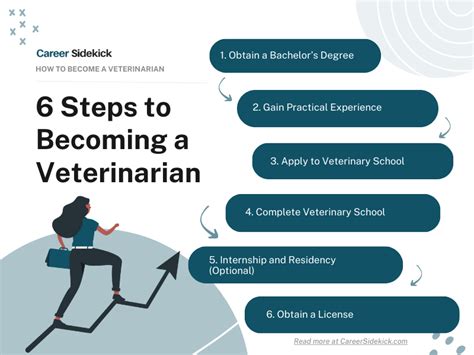
Becoming a veterinarian is a rewarding and challenging career path that requires a strong foundation in science, mathematics, and communication skills. As a veterinarian, you will have the opportunity to work with animals, diagnose and treat medical conditions, and make a positive impact on the lives of pets and their owners. In this article, we will outline the 5 steps to become a veterinarian and provide you with the information you need to get started on this exciting career path.
Key Points
- Earning a bachelor's degree in a science-related field is the first step to becoming a veterinarian
- Taking the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is a requirement for most veterinary programs
- Completing a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) program is essential for becoming a licensed veterinarian
- Obtaining a veterinary license is required to practice as a veterinarian in the United States
- Gaining practical experience through internships or volunteer work is crucial for building a successful veterinary career
Step 1: Earn a Bachelor’s Degree

The first step to becoming a veterinarian is to earn a bachelor’s degree in a science-related field, such as biology, chemistry, or animal science. Most veterinary programs require applicants to have a strong foundation in science and mathematics, so it’s essential to take courses in subjects like physics, biochemistry, and genetics. A bachelor’s degree typically takes four years to complete and provides a solid foundation for future studies.
Course Requirements
Some of the course requirements for a bachelor’s degree in a science-related field include:
- General biology
- General chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Physics
- Mathematics
- Statistics
- Genetics
- Biochemistry
Step 2: Take the Graduate Record Examination (GRE)

Most veterinary programs require applicants to take the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), which is a standardized test that measures verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, and analytical writing skills. The GRE is an essential component of the application process, and scores are used to evaluate an applicant’s potential for success in a veterinary program.
GRE Preparation
To prepare for the GRE, it’s essential to:
- Study for the test using official study materials
- Practice taking sample tests to improve your scores
- Focus on improving your weaknesses in verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, and analytical writing
Step 3: Complete a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) Program
A Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) program is a four-year graduate program that provides students with the knowledge and skills necessary to become a licensed veterinarian. DVM programs are accredited by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and include coursework in subjects like anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and toxicology.
DVM Curriculum
The DVM curriculum includes:
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Pharmacology
- Toxicology
- Pathology
- Clinical sciences
- Practice management
Step 4: Obtain a Veterinary License
To practice as a veterinarian in the United States, you must obtain a veterinary license. The licensing process typically involves passing the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE), which is a comprehensive exam that tests your knowledge and skills in veterinary medicine.
Licensing Requirements
The licensing requirements include:
- Graduating from an accredited DVM program
- Passing the NAVLE
- Meeting the licensing requirements of the state where you wish to practice
Step 5: Gain Practical Experience

Gaining practical experience through internships or volunteer work is essential for building a successful veterinary career. Practical experience provides you with the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills you’ve learned in a real-world setting and helps you develop the skills and confidence you need to succeed as a veterinarian.
Types of Practical Experience
Some types of practical experience include:
- Internships
- Volunteer work
- Research experience
- Clinical experience
What are the requirements for becoming a veterinarian?
+The requirements for becoming a veterinarian include earning a bachelor's degree in a science-related field, taking the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), completing a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) program, obtaining a veterinary license, and gaining practical experience.
How long does it take to become a veterinarian?
+Becoming a veterinarian typically takes eight years of education and training after high school, including four years of undergraduate study and four years of graduate study in a DVM program.
What is the job outlook for veterinarians?
+The job outlook for veterinarians is excellent, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics predicting a 18% increase in employment opportunities for veterinarians from 2020 to 2030.
Becoming a veterinarian requires a strong foundation in science, mathematics, and communication skills, as well as a passion for working with animals. By following these 5 steps, you can set yourself on the path to a rewarding and challenging career as a veterinarian. Remember to stay focused, work hard, and gain as much practical experience as possible to succeed in this exciting field.