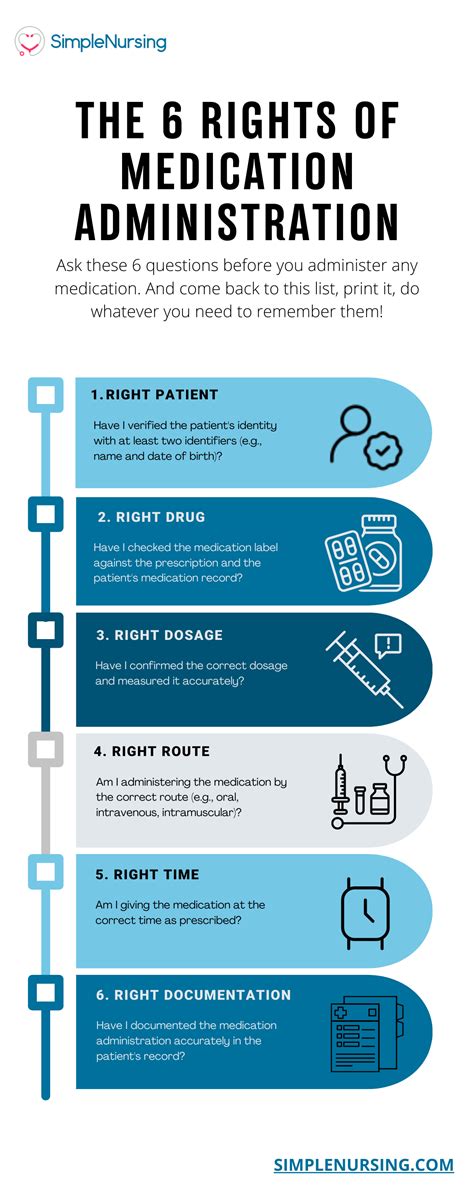
Gap insurance, or Guaranteed Asset Protection insurance, is a specialized form of coverage designed to protect vehicle owners in specific financial situations. It fills the gap between the actual cash value of a vehicle and the remaining balance on a loan or lease, providing crucial financial support in cases of total loss, theft, or write-off.
Understanding the extent of coverage offered by gap insurance is essential for anyone looking to protect their financial interests when purchasing or leasing a vehicle. This article will delve into the intricacies of gap insurance coverage, exploring its benefits, limitations, and real-world applications. By the end, readers should have a comprehensive understanding of how gap insurance can safeguard their finances and what factors influence the level of coverage provided.
Understanding Gap Insurance Coverage

Gap insurance coverage is a safety net for vehicle owners who have financed or leased their vehicles. It ensures that, in the event of a total loss or write-off, the insured individual is not left with a significant financial burden due to the outstanding loan or lease balance.
When a vehicle is purchased with financing, its value typically depreciates quickly, especially in the first few years of ownership. This means that the outstanding loan balance often exceeds the vehicle's actual cash value. Gap insurance steps in to cover this difference, ensuring that the policyholder is not responsible for paying off the entire loan amount out of pocket.
Key Factors Influencing Gap Insurance Coverage
- Vehicle Age and Depreciation: Gap insurance is particularly beneficial for new vehicles, as they depreciate rapidly in the initial years. The rate of depreciation can significantly impact the coverage provided by gap insurance.
- Loan or Lease Terms: The structure of the loan or lease agreement plays a vital role. Gap insurance often covers the difference between the vehicle’s value and the loan balance, but this can vary depending on the terms of the financing.
- Vehicle Usage: Gap insurance policies may have restrictions or limitations based on the usage of the vehicle. For instance, some policies might not cover vehicles used for commercial purposes or those involved in frequent short-term rentals.
- Policy Exclusions: Like any insurance policy, gap insurance comes with exclusions. It’s essential to understand what situations or scenarios are not covered by the policy to avoid any surprises.
Real-World Examples of Gap Insurance Coverage
Let’s illustrate how gap insurance coverage works with a hypothetical scenario.
Imagine John purchases a new car for $30,000 and finances it with a 60-month loan at an interest rate of 5%. After two years, the car is involved in an accident and deemed a total loss. At this point, the car's actual cash value has depreciated to $18,000, but the outstanding loan balance is $22,000.
Without gap insurance, John would be responsible for paying the $4,000 difference between the vehicle's value and the loan balance. However, with gap insurance, the policy covers this gap, ensuring John doesn't incur additional financial strain.
| Scenario | Vehicle Value | Loan Balance | Gap Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Loss | $18,000 | $22,000 | $4,000 |

When Gap Insurance is Most Beneficial

Gap insurance is especially advantageous in situations where the vehicle’s value depreciates faster than the loan balance is paid off. This scenario is common with new vehicles and longer loan terms. Here are some circumstances where gap insurance can be particularly beneficial:
- New Vehicle Purchases: As mentioned, new vehicles often depreciate rapidly, making gap insurance a valuable asset for protecting against financial loss.
- Long Loan Terms: Longer loan terms can result in a situation where the loan balance exceeds the vehicle's value. Gap insurance ensures that the policyholder isn't left paying for a vehicle they no longer have.
- Lease Agreements: Gap insurance is commonly offered for leased vehicles, providing protection in cases of early termination or total loss. It ensures that the lessee isn't responsible for the remaining lease payments or excessive fees.
- High-Value Vehicles: Vehicles with a higher initial cost tend to depreciate more slowly. However, gap insurance can still be beneficial, especially if the owner plans to keep the vehicle for an extended period.
Comparative Analysis: Gap Insurance vs. Traditional Auto Insurance
While gap insurance and traditional auto insurance both provide coverage for vehicles, they serve different purposes and offer distinct benefits.
| Comparison | Gap Insurance | Traditional Auto Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Type | Specialized coverage for the difference between vehicle value and loan balance | Comprehensive and collision coverage for vehicle repairs and liability |
| Key Benefits | Protects against financial loss in cases of total loss, theft, or write-off | Covers vehicle repairs, medical expenses, and liability in accidents |
| Coverage Duration | Varies, often for the duration of the loan or lease | Typically renewable annually |
| Cost | Relatively affordable, often included in loan or lease packages | Varies based on factors like driver history, vehicle type, and coverage limits |
Future Implications and Industry Trends
The automotive industry is evolving, and so are the financial products associated with it. Here are some potential future implications and industry trends related to gap insurance:
- Increased Awareness: As consumers become more financially savvy, the demand for gap insurance is likely to rise. Educating potential buyers about the benefits of gap insurance can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
- Technological Integration: The insurance industry is embracing technology, and gap insurance providers may integrate digital tools to streamline claims processes and enhance customer experiences.
- Customized Policies: With a better understanding of consumer needs, insurance providers might offer more tailored gap insurance policies, providing flexible coverage options to suit different financial situations.
- Alternative Vehicles: The rise of electric and hybrid vehicles may impact depreciation rates and, consequently, the need for gap insurance. Insurance providers will need to adapt their policies to accommodate these evolving vehicle types.
Conclusion: Navigating Financial Security with Gap Insurance
Gap insurance is a vital tool for anyone looking to protect their financial interests when purchasing or leasing a vehicle. By understanding the coverage provided, policyholders can make informed decisions and ensure they are adequately protected in the event of a total loss or write-off.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, gap insurance will remain a crucial component of financial planning for vehicle owners. By staying informed about the latest industry trends and policy options, individuals can navigate the complex world of vehicle financing with confidence and peace of mind.
How long does gap insurance coverage typically last?
+The duration of gap insurance coverage can vary. It often lasts for the duration of the loan or lease agreement. Some policies may provide coverage for a specific period, such as the first few years of ownership, while others might offer coverage until the loan is fully repaid.
Is gap insurance always necessary when financing a vehicle?
+While gap insurance is not mandatory, it is highly recommended, especially for new vehicles. The rapid depreciation of a new car’s value can leave you with a significant financial gap in the event of a total loss. Gap insurance provides peace of mind and financial protection in such situations.
Can gap insurance be purchased separately, or is it typically included in loan or lease packages?
+Gap insurance is often included in loan or lease packages, especially for new vehicles. However, it can also be purchased separately from insurance providers or dealerships. It’s essential to review the terms and conditions carefully to ensure the coverage meets your specific needs.