When considering the fundamental nature of a concept, it's essential to delve into its underlying structure and purpose. The question of whether something is a function hinges on its ability to map inputs to outputs in a consistent and well-defined manner. In the realm of mathematics, a function is defined as a relation between a set of inputs, known as the domain, and a set of possible outputs, known as the range. This relationship is characterized by the property that each input is associated with exactly one output.
Defining Characteristics of a Function
To determine if a given concept or relation constitutes a function, several key criteria must be examined. Firstly, the relation must be defined for every element in its domain. Secondly, for each input, there must be exactly one output. This means that if an input is repeated, the output must also be the same. This characteristic is often referred to as the “vertical line test” in graphical terms, where no vertical line intersects the graph of the relation in more than one place.
Domain and Range Considerations
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values for which the function is defined. Similarly, the range is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce. Understanding the domain and range is crucial in determining the behavior and applicability of a function. For instance, the square root function has a domain of non-negative real numbers because the square of any real number is non-negative, and its range consists of all non-negative real numbers.
| Function Type | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Function (y = mx + b) | All Real Numbers | All Real Numbers |
| Quadratic Function (y = ax^2 + bx + c) | All Real Numbers | Depends on the coefficient 'a' |
| Exponential Function (y = a^x) | All Real Numbers | All Positive Real Numbers |

Functional Relationships in Real-World Applications
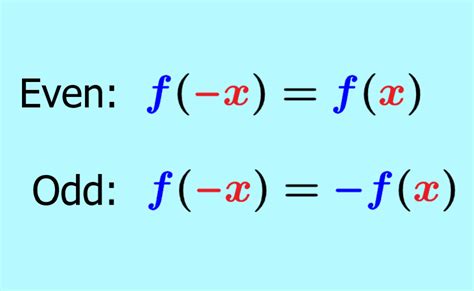
Beyond the abstract realm of mathematics, functions play a vital role in describing and analyzing real-world phenomena. In physics, for example, the position of an object as a function of time can be used to describe its motion. Similarly, in economics, the demand for a product can be modeled as a function of its price. These functional relationships are indispensable for making predictions, optimizing processes, and understanding complex systems.
Notable Examples and Case Studies
A classic example of a functional relationship is the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, where pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) of a gas are related. This equation serves as a function that maps the values of n (number of moles), R (gas constant), and T to the product PV. Such functional descriptions are pivotal in chemistry and physics for predicting the behavior of gases under various conditions.
Key Points
- A function is a relation between a set of inputs (domain) and a set of possible outputs (range) where each input is associated with exactly one output.
- The domain and range are critical in defining a function and determining its applicability.
- Functions are used extensively in mathematics, science, and engineering to model real-world phenomena and make predictions.
- Understanding whether a relation constitutes a function involves examining its definition, domain, and the uniqueness of its outputs for each input.
- Real-world applications of functions include describing the motion of objects, modeling economic systems, and predicting the behavior of physical and chemical systems.
Functional Analysis and Its Implications
Delving deeper into the nature of functions and their applications, it becomes clear that functional analysis is a powerful tool for understanding complex systems. By examining how inputs are mapped to outputs, scientists and engineers can identify patterns, optimize processes, and predict future behaviors. This analytical approach underpins much of modern science and technology, from designing electronic circuits to modeling climate change.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
As computational power and data analysis techniques continue to evolve, the study and application of functions are likely to expand into new areas. For instance, machine learning algorithms often rely on complex functional relationships to learn from data and make predictions. The integration of functional analysis with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) promises to reveal new insights and applications across various disciplines.
What distinguishes a function from a general relation?
+A function is distinguished from a general relation by the requirement that each input in its domain must correspond to exactly one output. This uniqueness of output for each input is what defines a relation as a function.
How are functions used in real-world applications?
+Functions are used in a wide array of real-world applications, including physics to describe the motion of objects, in economics to model supply and demand, and in chemistry to predict the behavior of gases and chemical reactions. They provide a mathematical framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of complex systems.
What role do functions play in modern technology and science?
+Functions play a pivotal role in modern technology and science, serving as the foundation for mathematical models that describe and predict the behavior of physical, biological, and economic systems. They are essential in fields such as engineering, computer science, and data analysis, where they are used to optimize processes, make predictions, and understand complex phenomena.
In conclusion, the concept of a function is fundamental to understanding and analyzing the world around us. From the abstract mathematical definitions to the practical applications in science and technology, functions provide a powerful framework for describing relationships and making predictions. As our understanding of the world and its complexities evolves, so too will the role and application of functions in helping us navigate and improve our understanding of reality.