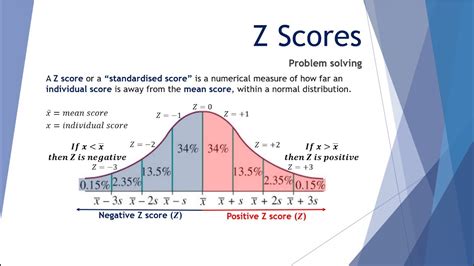
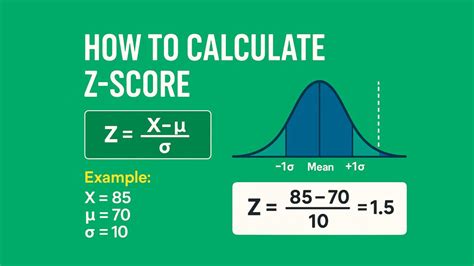
To calculate the Z score easily, it's essential to understand what a Z score is and its significance in statistics. A Z score, also known as a standard score, indicates how many standard deviations an element is from the mean. The formula to calculate the Z score is straightforward: Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value of the element, μ is the mean of the dataset, and σ is the standard deviation of the dataset.
Understanding the Z Score Formula
The Z score formula is fundamental in understanding how data points relate to the average of the dataset. By calculating the Z score, you can determine the relative position of a data point within the dataset. A Z score of 0 means the data point is equal to the mean, a positive Z score indicates the data point is above the mean, and a negative Z score indicates the data point is below the mean.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Z Score
Calculating the Z score involves a few simple steps:
- Find the mean (μ) of the dataset: The mean is the average of all the data points. To find the mean, add up all the data points and divide by the number of data points.
- Find the standard deviation (σ) of the dataset: The standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. It represents how spread out the data points are from the mean.
- Choose a data point (X): Select the data point for which you want to calculate the Z score.
- Apply the Z score formula: Plug the values into the formula Z = (X - μ) / σ to calculate the Z score.
| Dataset | Mean (μ) | Standard Deviation (σ) |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 3 | 1.414 |
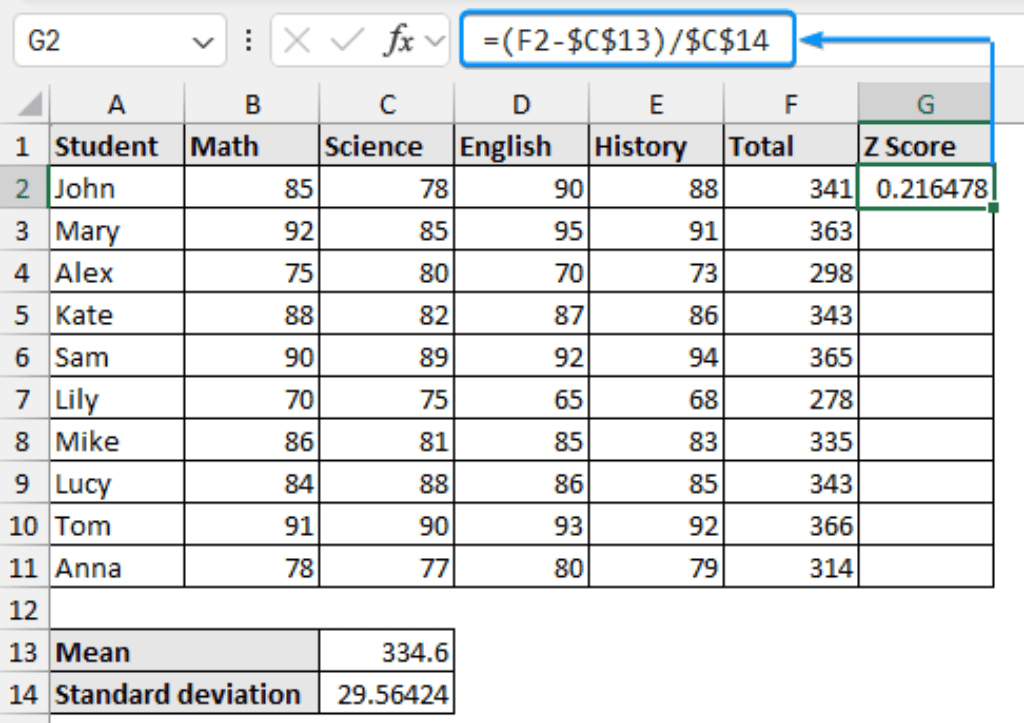
For example, if you have a dataset of exam scores with a mean of 80 and a standard deviation of 10, and you want to find the Z score of a student who scored 90, you would use the Z score formula as follows: Z = (90 - 80) / 10 = 1. This means the student's score is 1 standard deviation above the mean.
Interpreting Z Scores
Interpreting Z scores is as important as calculating them. A Z score tells you how many standard deviations away from the mean your data point is. Generally, a Z score:
- Near 0: Indicates the data point is close to the mean.
- Between -1 and 1: Suggests the data point is within 1 standard deviation of the mean, which typically includes about 68% of the data points in a normal distribution.
- Between -2 and -1 or 1 and 2: Indicates the data point is within 2 standard deviations of the mean, which usually encompasses about 95% of the data points.
- Greater than 2 or less than -2: Suggests the data point is more than 2 standard deviations away from the mean, placing it in the outer ranges of the distribution, which may indicate an outlier.
Key Points
- The Z score formula is Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value of the data point, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.
- Calculating the Z score helps in understanding how many standard deviations away from the mean a data point is.
- Interpreting Z scores is crucial for understanding data distribution and identifying outliers.
- Z scores are used in various statistical analyses, including hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
- The interpretation of Z scores depends on the context of the data and the specific analysis being performed.
Common Applications of Z Scores
Z scores have numerous applications in statistics and data analysis, including:
- Hypothesis Testing: Z scores are used to test hypotheses about the population mean.
- Confidence Intervals: Z scores help in constructing confidence intervals for the population mean.
- Comparing Data Points: Z scores enable the comparison of data points from different datasets by standardizing them.
- Identifying Outliers: Data points with Z scores greater than 2 or less than -2 are often considered outliers.
In conclusion, calculating the Z score easily requires a good understanding of the formula and the context in which it is applied. By following the steps outlined and understanding the interpretation of Z scores, you can effectively use this statistical tool in your data analysis.
What does a positive Z score indicate?
+A positive Z score indicates that the data point is above the mean of the dataset.
How do you calculate the standard deviation?
+The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean.
What is the significance of a Z score of 0?
+A Z score of 0 indicates that the data point is equal to the mean of the dataset.
Meta Description: Learn how to calculate Z scores easily with our step-by-step guide, understand the Z score formula, and interpret Z scores for effective data analysis.