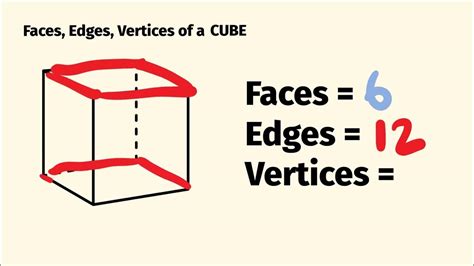
A cube, one of the most fundamental geometric shapes, has several distinct features that define its structure and properties. Among these, the corners or vertices of a cube are crucial, as they are the points where the edges of the cube meet. Understanding the characteristics of these corners is essential for various applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and design. In this article, we will delve into the concept of the 8 corners of a cube, exploring their significance, properties, and how they relate to the overall geometry of the cube.
Introduction to Cubes and Their Corners
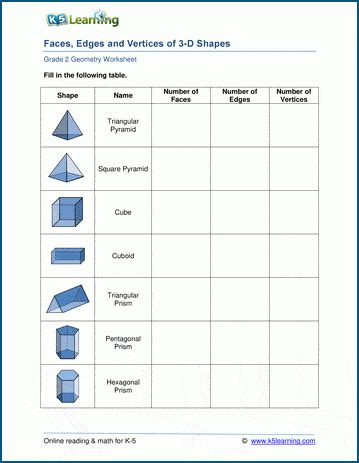
A cube is a three-dimensional solid object that is bounded by six square faces, with each face being a flat surface. It has 12 straight edges and 8 corners or vertices. Each corner is the point where three edges and three faces of the cube meet. The corners are critical in defining the cube’s shape, volume, and surface area. The symmetry and properties of a cube’s corners make it a versatile shape used in construction, packaging, and design.
Properties of a Cube’s Corners
Each corner of a cube has specific properties that contribute to the overall geometry of the cube. For instance, all corners of a cube are right angles (90 degrees), which means that the edges meeting at a corner are perpendicular to each other. This right angle property at each corner is what gives a cube its structural integrity and makes it a stable shape. Moreover, the symmetry of a cube is reflected in its corners, as each corner is identical in terms of the angles and edges it contains.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Angle at Each Corner | 90 degrees (right angle) |
| Number of Edges Meeting at a Corner | 3 |
| Number of Faces Meeting at a Corner | 3 |
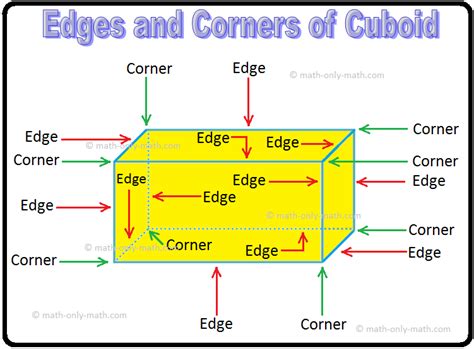
Mathematical Significance of a Cube’s Corners
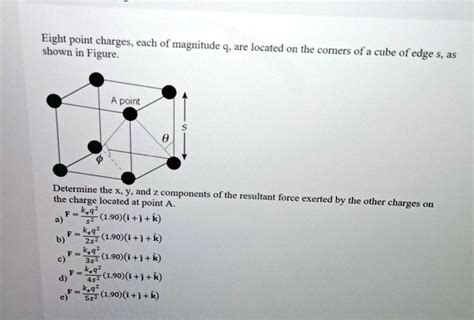
Mathematically, the corners of a cube are significant in calculating its volume and surface area. The formula for the volume of a cube, V = s^3, where s is the length of a side, inherently considers the corners, as the length of a side is measured from one corner to the opposite corner along an edge. Similarly, the surface area of a cube, A = 6s^2, reflects the properties of its corners, as the area of each face is determined by the length of its sides, which are defined by the corners.
Geometric Transformations and Corners
When a cube undergoes geometric transformations such as rotations, translations, or reflections, its corners play a pivotal role. These transformations can change the position and orientation of the cube in space but do not alter the properties of its corners. Understanding how transformations affect the corners of a cube is vital in fields like computer graphics, where such transformations are used to create animations and simulations.
Key Points
- A cube has 8 corners or vertices, each being the point where three edges and three faces meet.
- Each corner of a cube is a right angle, contributing to the cube's structural integrity and stability.
- The properties of a cube's corners are crucial in mathematical calculations such as volume and surface area.
- Geometric transformations affect the position and orientation of a cube but not the properties of its corners.
- Understanding the corners of a cube is essential for various applications in design, engineering, and physics.
Practical Applications of Cube Corners
The unique properties of a cube’s corners make them useful in a variety of practical applications. In packaging, cubes are often used because their corners provide additional structural support, making them ideal for containing and protecting products during transportation. In construction, the stability provided by the right angles at the corners of cubes (or brick blocks) is crucial for building safe and durable structures.
Design and Engineering Considerations
When designing objects or structures that incorporate cubic shapes, engineers and designers must consider the properties of the corners. For instance, in mechanical engineering, the corners of cubic components can be critical in determining the overall strength and durability of a device or machine. Similarly, in architecture, the aesthetic appeal of a building can be enhanced by the creative use of cubic shapes and their corners.
What is the significance of the right angles at the corners of a cube?
+The right angles at the corners of a cube provide structural integrity and stability, making the cube a versatile shape for various applications.
How do the corners of a cube affect its volume and surface area calculations?
+The corners of a cube are crucial in defining the length of its sides, which are used in the formulas for calculating the volume (V = s^3) and surface area (A = 6s^2) of the cube.
What role do the corners play in geometric transformations of a cube?
+The corners of a cube are key points in geometric transformations such as rotations, translations, and reflections, as these transformations change the cube's position and orientation in space but not the properties of its corners.
In conclusion, the 8 corners of a cube are fundamental to its geometry and properties, influencing its stability, volume, surface area, and behavior under geometric transformations. Understanding the significance and properties of these corners is essential for a wide range of applications, from design and engineering to mathematics and physics. By appreciating the role of the corners, individuals can better utilize cubic shapes in creative and functional ways, contributing to advancements in various fields.