Understanding and calculating average velocity is a fundamental concept in physics, crucial for grasping the motion of objects. The average velocity of an object is defined as the total displacement divided by the total time taken. It's a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (amount of movement) and direction. In this article, we will delve into the concept of average velocity, its calculation, and its significance in understanding the dynamics of moving objects.
Key Points
- Average velocity is calculated as the total displacement divided by the total time taken.
- It's a vector quantity, with both magnitude and direction.
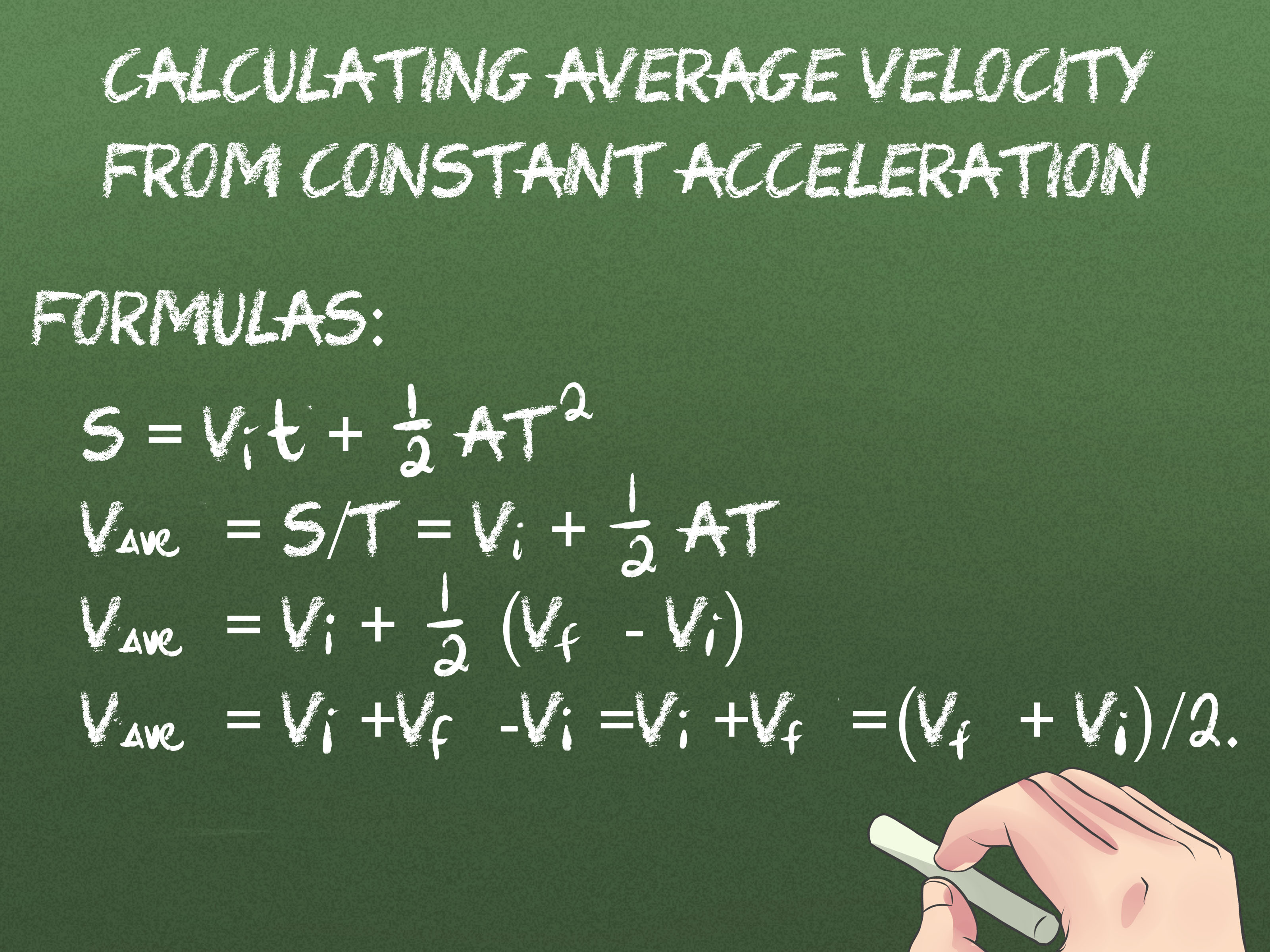
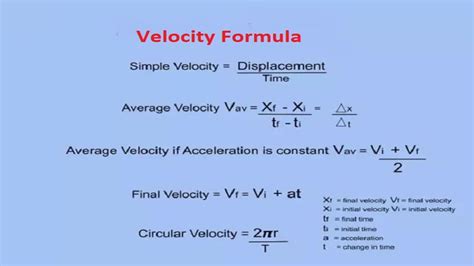
- The formula for average velocity is v_avg = Δx / Δt, where Δx is the displacement and Δt is the time interval.
- Average velocity can be constant or changing, depending on whether the object's motion is uniform or accelerated.
- Understanding average velocity is crucial for analyzing and predicting the motion of objects in physics and engineering.
Understanding Average Velocity

Average velocity is a key concept in understanding how objects move. Unlike speed, which only considers the magnitude of movement (how fast an object is moving), velocity also takes into account the direction of movement. This makes velocity a more precise measure when describing the motion of objects, especially in scenarios where direction changes are significant.
Calculating Average Velocity
The calculation of average velocity is straightforward and involves the formula v_avg = Δx / Δt, where Δx (delta x) represents the total displacement of the object, and Δt (delta t) represents the total time taken for this displacement. Displacement is a vector quantity and is different from distance, which is a scalar. Displacement considers the shortest path between the initial and final positions and is direction-sensitive, whereas distance is the total length of the path traveled.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| v_avg | Average velocity |
| Δx | Displacement (final position - initial position) |
| Δt | Time interval |
For example, if an object moves from point A to point B, covering a displacement of 20 meters in 4 seconds, its average velocity would be v_avg = 20 m / 4 s = 5 m/s. This means the object moved at an average velocity of 5 meters per second towards the direction from A to B.
Significance of Average Velocity
Average velocity is significant because it helps in understanding the overall motion of an object over a period. It’s crucial in physics and engineering for analyzing and predicting the motion of vehicles, projectiles, and other moving objects. Understanding average velocity also helps in comprehending more complex concepts like acceleration and deceleration, which are essential for designing safety features in vehicles, predicting the trajectory of projectiles, and much more.
Practical Applications of Average Velocity

The concept of average velocity has numerous practical applications. In transportation, understanding average velocity is crucial for estimating travel times, designing traffic patterns, and ensuring safety. In sports, athletes and coaches analyze average velocities to improve performance and strategy. Additionally, in environmental studies, average velocity of water or air is essential for understanding currents, wind patterns, and their impacts on ecosystems and climate.
Challenges and Limitations
While calculating average velocity is relatively straightforward, challenges arise when dealing with complex motions or when precise measurements of displacement and time are difficult to obtain. Furthermore, average velocity only provides a snapshot of an object’s motion over a specified interval and does not account for variations in speed or direction within that interval. For more detailed analyses, concepts like instantaneous velocity and acceleration must be considered.
In conclusion, average velocity is a fundamental concept in physics that offers valuable insights into the motion of objects. Its calculation, based on displacement and time, provides a straightforward yet powerful tool for analyzing motion. Understanding average velocity is not only essential for academic purposes but also has practical applications across various fields, making it a crucial piece of knowledge for both physicists and engineers.
What is the difference between average velocity and average speed?
+Average velocity considers both the magnitude and direction of an object’s motion, whereas average speed only considers the magnitude. Thus, average velocity is a vector quantity, and average speed is a scalar quantity.
How do you calculate the average velocity of an object that changes direction?
+To calculate the average velocity of an object that changes direction, you need to determine the total displacement (considering the direction) and the total time taken. The formula remains v_avg = Δx / Δt, but Δx must account for the change in direction.
What are some practical applications of understanding average velocity?
+Understanding average velocity has practical applications in transportation (estimating travel times, designing traffic patterns), sports (analyzing athlete performance), and environmental studies (understanding water and air currents). It’s also crucial in engineering for predicting the motion of objects and designing safety features.