Understanding population density is crucial for urban planning, resource allocation, and demographic analysis. It is defined as the number of people living per unit area, typically expressed as people per square kilometer or square mile. Calculating population density may seem like a complex task, but it can be simplified into a straightforward process. In this article, we will explore the steps and considerations involved in calculating population density, along with real-world examples and implications.
Key Points
- Population density is calculated by dividing the total population by the total area.
- Understanding the formula and units involved is crucial for accurate calculations.
- Real-world examples illustrate how population density varies significantly across different regions and cities.
- Implications of population density include effects on infrastructure, services, and environmental conditions.
- Technological tools and databases are available to facilitate population density calculations and analysis.
Understanding the Basics of Population Density Calculation
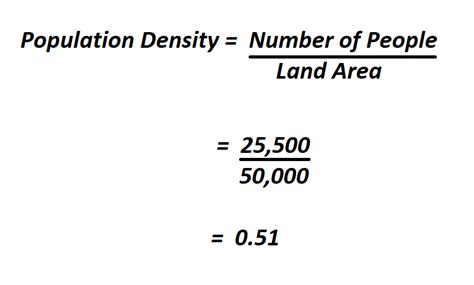
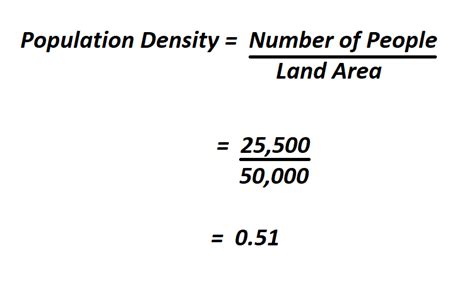
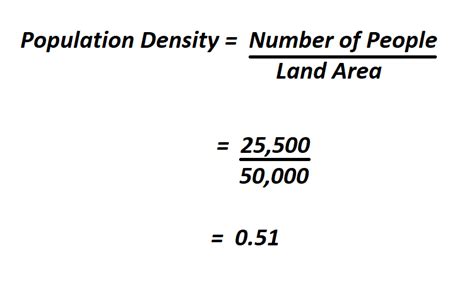
The formula for calculating population density is straightforward: Population Density = Total Population / Total Area. The challenge often lies in obtaining accurate and up-to-date figures for both the population and the area. For instance, the total population can be sourced from recent census data, while the total area might require geographical information system (GIS) data or official land use records.
Units of Measurement
The units used to express population density can vary, with people per square kilometer (km²) and people per square mile (mi²) being the most common. The choice of unit depends on the context and the audience, with international comparisons often favoring people per km² due to its widespread use. For example, if a city has a population of 500,000 and covers an area of 200 km², its population density would be 2,500 people per km².
| City | Population | Area (km²) | Population Density (people/km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York City | 8,420,000 | 784 | 10,733 |
| London | 8,905,000 | 1,579 | 5,639 |
| Paris | 2,165,000 | 1,054 | 2,056 |
Applications and Implications of Population Density

Population density has far-reaching implications for urban planning, public health, and environmental sustainability. High population densities can strain local resources, such as water, energy, and transportation, while also increasing the risk of disease transmission and decreasing air quality. On the other hand, densely populated areas can also foster economic growth, cultural diversity, and innovation, making them attractive for businesses, artists, and young professionals.
Technological Tools for Analysis
Advancements in GIS, remote sensing, and big data analytics have made it easier to calculate and analyze population density with high accuracy. These tools enable the integration of demographic data with spatial information, allowing for the creation of detailed maps and models that can guide urban planning decisions. Furthermore, online databases and platforms provide access to up-to-date population and area data, facilitating research and comparative studies across different regions.
The calculation of population density is a fundamental aspect of understanding the dynamics of human settlement and its impact on the environment. By applying the formula and considering the nuances of population and area measurements, individuals can gain insights into the demographic characteristics of different regions. This knowledge is essential for policymakers, urban planners, and researchers aiming to create more sustainable, equitable, and thriving communities.
What are the main factors that influence population density?
+Factors influencing population density include geographical features, climate, economic opportunities, and access to services and infrastructure. These factors can either attract or deter population growth in specific areas.
How does population density affect the environment?
+High population density can lead to increased pollution, resource consumption, and habitat destruction. However, dense populations can also promote more efficient use of resources, reduce the need for personal vehicles, and encourage sustainable practices.
What role does technology play in calculating and analyzing population density?
+Technology, including GIS, remote sensing, and big data analytics, enables the precise calculation of population density and its spatial distribution. It also facilitates the analysis of demographic trends, prediction of future population growth, and optimization of urban planning strategies.