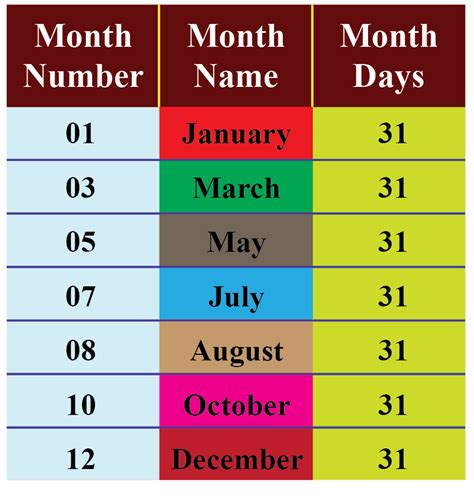
To determine the number of days in 6 months, we need to consider the varying lengths of months. Since months have either 30 or 31 days, except for February which has 28 or 29 days, the calculation isn't straightforward. However, for simplicity and general estimation, we can use an average month length. The average month has approximately 30.44 days, considering the 365-day year (366 in leap years). This average is derived from dividing the total number of days in a year by 12 months.
Calculation Approach
Using the average month length of 30.44 days, we can calculate the number of days in 6 months. Multiply the average days per month by the number of months: 30.44 days/month * 6 months.
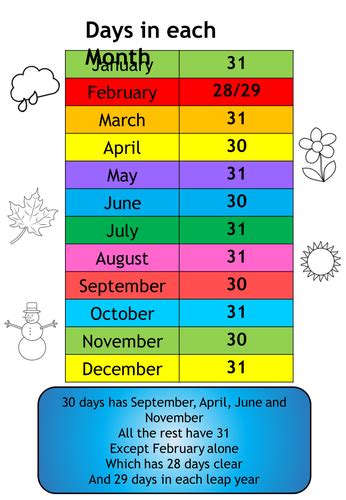
This calculation yields approximately 182.64 days for 6 months in a non-leap year. However, for a more precise calculation without using averages, we must consider the actual number of days in each month. For the first 6 months of the year (January to June), the total is: 31 (January) + 28 or 29 (February) + 31 (March) + 30 (April) + 31 (May) + 30 (June) = 181 or 182 days in a non-leap year and 182 or 183 days in a leap year, respectively.
Varying Year Types
The distinction between leap and non-leap years is crucial because it affects the total number of days in a year and, consequently, the average length of a month. Leap years, which occur every 4 years, have 366 days instead of the usual 365, with the extra day added to February, making it a 29-day month in those years.
| Year Type | Total Days in Year | Average Days per Month |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Leap Year | 365 | 30.42 |
| Leap Year | 366 | 30.44 |

The actual calculation of days in 6 months, without using averages, depends on which 6 months are being considered. For instance, the first half of a non-leap year (January to June) contains 181 days, while the same period in a leap year contains 182 days.
Key Considerations
When calculating the number of days in a period, it’s crucial to consider the start and end dates to accurately account for the months included and whether the period spans a leap year. For general purposes and rough estimates, using an average can provide a close approximation, but for precise calculations, the specific months and year type must be taken into account.
Key Points
- The number of days in 6 months can vary from 181 to 183 days, depending on the months included and whether it's a leap year.
- Using an average month length can provide a rough estimate but is less accurate than calculating based on specific months.
- Leap years affect the total number of days in a year and the average length of a month.
- For precise calculations, consider the actual days in each month and whether the period includes a leap year.
- Understanding the distinction between leap and non-leap years is crucial for accurate time-related calculations.
In conclusion, while there's a general estimation for the number of days in 6 months, the actual count can vary based on several factors, including the specific months in question and the occurrence of a leap year. This understanding is vital for various applications, from simple calendar planning to complex astronomical calculations.
How do leap years affect the calculation of days in 6 months?
+Leap years add an extra day to February, which can increase the total days in a 6-month period that includes February by one day compared to non-leap years.
What is the most accurate way to calculate the number of days in 6 months?
+The most accurate way is to count the actual days in each month of the period in question, taking into account whether it’s a leap year or not.
Why is understanding the difference between leap and non-leap years important?
+Understanding this difference is crucial for accurate calculations in various fields, including finance, calendar design, and astronomy, where precise timing is essential.