Calculating the Damping Factor (DF) is a crucial step in various engineering and scientific applications, including signal processing, control systems, and mechanical engineering. The Damping Factor is a dimensionless quantity that describes the amount of damping in a system, which is essential for understanding how the system responds to external forces or disturbances. In this article, we will delve into the world of Damping Factor calculation, exploring the theoretical foundations, practical applications, and step-by-step calculation procedures.
Key Points
- The Damping Factor (DF) is a critical parameter in understanding system behavior and response to external forces.
- DF calculation involves understanding the system's damping ratio, natural frequency, and damping coefficient.
- Practical applications of DF calculation include signal processing, control systems, and mechanical engineering.
- A step-by-step approach to calculating DF involves identifying system parameters, selecting the appropriate formula, and performing calculations.
- DF calculation has significant implications for system design, optimization, and performance evaluation.
Understanding the Damping Factor
The Damping Factor is a measure of the amount of damping in a system, which is essential for understanding how the system responds to external forces or disturbances. The DF is typically denoted by the symbol ζ (zeta) and is defined as the ratio of the damping coefficient © to the critical damping coefficient (cc). The critical damping coefficient is the minimum amount of damping required to return the system to its equilibrium state without oscillations. A DF value of 1 indicates critical damping, while values less than 1 indicate underdamping, and values greater than 1 indicate overdamping.
Damping Factor Calculation
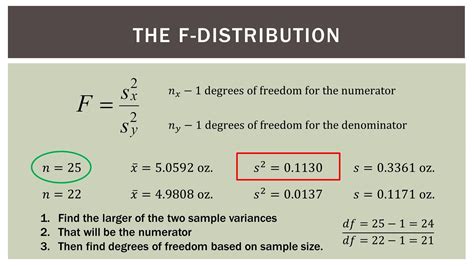
Calculating the Damping Factor involves understanding the system’s damping ratio, natural frequency, and damping coefficient. The damping ratio (ζ) is defined as the ratio of the damping coefficient © to the critical damping coefficient (cc). The natural frequency (ωn) is the frequency at which the system would oscillate if it were undamped. The damping coefficient © is a measure of the amount of damping in the system. The DF can be calculated using the following formula: ζ = c / cc, where cc = 2 * ωn * m, and m is the mass of the system.
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Damping Ratio | ζ | Dimensionless |
| Natural Frequency | ωn | rad/s |
| Damping Coefficient | c | Ns/m |
| Critical Damping Coefficient | cc | Ns/m |
| Mass | m | kg |
Practical Applications of Damping Factor Calculation

The Damping Factor has numerous practical applications in various fields, including signal processing, control systems, and mechanical engineering. In signal processing, the DF is used to design filters and analyze system responses. In control systems, the DF is used to design controllers and optimize system performance. In mechanical engineering, the DF is used to design and optimize mechanical systems, such as suspension systems and vibration isolation systems.
Step-by-Step Calculation Procedure
To calculate the Damping Factor, follow these steps:
- Identify the system parameters, including the damping ratio, natural frequency, and damping coefficient.
- Select the appropriate formula for calculating the Damping Factor, depending on the system parameters available.
- Perform the calculations, ensuring that the units are consistent and the parameters are accurately measured or estimated.
- Verify the results, ensuring that the calculated DF value is reasonable and consistent with the system’s behavior.
What is the significance of the Damping Factor in system design?
+The Damping Factor is a critical parameter in system design, as it determines the system's response to external forces or disturbances. A well-designed system with an optimal Damping Factor can ensure stable and efficient operation, while a poorly designed system can result in oscillations, instability, or even failure.
How does the Damping Factor affect system performance?
+The Damping Factor has a significant impact on system performance, as it determines the system's ability to respond to external forces or disturbances. A system with a high Damping Factor can result in overdamping, leading to slow response times and reduced system performance. On the other hand, a system with a low Damping Factor can result in underdamping, leading to oscillations and instability.
What are the common challenges in calculating the Damping Factor?
+The common challenges in calculating the Damping Factor include accurately measuring or estimating system parameters, selecting the appropriate formula, and ensuring consistent units. Additionally, small errors in parameter estimation can result in significant errors in DF calculation, which can have significant implications for system design and performance evaluation.
In conclusion, calculating the Damping Factor is a crucial step in understanding system behavior and response to external forces or disturbances. By following a step-by-step approach and ensuring accurate parameter estimation, engineers and scientists can design and optimize systems with optimal Damping Factor values, resulting in stable and efficient operation. The Damping Factor has significant implications for system design, optimization, and performance evaluation, and its calculation requires a deep understanding of system parameters and behavior.