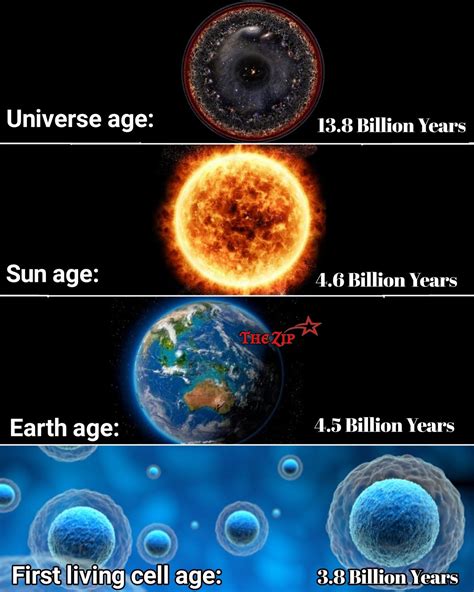
The Sun, the star at the center of our solar system, has been a subject of human fascination for centuries. One of the most fundamental questions about the Sun is its age. Understanding the Sun's age is crucial for understanding the formation and evolution of our solar system. The age of the Sun is estimated to be around 4.6 billion years, based on a variety of methods, including the study of meteorites, the observation of the Sun's energy output, and the analysis of the abundances of certain elements in the Sun's core.
The most widely accepted method for determining the Sun's age is through the study of meteorites. Meteorites are fragments of asteroids that have fallen to Earth, and they provide a snapshot of the early solar system. By dating the meteorites using radiometric methods, scientists can determine the age of the solar system, which is approximately 4.567 billion years. This age is consistent with the age of the oldest rocks on Earth, which are around 4.4 billion years old. The Sun is thought to have formed around 30-50 million years before the formation of the Earth, which would put its age at around 4.6 billion years.
Key Points
- The Sun's age is estimated to be around 4.6 billion years based on various methods.
- The study of meteorites provides a snapshot of the early solar system and is used to determine the Sun's age.
- Radiometric dating of meteorites indicates that the solar system is approximately 4.567 billion years old.
- The Sun is thought to have formed 30-50 million years before the formation of the Earth.
- The age of the Sun is consistent with the age of the oldest rocks on Earth, which are around 4.4 billion years old.
Methods for Determining the Sun’s Age

There are several methods that scientists use to determine the Sun’s age. One of the most important methods is the study of the Sun’s energy output. The Sun’s energy output is determined by its mass, composition, and age. By measuring the Sun’s energy output and comparing it to theoretical models, scientists can estimate the Sun’s age. Another method is the analysis of the abundances of certain elements in the Sun’s core. The abundances of these elements, such as helium and hydrogen, can provide clues about the Sun’s age and evolution.
Seismology and the Sun’s Interior
Seismology, the study of earthquakes and other seismic activity, can also be used to determine the Sun’s age. By studying the Sun’s seismic activity, scientists can gain insights into the Sun’s internal structure and composition. The Sun’s interior is composed of a core, a radiative zone, and a convective zone. The core is the hottest part of the Sun, with temperatures reaching over 15 million degrees Celsius. The radiative zone is the layer outside the core, where energy generated by nuclear reactions in the core is transferred through radiation. The convective zone is the outermost layer, where energy is transferred through convection. By studying the Sun’s seismic activity, scientists can determine the size and composition of these layers, which can provide clues about the Sun’s age.
| Layer | Temperature (°C) | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Core | 15,000,000 | Hydrogen and helium |
| Radiative zone | 7,000,000 | Hydrogen and helium |
| Convective zone | 5,500 | Hydrogen and helium |
Implications of the Sun’s Age

The Sun’s age has significant implications for our understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system. The Sun’s age provides a timescale for the formation of the planets, the evolution of life on Earth, and the potential for life on other planets. The Sun’s age also provides clues about the Sun’s future evolution, including its eventual transition into a red giant and its final stages as a white dwarf. Understanding the Sun’s age is essential for understanding the complex and dynamic history of our solar system.
The Sun's age also has implications for the search for extraterrestrial life. The discovery of exoplanets, planets that orbit stars other than the Sun, has raised hopes that life may exist elsewhere in the universe. The Sun's age provides a benchmark for the potential for life on other planets. By studying the ages of other stars and their planetary systems, scientists can gain insights into the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
What is the estimated age of the Sun?
+The estimated age of the Sun is around 4.6 billion years, based on various methods, including the study of meteorites, the observation of the Sun’s energy output, and the analysis of the Sun’s internal structure and composition.
How do scientists determine the Sun’s age?
+Scientists use a variety of methods to determine the Sun’s age, including the study of meteorites, the observation of the Sun’s energy output, and the analysis of the Sun’s internal structure and composition.
What are the implications of the Sun’s age for our understanding of the solar system?
+The Sun’s age provides a timescale for the formation of the planets, the evolution of life on Earth, and the potential for life on other planets. The Sun’s age also provides clues about the Sun’s future evolution, including its eventual transition into a red giant and its final stages as a white dwarf.