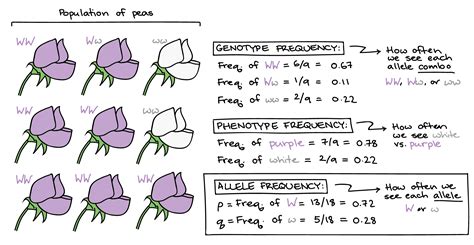
The study of allele frequency is a crucial aspect of genetics, as it helps us understand the distribution of different genetic variants within a population. Allele frequency refers to the proportion of a specific allele or genetic variant within a given population. Calculating allele frequency is essential in various fields, including genetics, epidemiology, and evolutionary biology. In this article, we will explore five ways to find allele frequency, highlighting the methods, tools, and techniques used in this process.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of allele frequency and its importance in genetics
- Five methods for calculating allele frequency: Hardy-Weinberg principle, gene sequencing, genotyping arrays, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), and bioinformatics tools
- Application of allele frequency in fields such as genetic epidemiology and evolutionary biology
- Challenges and limitations in estimating allele frequency, including sampling bias and genetic drift
- Importance of accurate allele frequency estimation in disease association studies and personalized medicine
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
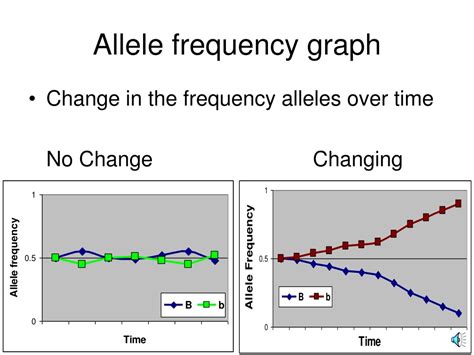
The Hardy-Weinberg principle is a fundamental concept in population genetics that provides a mathematical framework for calculating allele frequency. This principle assumes that a population is in equilibrium, meaning that the allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from one generation to the next. The Hardy-Weinberg equation is given by p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1, where p and q are the frequencies of the two alleles, and p^2, 2pq, and q^2 represent the frequencies of the three genotypes. By using this equation, researchers can estimate allele frequency and genotype frequency in a population.
Gene Sequencing and Allele Frequency
Gene sequencing is a powerful tool for determining allele frequency. With the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, it is now possible to sequence entire genomes and identify genetic variants at a high resolution. By analyzing sequencing data, researchers can estimate allele frequency by counting the number of reads that correspond to each allele. This approach has been widely used in various studies, including genetic epidemiology and evolutionary biology. For example, a study published in the journal Nature Genetics used NGS to estimate allele frequency in a population of individuals with a rare genetic disorder.
| Method | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hardy-Weinberg principle | Mathematical framework for calculating allele frequency | Simple, widely used, and well-established |
| Gene sequencing | Determining allele frequency through sequencing data | High resolution, accurate, and comprehensive |
| Genotyping arrays | Measuring allele frequency using microarrays | High-throughput, cost-effective, and widely available |
| PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) | Amplifying specific DNA sequences to estimate allele frequency | Sensitive, specific, and widely used |
| Bioinformatics tools | Analyzing sequencing data to estimate allele frequency | Fast, accurate, and comprehensive |

Genotyping Arrays and Allele Frequency
Genotyping arrays are a type of microarray technology that allows researchers to measure allele frequency in a high-throughput manner. These arrays typically consist of thousands of probes that are designed to detect specific genetic variants. By analyzing the signal intensity of each probe, researchers can estimate allele frequency and genotype frequency in a population. Genotyping arrays have been widely used in genetic epidemiology and evolutionary biology, and have been instrumental in identifying genetic variants associated with complex diseases.
PCR and Allele Frequency
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a widely used technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences. By using PCR, researchers can amplify a specific genetic variant and estimate its frequency in a population. This approach has been widely used in various studies, including genetic epidemiology and evolutionary biology. For example, a study published in the journal PNAS used PCR to estimate allele frequency in a population of individuals with a rare genetic disorder.
Bioinformatics Tools and Allele Frequency
Bioinformatics tools play a crucial role in estimating allele frequency from sequencing data. These tools use sophisticated algorithms to analyze sequencing data and estimate allele frequency. Some popular bioinformatics tools for estimating allele frequency include GATK (Genome Analysis Toolkit), SAMtools, and VCFtools. These tools have been widely used in various studies, including genetic epidemiology and evolutionary biology, and have been instrumental in identifying genetic variants associated with complex diseases.
What is allele frequency and why is it important?
+Allele frequency refers to the proportion of a specific allele or genetic variant within a given population. It is essential in understanding the distribution of genetic variants and their association with complex diseases.
How is allele frequency calculated using the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
+The Hardy-Weinberg principle provides a mathematical framework for calculating allele frequency. The equation p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 is used, where p and q are the frequencies of the two alleles.
What are the advantages and limitations of using gene sequencing to estimate allele frequency?
+Gene sequencing offers high resolution and accuracy in estimating allele frequency. However, it can be expensive and time-consuming, and may require sophisticated bioinformatics tools to analyze the data.
How do genotyping arrays and PCR differ in estimating allele frequency?
+Genotyping arrays measure allele frequency in a high-throughput manner, while PCR amplifies specific DNA sequences to estimate allele frequency. Both methods have their advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the research question and available resources.
What are the applications of allele frequency estimation in genetic epidemiology and evolutionary biology?
+Allele frequency estimation has been instrumental in identifying genetic variants associated with complex diseases and understanding the evolutionary history of populations. It has also been used to develop personalized medicine approaches and to understand the genetic basis of disease susceptibility.
In conclusion, estimating allele frequency is a crucial aspect of genetics, and various methods are available to achieve this goal. The choice of method depends on the research question, study design, and available resources. By understanding the advantages and limitations of each method, researchers can select the most suitable approach for their study and contribute to our understanding of the genetic basis of complex diseases.