Zealand. Their ability to curl into a ball for defense, using their spines as a protective mechanism, is perhaps one of their most recognizable features. However, there is more to hedgehogs than their defensive capabilities. Let's delve into five interesting facts about hedgehog life, exploring their habits, social behaviors, and the challenges they face in the wild.
Key Points
- Hedgehogs are primarily nocturnal, with most of their activity occurring at night.
- They are omnivores, with a diet that includes insects, fruits, and vegetation.
- Hedgehogs have a unique way of communicating, mainly through a series of clicks, snuffles, and grunts.
- They are solitary animals, typically only coming together during the breeding season.
- Hedgehogs face numerous threats, including habitat loss, road accidents, and climate change, which affect their food supply and habitat quality.
Hedgehog Diet and Foraging

Hedgehogs are not picky eaters; they are omnivores, which means their diet consists of a wide range of food sources. Insects, such as beetles and worms, are a staple in their diet, providing essential proteins. They also consume fruits, berries, and other vegetation. In urban areas, hedgehogs have been known to visit gardens, where they might eat pet food left outdoors or even raid gardens for fruits and vegetables. Their foraging behavior is mostly nocturnal, using their keen sense of smell and hearing to locate food in the dark. This adaptability in their diet has helped hedgehogs thrive in various environments, from forests to backyards.
Reproduction and Lifespan
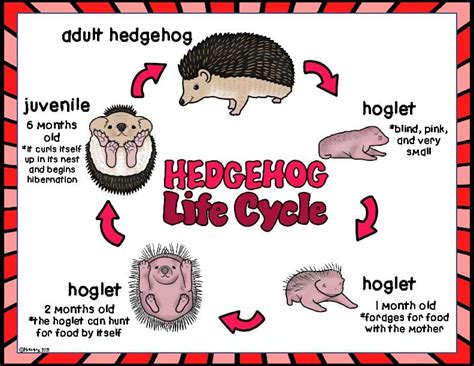
The reproductive habits of hedgehogs are quite interesting. They are seasonal breeders, with the mating season typically occurring in the spring and early summer. After a gestation period of about 4-6 weeks, a female hedgehog gives birth to a litter of 2-10 hoglets (baby hedgehogs). The hoglets are born blind and without spines, but they develop quickly. Their eyes open after about two weeks, and they start to venture out of the nest after 4-6 weeks. Hedgehogs can live for approximately 4-7 years in the wild, although their lifespan in captivity can extend up to 10 years with proper care and nutrition.
| Category | Data |
|---|---|
| Gestation Period | 4-6 weeks |
| Litter Size | 2-10 hoglets |
| Wild Lifespan | 4-7 years |
| Captivity Lifespan | Up to 10 years |
Defense Mechanisms and Social Behavior

One of the most iconic features of hedgehogs is their ability to curl into a ball when threatened, using their spines for defense. This unique mechanism deters predators, as the spines can cause pain and make it difficult for predators to get a good grip. Besides this physical defense, hedgehogs are generally solitary animals and have a simple form of communication that includes clicking, snuffling, and grunting sounds. They are not highly social creatures and typically only come together during the breeding season. Their solitary nature and nocturnal lifestyle mean that they often go unnoticed by humans, even in urban areas.
Conservation Status and Threats
Unfortunately, hedgehogs face several threats in the wild. Habitat loss and fragmentation, due to urbanization and agricultural expansion, reduce their living space and make it harder for them to find food and mates. Road accidents are another significant threat, as hedgehogs are often hit by cars when they try to cross roads. Climate change also affects hedgehog populations by altering their food supply and changing the timing of their breeding season. In some parts of their range, hedgehogs are considered to be of “least concern” by the IUCN, but their populations are declining in many areas, highlighting the need for conservation efforts.
What is the primary defense mechanism of hedgehogs?
+The primary defense mechanism of hedgehogs is their ability to curl into a ball, using their spines to deter predators.
Are hedgehogs social animals?
+No, hedgehogs are generally solitary animals and only come together during the breeding season.
What are some of the main threats to hedgehog populations?
+Hedgehogs face threats such as habitat loss, road accidents, and climate change, which affect their food supply and habitat quality.
In conclusion, hedgehogs are fascinating creatures with unique adaptations and behaviors. Understanding their diet, reproduction habits, defense mechanisms, and the challenges they face is crucial for appreciating these small mammals. As we continue to urbanize and alter natural habitats, it’s essential to consider the impact on wildlife like hedgehogs and work towards creating more inclusive and sustainable environments for all species to thrive.



