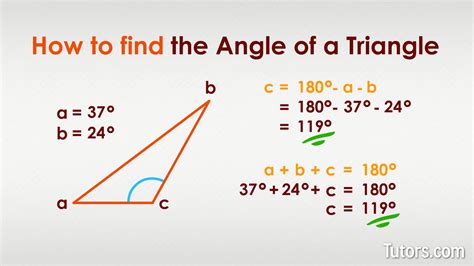
Understanding and finding angles is a crucial aspect of various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and design. Angles are used to describe the relationship between two lines or planes, and their measurement is essential in calculating distances, heights, and shapes. In this article, we will explore five ways to find angles, including using trigonometry, geometry, and measurement tools.
Key Points
- Trigonometry is a fundamental method for finding angles in right triangles.
- Geometry provides various theorems and properties to calculate angles in different types of triangles and polygons.
- Measurement tools, such as protractors and angle gauges, can be used to find angles directly.
- Coordinate geometry involves using coordinates to calculate angles between lines and planes.
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software and other digital tools can also be used to find angles in complex shapes and designs.
Method 1: Trigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles. In a right triangle, the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent can be used to find angles. For example, if we know the length of the opposite side and the hypotenuse of a right triangle, we can use the sine function to find the angle. The formula for sine is sin(θ) = opposite side / hypotenuse. By rearranging this formula, we can solve for θ: θ = arcsin(opposite side / hypotenuse). Similarly, the cosine and tangent functions can be used to find angles in right triangles.
Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric identities are equations that relate the trigonometric functions to each other. These identities can be used to simplify trigonometric expressions and solve equations involving trigonometric functions. For example, the Pythagorean identity states that sin^2(θ) + cos^2(θ) = 1. This identity can be used to find the value of one trigonometric function if we know the value of the other. Trigonometric identities are essential in finding angles and solving problems in trigonometry.
Method 2: Geometry

Geometry provides various theorems and properties that can be used to calculate angles in different types of triangles and polygons. For example, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. If we know two angles of a triangle, we can use this property to find the third angle. Additionally, the properties of congruent and similar triangles can be used to find angles in more complex shapes. Geometry also involves the study of polygons, circles, and other geometric figures, which can be used to find angles in various contexts.
Types of Angles
There are several types of angles, including acute, right, obtuse, and straight angles. Acute angles are less than 90 degrees, right angles are exactly 90 degrees, obtuse angles are greater than 90 degrees, and straight angles are exactly 180 degrees. Understanding the different types of angles is essential in finding and calculating angles in various contexts. Geometry also involves the study of angle relationships, such as complementary and supplementary angles, which can be used to find angles in different situations.
Method 3: Measurement Tools
Measurement tools, such as protractors and angle gauges, can be used to find angles directly. A protractor is a circular or semicircular tool with degree markings that can be used to measure angles. An angle gauge is a tool with a movable arm that can be used to measure angles in various contexts. These tools are commonly used in engineering, architecture, and design to find angles and calculate distances and shapes.
Accuracy and Precision
When using measurement tools to find angles, it is essential to consider accuracy and precision. Accuracy refers to how close the measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to how consistent the measurements are. To achieve high accuracy and precision, it is essential to use high-quality measurement tools and follow proper measurement techniques. Additionally, it is essential to consider the limitations of the measurement tool and the context in which the angle is being measured.
Method 4: Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate geometry involves using coordinates to calculate angles between lines and planes. In a two-dimensional coordinate system, the angle between two lines can be found using the slope formula: tan(θ) = (m2 - m1) / (1 + m1*m2), where m1 and m2 are the slopes of the two lines. In a three-dimensional coordinate system, the angle between two planes can be found using the normal vector formula: cos(θ) = (n1 · n2) / (|n1| * |n2|), where n1 and n2 are the normal vectors to the two planes.
Applications of Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate geometry has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and computer science. It is used to describe the motion of objects, calculate distances and shapes, and perform transformations and projections. Coordinate geometry is also used in computer-aided design (CAD) software and other digital tools to create and manipulate complex shapes and designs.
Method 5: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
CAD software and other digital tools can be used to find angles in complex shapes and designs. These tools provide various functions and commands that can be used to calculate angles, including trigonometric functions, geometric properties, and measurement tools. CAD software is commonly used in engineering, architecture, and design to create and manipulate complex shapes and designs.
Advantages of CAD Software
CAD software provides several advantages over traditional methods of finding angles, including increased accuracy and precision, improved efficiency, and enhanced visualization. CAD software can also be used to simulate and analyze complex systems and designs, allowing users to test and optimize their designs before physical prototyping.
What is the most accurate method for finding angles?
+The most accurate method for finding angles depends on the context and the tools available. Trigonometry and geometry provide exact methods for finding angles, while measurement tools and CAD software provide approximate methods. The choice of method depends on the required level of accuracy and precision.
How do I choose the right method for finding angles?
+The choice of method for finding angles depends on the context and the tools available. Consider the type of triangle or shape, the required level of accuracy and precision, and the tools and software available. It is also essential to consider the limitations and potential errors of each method.
What are the common applications of finding angles?
+Finding angles has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, architecture, and design. It is used to describe the motion of objects, calculate distances and shapes, and perform transformations and projections. Finding angles is also essential in creating and manipulating complex shapes and designs.
In conclusion, finding angles is a crucial aspect of various fields, and there are several methods available to do so. Trigonometry, geometry, measurement tools, coordinate geometry, and CAD software provide different approaches to finding angles, each with its own advantages and limitations. By understanding the different methods and choosing the right one for the context, users can accurately and efficiently find angles and solve problems in various fields.