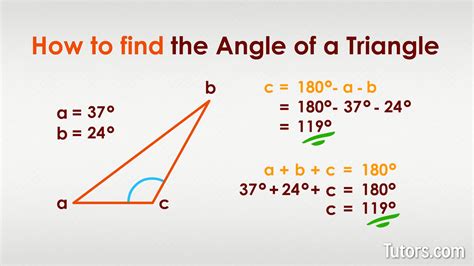
Calculating the angle of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry and trigonometry. Whether you're dealing with a right-angled triangle, an acute triangle, or an obtuse triangle, understanding how to find the angles is crucial for various applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and more. In this article, we'll delve into the methods and formulas used to calculate the angles of triangles, providing you with a comprehensive guide to make these calculations easily and accurately.
Key Points
- Understanding the types of triangles and their properties is essential for calculating angles.
- The Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, and tangent) are fundamental tools for finding angles in right-angled triangles.
- The Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines can be applied to find angles in non-right-angled triangles.
- Practical applications of triangle angle calculations are found in physics, engineering, and construction.
- Using calculators and software can simplify the process of calculating angles, but understanding the underlying principles is crucial.
Understanding Triangles and Their Properties
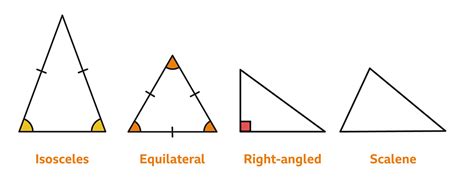
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. The sum of the interior angles of any triangle is always 180 degrees. There are several types of triangles, including right-angled triangles (with one 90-degree angle), acute triangles (all angles less than 90 degrees), obtuse triangles (one angle greater than 90 degrees), and equiangular triangles (all angles equal). Each type of triangle has its unique properties and methods for calculating angles.
Calculating Angles in Right-Angled Triangles
In a right-angled triangle, one of the angles is 90 degrees. The Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides, is a powerful tool for finding the lengths of sides. However, to find the angles, we use trigonometric ratios: sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan). These ratios are defined as the ratios of the lengths of the sides of the triangle and can be used to find any angle given the lengths of two sides.
| Trigonometric Ratio | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sine (sin) | Opposite side / Hypotenuse |
| Cosine (cos) | Adjacent side / Hypotenuse |
| Tangent (tan) | Opposite side / Adjacent side |
Calculating Angles in Non-Right-Angled Triangles
For triangles that are not right-angled, we use the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines to find angles. The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for all three sides and angles. The Law of Cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles, allowing us to find an angle given the lengths of all three sides.
Applying the Law of Sines
The Law of Sines is particularly useful when we know two angles and one side (AAS), or two sides and one angle that is not the included angle (SSA). The formula is ( \frac{a}{\sin(A)} = \frac{b}{\sin(B)} = \frac{c}{\sin©} ), where ( a, b, ) and ( c ) are the sides opposite angles ( A, B, ) and ( C ), respectively.
Applying the Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines is useful for finding an angle when all three sides are known (SSS), or when two sides and the included angle are known (SAS). The formula to find an angle is ( \cos© = \frac{a^2 + b^2 - c^2}{2ab} ), where ( C ) is the angle opposite side ( c ), and ( a, b, ) and ( c ) are the sides of the triangle.
What is the easiest way to calculate the angle of a triangle?
+The easiest way often involves using trigonometric ratios for right-angled triangles or the Law of Sines and Cosines for other triangles. The choice depends on what information you have about the triangle.
Can I use a calculator to find the angles of a triangle?
+Yes, calculators and software can simplify the process of calculating angles by using built-in trigonometric functions. However, understanding the underlying principles is important for applying these tools correctly.
What are some practical applications of calculating triangle angles?
+Calculating triangle angles has numerous applications in physics (projectile motion), engineering (design and construction), and construction (building design and surveying), among others.
In conclusion, calculating the angle of a triangle can be straightforward with the right approach and tools. Understanding the properties of different types of triangles and applying the appropriate formulas, whether it’s trigonometric ratios for right-angled triangles or the Law of Sines and Cosines for other triangles, is key to easily finding the angles of any triangle. By mastering these concepts, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of problems in mathematics, science, and engineering.