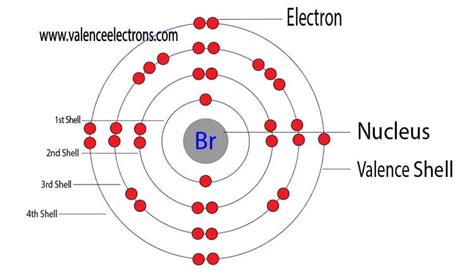
Bromine, a halogen element with the atomic number 35, has a unique electron configuration that determines its valence electrons count. To understand the number of valence electrons in bromine, we first need to look at its electron configuration. The electron configuration of bromine is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵. From this configuration, we can see that the outermost energy level (valence shell) of bromine is the fourth shell, which contains 4s and 4p orbitals.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost principal energy level of an atom. These electrons participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms. In the case of bromine, the valence shell is the fourth shell, and it contains 7 electrons (4s² and 4p⁵). The number of valence electrons in an atom is crucial because it determines the atom’s reactivity and its ability to form chemical bonds.
Counting Valence Electrons in Bromine
To count the valence electrons in bromine, we consider the electrons in the 4s and 4p orbitals, which are in the outermost energy level. The 4s orbital contains 2 electrons, and the 4p orbital contains 5 electrons, giving a total of 7 valence electrons. This count is critical for understanding bromine’s chemical properties, such as its tendency to gain one electron to form a stable anion (Br⁻) with a full outer shell, similar to the noble gas krypton.
| Orbital | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| 4s | 2 |
| 4p | 5 |
| Total Valence Electrons | 7 |
The understanding of valence electrons in bromine is foundational for predicting its chemical behavior, including its reactivity with metals and nonmetals, and its role in various chemical reactions. This knowledge is also essential for understanding the properties of compounds that contain bromine, such as hydrogen bromide (HBr) and bromine water (Br₂ in water), which have applications in chemistry and industry.
Applications and Chemical Properties

Bromine’s chemical properties, largely determined by its valence electrons, make it useful in a variety of applications. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and as a disinfectant in water treatment. The ability of bromine to form a wide range of compounds, due to its reactive nature, also makes it an important element in organic chemistry synthesis.
Chemical Reactivity
The reactivity of bromine is influenced by its electron configuration and the number of valence electrons. Bromine can easily accept one electron to form a stable ion, which is a key aspect of its chemical reactivity. This reactivity is also why bromine is often used as a reactant in organic synthesis, where it can participate in substitution and addition reactions.
Key Points
- Bromine has 7 valence electrons, which influences its chemical reactivity and ability to form compounds.
- The electron configuration of bromine is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵, with the 4s and 4p orbitals being the valence shell.
- Bromine tends to gain one electron to achieve a stable octet configuration, similar to the noble gases.
- The understanding of bromine's valence electrons is crucial for predicting its chemical behavior and properties.
- Bromine's applications include pharmaceutical production, water treatment, and as a reactant in organic synthesis.
In conclusion, the count of valence electrons in bromine provides a foundational understanding of its chemical properties and reactivity. This knowledge is essential for predicting how bromine will behave in various chemical reactions and for understanding its applications in different fields. By examining the electron configuration and focusing on the outermost energy level, we can derive the number of valence electrons and understand the implications for bromine's chemical behavior.
What determines the number of valence electrons in an atom?
+The number of valence electrons in an atom is determined by the electron configuration, specifically the number of electrons in the outermost principal energy level (valence shell).
How do valence electrons influence the chemical properties of an element?
+Valence electrons determine an element’s reactivity and its ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons influences how easily an atom can gain, lose, or share electrons to form compounds.
What is the significance of bromine gaining one electron to form a stable anion?
+Gaining one electron allows bromine to achieve a stable octet configuration, similar to the noble gases, which have a full outer energy level. This stability is a driving force behind many of bromine’s chemical reactions.