Opportunity cost is a fundamental concept in economics that refers to the value of the next best alternative that is given up when a choice is made. It is a crucial aspect of decision-making in various fields, including business, finance, and personal finance. Calculating opportunity cost can be a complex task, but it can be simplified by understanding the basic principles and using the right tools. In this article, we will explore the concept of opportunity cost, its importance, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to calculate it easily.
Key Points
- Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative given up when a choice is made.
- It is a crucial aspect of decision-making in various fields, including business, finance, and personal finance.
- Calculating opportunity cost involves identifying the alternative options, estimating their values, and comparing them to the chosen option.
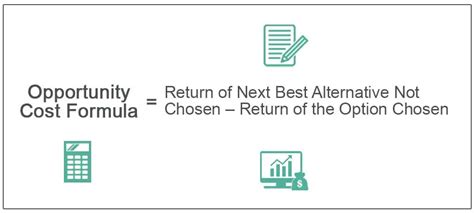
- The opportunity cost formula is: Opportunity Cost = Value of Next Best Alternative - Value of Chosen Option.
- Understanding opportunity cost can help individuals and organizations make informed decisions and maximize their returns.
Understanding Opportunity Cost

Opportunity cost is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world implications. For instance, when a company decides to invest in a new project, it must consider the opportunity cost of not investing in other projects or assets. Similarly, when an individual chooses to pursue a career in one field, they must consider the opportunity cost of not pursuing a career in another field. Opportunity cost is essential because it helps individuals and organizations evaluate the trade-offs involved in making decisions.
Types of Opportunity Cost
There are two main types of opportunity cost: explicit and implicit. Explicit opportunity cost refers to the direct cost of choosing one option over another. For example, if a company chooses to invest in a new project, the explicit opportunity cost is the cost of the project itself. Implicit opportunity cost, on the other hand, refers to the indirect cost of choosing one option over another. For example, if a company chooses to invest in a new project, the implicit opportunity cost is the potential revenue that could have been earned if the company had invested in a different project.
| Type of Opportunity Cost | Description |
|---|---|
| Explicit Opportunity Cost | Direct cost of choosing one option over another. |
| Implicit Opportunity Cost | Indirect cost of choosing one option over another. |
Calculating Opportunity Cost
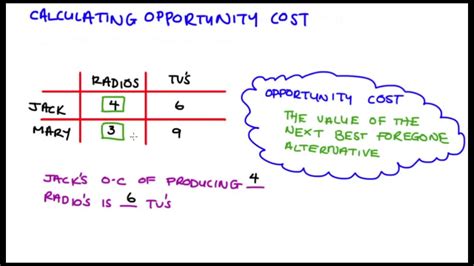
Calculating opportunity cost involves identifying the alternative options, estimating their values, and comparing them to the chosen option. The opportunity cost formula is: Opportunity Cost = Value of Next Best Alternative - Value of Chosen Option. For example, suppose a company is considering two investment options: Option A and Option B. Option A has a potential return of 100,000, while Option B has a potential return of 120,000. If the company chooses Option A, the opportunity cost is $20,000, which is the difference between the potential return of Option B and Option A.
Opportunity Cost Formula
The opportunity cost formula is a simple and effective way to calculate the opportunity cost of a decision. The formula is: Opportunity Cost = Value of Next Best Alternative - Value of Chosen Option. This formula can be applied to various scenarios, including business, finance, and personal finance. For example, if an individual is considering two career options: Career A and Career B. Career A has a potential salary of 50,000, while Career B has a potential salary of 60,000. If the individual chooses Career A, the opportunity cost is $10,000, which is the difference between the potential salary of Career B and Career A.
To illustrate the opportunity cost formula, let's consider a real-world example. Suppose a company is considering two investment options: a bond with a 5% return and a stock with a 10% return. If the company invests in the bond, the opportunity cost is the potential return of the stock, which is 5% (10% - 5%). This means that the company is giving up a potential return of 5% by choosing the bond over the stock.
Importance of Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is a crucial aspect of decision-making because it helps individuals and organizations evaluate the trade-offs involved in making decisions. By considering the opportunity cost of a decision, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions and maximize their returns. Opportunity cost is also essential in evaluating the effectiveness of a decision. For example, if a company invests in a new project, the opportunity cost of that decision is the potential return of the next best alternative. If the actual return of the project is lower than the opportunity cost, then the decision to invest in the project may not have been the best option.
Real-World Applications
Opportunity cost has numerous real-world applications, including business, finance, and personal finance. In business, opportunity cost is used to evaluate investment decisions, such as whether to invest in a new project or not. In finance, opportunity cost is used to evaluate investment options, such as whether to invest in a bond or a stock. In personal finance, opportunity cost is used to evaluate career options, such as whether to pursue a career in one field or another.
What is opportunity cost?
+Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative given up when a choice is made.
How is opportunity cost calculated?
+Opportunity cost is calculated by identifying the alternative options, estimating their values, and comparing them to the chosen option. The opportunity cost formula is: Opportunity Cost = Value of Next Best Alternative - Value of Chosen Option.
Why is opportunity cost important?
+Opportunity cost is important because it helps individuals and organizations evaluate the trade-offs involved in making decisions and make informed decisions to maximize their returns.
In conclusion, calculating opportunity cost is a crucial aspect of decision-making in various fields, including business, finance, and personal finance. By understanding the concept of opportunity cost and using the opportunity cost formula, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions and maximize their returns. Opportunity cost is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world implications, and its importance cannot be overstated. As individuals and organizations continue to make decisions, it is essential to consider the opportunity cost of those decisions to ensure that they are making the best possible choices.


