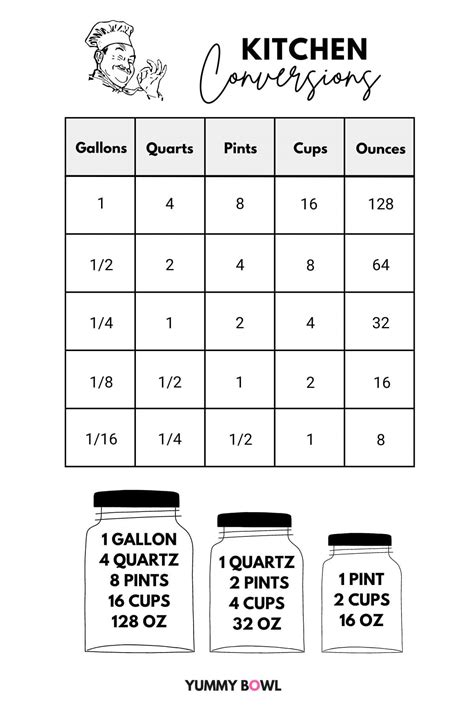
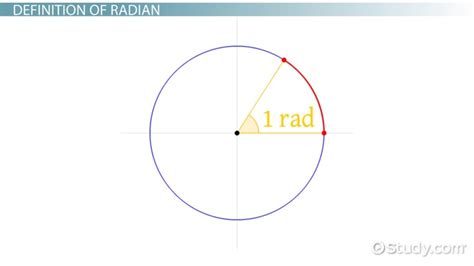
The concept of radians in a circle is a fundamental aspect of geometry and trigonometry. A radian is a unit of measurement for angles, defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. In this context, understanding the relationship between radians and the properties of a circle is essential for various mathematical and real-world applications.
To delve into the specifics of 5 radians in a circle, it's crucial to first establish the relationship between radians and degrees, as well as the characteristics of a circle. A full circle, or 360 degrees, is equivalent to 2π radians. This relationship can be used to convert between degrees and radians. Given that 5 radians is slightly more than 2π (since π is approximately 3.14159), 5 radians would be more than a half circle but less than a full circle.
Key Points
- 1 radian is defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle.
- The entire circle is 2π radians, equivalent to 360 degrees.
- 5 radians is more than half a circle (π radians) but less than a full circle (2π radians).
- To find the degree measure of 5 radians, we use the conversion factor: 1 radian = 180/π degrees.
- Calculation: 5 radians * (180/π) degrees/radian ≈ 286.4789 degrees.
Conversion of 5 Radians to Degrees
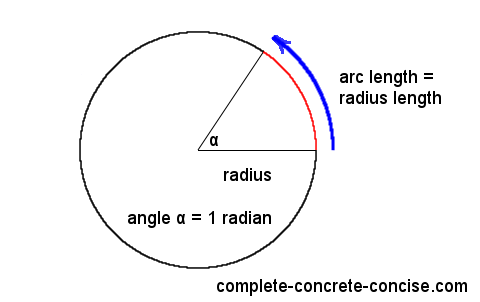
The conversion from radians to degrees can be achieved by using the conversion factor derived from the relationship between radians and degrees: 1 radian = 180/π degrees. To convert 5 radians into degrees, we multiply 5 by 180/π.
This calculation yields approximately 286.4789 degrees. Therefore, 5 radians corresponds to slightly less than 360 degrees, reaffirming that it represents an angle greater than a half circle but less than a full circle.
Geometric and Trigonometric Implications
Understanding the value of 5 radians in terms of degrees has significant implications for geometric and trigonometric calculations. For instance, in trigonometry, the sine, cosine, and tangent functions are often evaluated in radian measure. Knowing the degree equivalent of 5 radians can facilitate calculations and visualizations in various contexts, such as determining the length of an arc, the area of a sector, or solving triangles.
| Angle in Radians | Equivalent Angle in Degrees | Trigonometric Function Values |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Approximately 286.4789 | Varying values for sine, cosine, and tangent |
| π | 180 | Sine = 0, Cosine = -1, Tangent = 0 |
| 2π | 360 | Sine = 0, Cosine = 1, Tangent = 0 |
Practical Applications
The concept of radians and their conversion to degrees has numerous practical applications. In engineering, for instance, understanding angular measurements in radians is essential for designing circular motion mechanisms, calculating stresses in rotational systems, and analyzing the performance of motors and gears. In physics, radians are used to describe wave phenomena, including light and sound waves, and in the study of rotational dynamics.
In conclusion, 5 radians represents an angle of approximately 286.4789 degrees, which is more than a half circle but less than a full circle. This understanding is fundamental to various mathematical and scientific disciplines, offering a basis for further exploration into geometric, trigonometric, and physical phenomena.
What is the definition of a radian?
+A radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle.
How do you convert radians to degrees?
+To convert radians to degrees, multiply the angle in radians by 180/π.
What are the practical applications of understanding radians and their conversion to degrees?
+Practical applications include engineering design, physics, particularly in the study of rotational dynamics and wave phenomena, and mathematics, especially in geometry and trigonometry.