Calculating resistance is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering and physics, crucial for understanding and designing electronic circuits. Resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), is the opposition to the flow of current in an electrical circuit. It depends on the material, length, and cross-sectional area of the conductor. To calculate resistance easily, one must understand the basic principles and formulas involved.
Understanding the Basics of Resistance
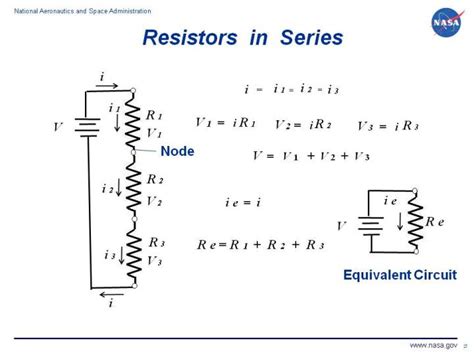
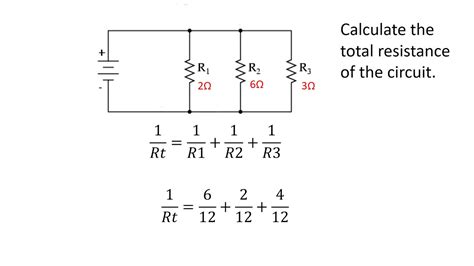
Resistance is a critical property of any conductor, including wires, resistors, and other components in an electrical circuit. The resistance of a conductor is determined by its resistivity (ρ), length (L), and cross-sectional area (A). The formula to calculate resistance ® is given by R = ρ(L/A). This formula shows that resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area.
Resistivity of Common Materials
Resistivity is a material property that varies significantly among different materials. Conductors like copper and aluminum have low resistivity, making them ideal for carrying electrical currents over long distances. On the other hand, insulators like glass and rubber have high resistivity, making them useful for preventing the flow of electrical current. The resistivity of a material is usually given in ohm-meters (Ωm) and is a key factor in calculating the resistance of a conductor.
| Material | Resistivity (Ωm) |
|---|---|
| Copper | 1.68 × 10^-8 |
| Aluminum | 2.65 × 10^-8 |
| Silver | 1.59 × 10^-8 |
| Gold | 2.44 × 10^-8 |
Calculating Resistance with Formulas
The formula R = ρ(L/A) is the most straightforward way to calculate resistance. However, in practice, the resistance of a component like a resistor is usually given directly, and its value is chosen based on the requirements of the circuit. For example, in a simple circuit with a voltage source and a resistor, the current (I) flowing through the resistor can be calculated using Ohm’s Law, V = IR, where V is the voltage across the resistor, and R is its resistance.
Ohm’s Law and Power Calculation
Ohm’s Law (V = IR) and the power formula (P = VI) are essential tools for calculating resistance and understanding the behavior of electrical circuits. By rearranging Ohm’s Law, one can solve for resistance as R = V/I. This is particularly useful when the voltage and current are known, and the resistance needs to be calculated.
Key Points
- Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current in an electrical circuit.
- The formula to calculate resistance is R = ρ(L/A), where ρ is the resistivity, L is the length, and A is the cross-sectional area.
- Ohm's Law, V = IR, can be used to calculate resistance if voltage and current are known.
- Understanding the resistivity of materials is crucial for designing efficient circuits.
- Calculating resistance is essential for determining the behavior and efficiency of electrical circuits.
Practical Applications and Considerations
In practical applications, calculating resistance is not just about using formulas; it also involves considering the physical properties of materials and the conditions under which they operate. For instance, the resistance of a conductor increases with temperature, a phenomenon known as thermal resistance. This effect must be considered in the design of circuits that operate over a range of temperatures.
Temperature Effects on Resistance
The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) is a measure of how much the resistance of a material changes with temperature. Materials with a positive TCR increase in resistance as temperature increases, while those with a negative TCR decrease. This property is critical in the design of temperature-sensitive circuits and in ensuring the reliability of electrical systems under varying environmental conditions.
How does the length of a conductor affect its resistance?
+The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length. This means that as the length of the conductor increases, its resistance also increases, assuming all other factors remain constant.
What is the significance of resistivity in calculating resistance?
+Resistivity is a material property that determines how much a material resists the flow of electrical current. It is a critical factor in the calculation of resistance, as it directly influences the resistance of a conductor for given dimensions.
How does temperature affect the resistance of a conductor?
+For most conductors, an increase in temperature results in an increase in resistance. This is due to the increased vibration of atoms in the material, which impedes the flow of electrons. The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) quantifies this effect for different materials.
Calculating resistance is a fundamental skill in electrical engineering and physics, essential for designing, analyzing, and troubleshooting electrical circuits. By understanding the principles behind resistance, including the role of resistivity, length, cross-sectional area, and temperature, engineers and technicians can create more efficient, reliable, and safe electrical systems.