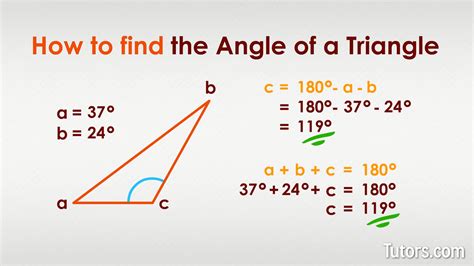
The angle of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry, and finding it is a crucial skill for various mathematical and real-world applications. In this article, we will delve into the world of triangle angles, exploring the different methods and formulas used to calculate them. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or a professional, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a deep understanding of how to find the angle of a triangle.
Key Points
- The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- The Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines are two fundamental formulas used to find the angle of a triangle.
- Trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, play a crucial role in calculating triangle angles.
- Right triangles, with one 90-degree angle, have unique properties that simplify angle calculations.
- Real-world applications, such as architecture, engineering, and physics, rely heavily on triangle angle calculations.
Understanding Triangle Angles
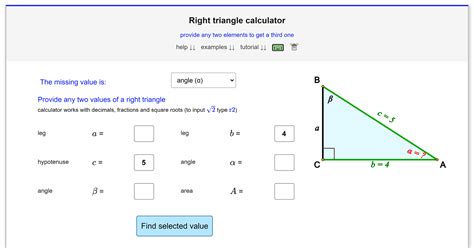
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. The angles of a triangle are formed by the intersection of two sides, and they can be classified into different types, such as acute, right, obtuse, and straight. The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees, which is a fundamental property known as the Angle Sum Property.
Types of Triangle Angles
There are several types of triangle angles, including:
- Acute angles: less than 90 degrees
- Right angles: exactly 90 degrees
- Obtuse angles: greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees
- Straight angles: exactly 180 degrees
Methods for Finding Triangle Angles
There are several methods for finding the angle of a triangle, including:
The Law of Sines
The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for all three sides and angles of a triangle. This law can be expressed mathematically as:
a / sin(A) = b / sin(B) = c / sin©
where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides, and A, B, and C are the angles opposite those sides.
The Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines states that the square of the length of a side is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides, minus twice the product of those lengths and the cosine of the angle between them. This law can be expressed mathematically as:
c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab * cos©
where c is the length of the side opposite angle C, and a and b are the lengths of the other two sides.
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, play a crucial role in calculating triangle angles. These functions relate the angles of a triangle to the ratios of the lengths of its sides. For example, the sine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle).
Right Triangles
Right triangles, with one 90-degree angle, have unique properties that simplify angle calculations. The Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides, is a fundamental concept in right triangle geometry.
| Trigonometric Function | Definition |
|---|---|
| Sine (sin) | Opposite side / Hypotenuse |
| Cosine (cos) | Adjacent side / Hypotenuse |
| Tangent (tan) | Opposite side / Adjacent side |

Real-World Applications
Triangle angle calculations have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: designing buildings, bridges, and other structures
- Engineering: calculating stresses, loads, and forces on materials
- Physics: understanding motion, gravity, and energy transfer
- Computer graphics: creating 3D models and animations
What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
+The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
What is the Law of Sines?
+The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for all three sides and angles of a triangle.
What is the difference between a right triangle and an oblique triangle?
+A right triangle has one 90-degree angle, while an oblique triangle has no right angles.
In conclusion, finding the angle of a triangle is a fundamental skill that requires a deep understanding of geometric concepts, trigonometric functions, and real-world applications. By mastering the methods and formulas outlined in this article, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of challenges and applications in various fields.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn how to find the angle of a triangle using the Law of Sines, Law of Cosines, and trigonometric functions. Discover real-world applications and expert insights in this comprehensive guide.” (147 characters)