The concept of deviation is a crucial aspect of statistical analysis, allowing researchers and analysts to understand the dispersion of data points within a dataset. Finding deviation is essential in various fields, including finance, engineering, and social sciences, as it helps in making informed decisions and predicting future trends. In this article, we will explore five ways to find deviation, discussing the methodologies, applications, and interpretations of each method.
Key Points
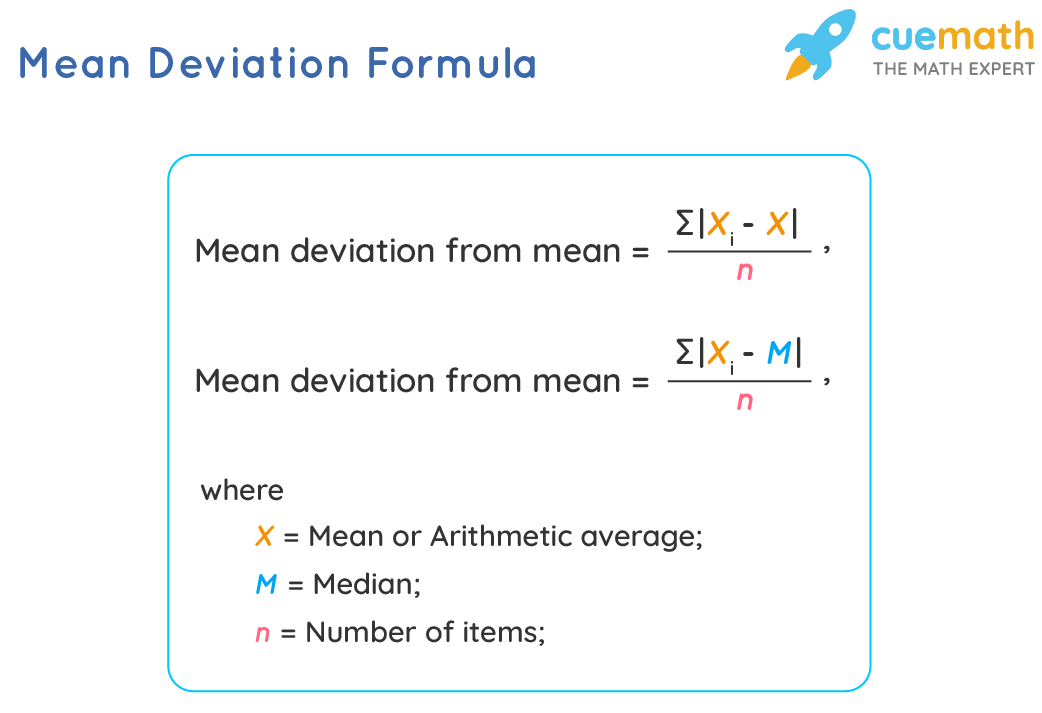
- Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) measures the average distance between data points and the mean.
- Standard Deviation (SD) is a widely used measure of dispersion that calculates the square root of the variance.
- Variance measures the average of the squared differences from the mean, providing a basis for standard deviation calculations.
- Range is the simplest measure of deviation, calculated as the difference between the highest and lowest data points.
- Interquartile Range (IQR) measures the difference between the 75th and 25th percentiles, providing a robust measure of dispersion.
Understanding Deviation and Its Importance
Deviation, in statistical terms, refers to the degree to which individual data points differ from the mean value of the dataset. Understanding deviation is crucial because it helps in assessing the risk, reliability, and consistency of data. A low deviation indicates that the data points are closely packed around the mean, suggesting consistency and predictability. On the other hand, a high deviation suggests that the data points are spread out, indicating variability and potential risk.
Method 1: Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD)
The Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) is a measure of dispersion that calculates the average distance between each data point and the mean. It is calculated by summing the absolute differences between each data point and the mean, then dividing by the number of data points. MAD is a useful measure because it is less sensitive to extreme values compared to other measures like standard deviation.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| MAD = Σ|xi - μ| / n | Where xi is each data point, μ is the mean, and n is the number of data points. |
Method 2: Standard Deviation (SD)
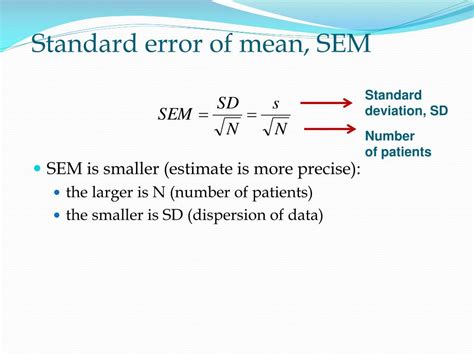
Standard Deviation (SD) is one of the most commonly used measures of dispersion. It is calculated as the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean. SD provides a comprehensive view of the data’s spread, with higher values indicating greater dispersion.
Formula: SD = √(Σ(xi - μ)^2 / (n - 1))
Method 3: Variance
Variance is a measure of dispersion that calculates the average of the squared differences from the mean. It is a fundamental concept in statistics, as it provides the basis for calculating standard deviation. Variance is sensitive to extreme values, making it less robust than other measures for datasets with outliers.
Formula: Variance = Σ(xi - μ)^2 / (n - 1)
Method 4: Range
The Range is the simplest measure of dispersion, calculated as the difference between the highest and lowest data points. While it provides a quick overview of the data’s spread, it is highly sensitive to outliers and does not account for the distribution of data points between the minimum and maximum values.
Formula: Range = Maximum value - Minimum value
Method 5: Interquartile Range (IQR)
The Interquartile Range (IQR) is a robust measure of dispersion that calculates the difference between the 75th percentile (Q3) and the 25th percentile (Q1). IQR is less sensitive to outliers compared to other measures and provides a good indication of the data’s central tendency and variability.
Formula: IQR = Q3 - Q1
Applications and Interpretations
Understanding deviation is crucial in various applications, including financial analysis, quality control, and predictive modeling. In finance, deviation helps in assessing the risk of investments, while in quality control, it aids in monitoring the consistency of manufacturing processes. In predictive modeling, deviation is essential for understanding the variability of predictions and improving model accuracy.
Real-World Example
A company producing light bulbs wants to understand the deviation in the lifespan of its products. By calculating the standard deviation of the lifespan, the company can determine the average variability of the bulbs’ lifespan, helping in quality control and warranty predictions.
What is the primary difference between standard deviation and variance?
+Standard deviation is the square root of variance. Variance measures the average of the squared differences from the mean, while standard deviation provides the square root of this average, offering a more interpretable measure of dispersion.
When should I use the Interquartile Range (IQR) instead of standard deviation?
+IQR is preferable when dealing with datasets that contain outliers or when the data distribution is skewed. IQR provides a more robust measure of dispersion that is less affected by extreme values.
How does the Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) compare to standard deviation in terms of sensitivity to outliers?
+MAD is less sensitive to outliers compared to standard deviation. This is because MAD calculates the average of absolute differences, which reduces the impact of extreme values. Standard deviation, however, squares these differences, amplifying the effect of outliers.
In conclusion, understanding deviation is fundamental in statistical analysis, offering insights into the dispersion and variability of data. By choosing the appropriate method for finding deviation, analysts can better understand their data, make informed decisions, and predict future trends with greater accuracy.



