Calculating the change in enthalpy, denoted as ΔH, is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics. It represents the total energy change of a system, including the energy absorbed or released as heat. To calculate ΔH easily, one must first understand the basic principles of thermodynamics and the equation that governs enthalpy changes.
Understanding Enthalpy and Its Equation
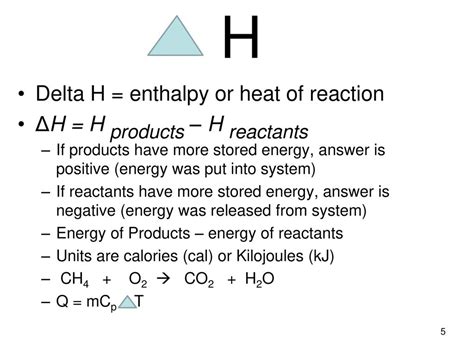
Enthalpy (H) is defined as the sum of the internal energy (U) of a system and the product of the pressure (P) and volume (V) of the system: H = U + PV. The change in enthalpy (ΔH) is given by the equation ΔH = ΔU + Δ(PV). For processes that occur at constant pressure, ΔH = Q, where Q is the heat transferred between the system and its surroundings.
Calculating ΔH for Chemical Reactions
For chemical reactions, ΔH can be calculated using the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) values of the reactants and products. The standard enthalpy of formation is the change in enthalpy when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states. The equation to calculate ΔH for a reaction is ΔH = Σ(ΔHf of products) - Σ(ΔHf of reactants).
| Compound | ΔHf (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| CO2(g) | -393.5 |
| H2O(l) | -285.8 |
| C(s) + O2(g) | 0 (by definition) |
| H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) | 0 (by definition) |

For example, to calculate ΔH for the combustion of carbon to form carbon dioxide: C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g), using the values from the table, ΔH = ΔHf(CO2) - [ΔHf(C) + ΔHf(O2)] = -393.5 kJ/mol - [0 + 0] = -393.5 kJ/mol.
Practical Applications and Considerations

In practical terms, calculating ΔH is crucial for understanding the energy changes in various processes, from industrial manufacturing to biological metabolism. For instance, in the production of ammonia (NH3) through the Haber-Bosch process, knowing the ΔH of the reaction (N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3) helps in designing the process conditions, such as temperature and pressure, to optimize the yield and minimize energy consumption.
Addressing Limitations and Potential Errors
One of the limitations in calculating ΔH is the availability and accuracy of ΔHf values. These values can vary slightly depending on the source and the specific conditions under which they were measured. Moreover, for complex reactions or those involving non-standard states, additional considerations such as the heat capacity of the reactants and products may be necessary to accurately calculate ΔH over a range of temperatures.
Key Points
- ΔH calculation is based on the equation ΔH = Σ(ΔHf of products) - Σ(ΔHf of reactants) for chemical reactions.
- Standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) values are used for reactants and products.
- Stoichiometric coefficients must be considered when calculating ΔH for reactions.
- Availability and accuracy of ΔHf values can affect the calculation.
- Complex reactions may require additional considerations such as heat capacity.
In conclusion, calculating ΔH is a straightforward process once the necessary data, such as ΔHf values, are available. Understanding the principles behind enthalpy changes and being aware of the potential limitations and sources of error are crucial for accurate calculations. By following the guidelines and considering the practical applications, one can easily calculate ΔH for various chemical reactions and processes.
What is the significance of ΔH in chemical reactions?
+ΔH signifies the total energy change of a system during a reaction, indicating whether the reaction is endothermic (ΔH > 0) or exothermic (ΔH < 0), which is crucial for understanding and controlling the reaction conditions.
How do I find ΔHf values for compounds?
+ΔHf values can be found in thermodynamic tables or databases, such as the NIST Chemistry WebBook or the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. These resources provide comprehensive lists of compounds with their corresponding ΔHf values.
Can ΔH be calculated for phase changes?
+Yes, ΔH can be calculated for phase changes, such as melting or boiling, using the equation ΔH = mL, where m is the mass of the substance and L is the latent heat of fusion or vaporization. This calculation provides the energy required for the phase change to occur.